| CROC 2016 - Elimination Round |
|---|
| Finished |
After a drawn-out mooclear arms race, Farmer John and the Mischievous Mess Makers have finally agreed to establish peace. They plan to divide the territory of Bovinia with a line passing through at least two of the n outposts scattered throughout the land. These outposts, remnants of the conflict, are located at the points (x1, y1), (x2, y2), ..., (xn, yn).
In order to find the optimal dividing line, Farmer John and Elsie have plotted a map of Bovinia on the coordinate plane. Farmer John's farm and the Mischievous Mess Makers' base are located at the points P = (a, 0) and Q = ( - a, 0), respectively. Because they seek a lasting peace, Farmer John and Elsie would like to minimize the maximum difference between the distances from any point on the line to P and Q.
Formally, define the difference of a line 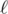 relative to two points P and Q as the smallest real number d so that for all points X on line
relative to two points P and Q as the smallest real number d so that for all points X on line 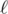 , |PX - QX| ≤ d. (It is guaranteed that d exists and is unique.) They wish to find the line
, |PX - QX| ≤ d. (It is guaranteed that d exists and is unique.) They wish to find the line 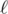 passing through two distinct outposts (xi, yi) and (xj, yj) such that the difference of
passing through two distinct outposts (xi, yi) and (xj, yj) such that the difference of 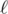 relative to P and Q is minimized.
relative to P and Q is minimized.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and a (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ a ≤ 10 000) — the number of outposts and the coordinates of the farm and the base, respectively.
The following n lines describe the locations of the outposts as pairs of integers (xi, yi) (|xi|, |yi| ≤ 10 000). These points are distinct from each other as well as from P and Q.
Print a single real number—the difference of the optimal dividing line. Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 6.
Namely: let's assume that your answer is a, and the answer of the jury is b. The checker program will consider your answer correct, if 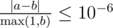 .
.
2 5
1 0
2 1
7.2111025509
3 6
0 1
2 5
0 -3
0.0000000000
In the first sample case, the only possible line 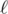 is y = x - 1. It can be shown that the point X which maximizes |PX - QX| is (13, 12), with
is y = x - 1. It can be shown that the point X which maximizes |PX - QX| is (13, 12), with  , which is
, which is 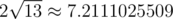 .
.
In the second sample case, if we pick the points (0, 1) and (0, - 3), we get 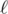 as x = 0. Because PX = QX on this line, the minimum possible difference is 0.
as x = 0. Because PX = QX on this line, the minimum possible difference is 0.
| Name |
|---|




