You are given a bipartite graph G = (U, V, E), U is the set of vertices of the first part, V is the set of vertices of the second part and E is the set of edges. There might be multiple edges.
Let's call some subset of its edges 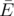 k-covering iff the graph
k-covering iff the graph 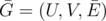 has each of its vertices incident to at least k edges. Minimal k-covering is such a k-covering that the size of the subset
has each of its vertices incident to at least k edges. Minimal k-covering is such a k-covering that the size of the subset 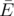 is minimal possible.
is minimal possible.
Your task is to find minimal k-covering for each 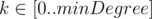 , where minDegree is the minimal degree of any vertex in graph G.
, where minDegree is the minimal degree of any vertex in graph G.
The first line contains three integers n1, n2 and m (1 ≤ n1, n2 ≤ 2000, 0 ≤ m ≤ 2000) — the number of vertices in the first part, the number of vertices in the second part and the number of edges, respectively.
The i-th of the next m lines contain two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui ≤ n1, 1 ≤ vi ≤ n2) — the description of the i-th edge, ui is the index of the vertex in the first part and vi is the index of the vertex in the second part.
For each 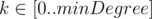 print the subset of edges (minimal k-covering) in separate line.
print the subset of edges (minimal k-covering) in separate line.
The first integer cntk of the k-th line is the number of edges in minimal k-covering of the graph. Then cntk integers follow — original indices of the edges which belong to the minimal k-covering, these indices should be pairwise distinct. Edges are numbered 1 through m in order they are given in the input.
3 3 7
1 2
2 3
1 3
3 2
3 3
2 1
2 1
0
3 3 7 4
6 1 3 6 7 4 5
1 1 5
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
0
1 5
2 4 5
3 3 4 5
4 2 3 4 5
5 1 2 3 4 5
| Name |
|---|




