- Microsoft Q#
You are given N qubits which are guaranteed to be in one of two basis states on N qubits. You are also given two bitstrings bits0 and bits1 which describe these basis states.
Your task is to perform necessary operations and measurements to figure out which state it was and to return 0 if it was the state described with bits0 or 1 if it was the state described with bits1. The state of the qubits after the operations does not matter.
You have to implement an operation which takes the following inputs:
- an array of qubits qs,
- two arrays of boolean values bits0 and bits1, representing the basis states in which the qubits can be. These arrays will have the same length as the array of qubits. bits0 and bits1 will differ in at least one position.
An array of boolean values represents a basis state as follows: the i-th element of the array is true if the i-th qubit is in state 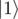 , and false if it is in state
, and false if it is in state 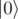 . For example, array [true; false] describes 2-qubit state
. For example, array [true; false] describes 2-qubit state 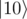 .
.
Your code should have the following signature:
namespace Solution {
open Microsoft.Quantum.Primitive;
open Microsoft.Quantum.Canon;
operation Solve (qs : Qubit[], bits0 : Bool[], bits1 : Bool[]) : Int
{
body
{
// your code here
}
}
}
| Name |
|---|



