Are you in love with algorithms? If you are don't miss this round and be algorithm's valentine ;)

On the night before valentine's day (exact time), Valentine Algorithm cUp 2015 is going to take place.
There will be 6 problems and 3 hours to solve them. All of them are written by me(PrinceOfPersia).
This competition is like surprise languages but too different. 3 days before the contest, I will publish tutorial of 5 new algorithm languages(not programming languages) with their compiler codes. Each language is going to be really simple to learn and have at most 6 or 7 commands (they're not like programming languages).
Your program should print the code written in the language the problem says and checker will run it (pay attention that inputs are encoded, don't try to read form input, just print the code). Don't use unnecessary wjitespaces.
Each command of a language, will have a number, shown by w(x) called order. There will be a counter cnt = 0 (initially), every time your code calls this command, cnt increases by x. The order of your code equals the final value of cnt.
Each problem has a limit for your code's order.
If your code gets CE or OLE (order limited exceeded) or WA, you will receive Wrong answer.
Example :
Language (named EXM) : This language is built to process on an integer. There are two valid commands :
- M x : multiply the number by x. (Order : w(x) ).
- I x : increase the number by x. (Order : w(1) ).
Your program returns the final value of that number.
Your task is given number n, the return value of your code must be number 2n + 1 .
Code in EXM:
M 2
I 1
C++ code (the code you will submit in submit page):
printf("M 2\nI 1\n");
Your code's order will be 2 + 1 = 3 .
UPD: You can download languages tutorial and their compilers here.
Attention: Compile the code for each language, in Windows : g++ -o lang lang.cpp -O2 -std=c++0x and in Mac and Linux g++ -o lang.out lang.cpp -O2 -std=c++0x.
Using in Windows:
For running your code that is saved in a file like x.txt, use exactly lang x.txt in cmd and if you want debug mode enabled, use lang x.txt -d (not lang -d x.txt).
Using in Mac OS X or Linux:
For running your code that is saved in a file like x.txt, use exactly ./lang.out x.txt in terminal and if you want debug mode enabled, use ./lang.out x.txt -d (not ./lang.out -d x.txt).
Sample problem:
Write a program in Prolan that given a string s containing only a and b deletes all bs and converts all as to d. Order shouldn't exceed 106 (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 100).
My code:
(b,)
(a,d)
If you have any question, feel free to ask.
UPD2: Scoring will be 500-1000-1500-2000-2500-3000.
By the way, the main characters of each problem is different from other problems. Actually, for each problem the main characters are an imaginary(or not!) couple :)
UPD3: IDXT's compiler had some bug, you can download the correct source here.
UPD4: For people who want to practice, the new archive(including languages tutorials and bugless compilers) can be found here.











The moment I realised when I don't have anyone to spend Valentine's Day with.
D:
But then I realised my country doesn't celebrate it.
:D
But then I realised I don't have a holiday because of it either.
D:
But then I realised that I'll be able to participate in this contest to improve my programming skills.
:D
But then I realised that I'm putting way too many "But then I realised"s.
D:
You're totally wrong. We celebrate valentine's day in Iran.
he's talking about his country which is Kazakhstan looking forward to the contest :D
No, he's not. Read it again :
But then I realised that I'll be able to write this contest to improve my programming skills.
So, he's talking about me.
oh my bad you're right :D
I've seen many people use "write" as an (incorrect) form of "take part in" a contest. Plus it actually makes sense if you interpret it that way.
Yeah you're right, I suck at English
could't you just read the file instead of a program that output that file?
No, I need to write a compiler for each language and I'm not sure admins add my languages.
Sounds interesting! It will be held here in CF? And what about scoring? It will depend only on order or time also makes sense?
In Gym. ACM-ICPC rules.
But UPD2: Scoring will be 500-1000-1500-2000-2500-3000. it seems to be a Codeforces-rules~~~
It's possible to use weighted ACM-ICPC rules: solved problems give 500/1000/something points, and solved problems add to the time penalty, just like Rockethon 2015.
ACM-ICPC rules is ranked by time and the solved number... What about the score?
"Are you in love with algorithms? If you are don't miss this round and be algorithm's valentine ;)
On the night before valentine's day (exact time), Valentine Algorithm cUp 2015 is going the take place."
When I saw title of the competition then one thing instantly came to my mind: "Somebody has posted Forever Alone guy in comments". :D
Of course, so many upvotes are waiting for being first with posting it, so why not take them xD?
I don't know if this is a bug or not but I can see the contest problems while I'm in coach mode..
It's a feature. Any coach-mode user can view every contest, even if it's pending. Just don't read the problems :)
Okay. I wasn't going to participate in the contest anyway.
But IMO I think it's better to add problems to such contests maybe about 30 minutes before the contest to seek maximum fairness.
Can someone explain solution of sample problem? In documentation, it said that (x, y) replaces the "first occurrences" of x by y. So I don't understand how to use this to deletes all bs and converts all as to d. Thanks in advance.
(b,)replaces the first occurrences of b by an empty string, that means it deletes it.The question is why is (b,) deleting all strings and not just the first b.
It just replaces "first" occurrence.
Read its tutorial again, after deleting the first one, we return to the first line and start over.
It would be nice sample problem with answers in every (algorithm) language, is it possible??
Clearly a single problem that has a solution in all five languages is impossible (the input in Autolan, Cursle, and Prolan is a string, while the input in DIT and IDXT is a sequence of four integers). However, here are some easy problems and solutions:
In Autolan, accept a string iff it has an even number of the letter
a. (0 is even.)In Cursle, replace the first occurrence of the letter
awith the lettere. It is guaranteed that the string has at least one lettera.In DIT/IDXT, move a number in storage 1 to storage 2. It is guaranteed that storage 2 is initially 0. You may leave anything in storage 1/3/4.
Prolan sample problem is given in the blog post.
This is different from Round #291, right?
Yes, Valentine Algorithm cUp 2015 is not Codeforces Round #291 (Div. 2) :)
Thanks!
sometimes only u want to be a laptop
As it is in Gym section, I guess it will not be rated. Am I ture?
Yes, you are ture.
Very unusual tasks! So maybe you have some chance to beat tourist in this contest? :P
Btw why we have 5 languages but have 6 tasks?
A language is used for two tasks, of course.
Now, which languages makes double appearance? I'm betting on Cursle.
Your assumption was wrong, so give me a treat. Thanks :)
"T d : go to the line Current_line + d (d could be negative). Order : w(1)" In DIT and IDXT why is this command necessary when it is possible to change any storage directly?
"In DIT, write a program to move a number from storage 1 to storage 2."
Now you see why T is necessary.
Oh! Damn. I confused line with storage. My bad! Thanks. :)
Is this contest d be rated ?
this might be my chance to hit div 1 lol
There are several comments asking this above.
A bunch of questions. Italics are what I got from inspecting compiler, which means I ask for confirmation.
Autolan:
Cursle:
Cursle, DIT, IDXT:
There might be more questions coming...
More question.
In DIXT, what happens if in an X instruction, the value of
bis a storage that points to the number 0? Compiler crashes, it seems.For Cursle doesn't command A(x) have an order?
Yes, w(1).
it seems that a "whitespaces" is wrote as "wjitespaces" :D
Awesome idea for a contest. Looking forward to take part!
Can I participate in a team with my girlfriend?
There seems to be a bug in the IDXT interpreter. When I compile it I get uninitialized variable warnings for a and b on lines 119 and 123. Additionally, the X operation does not work. To fix this, I added the lines
a = cm[ln].y; b = cm[ln].z;on line 119. This should appropriately initialize a and b for the X operation.For the Cursle interpreter, a better debugging output is:
cout << "Curren string: ";for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++) cout << a[i];for (int i = 0; i < b.size(); i++) cout << b[i];cout << " ,Pointer position (0-indexed): " << a.size();cout << " ,Current line: " << cur + 1 << endl;Does Codeforces server's time utterly lag? It is 18.35 MSK and I still see "8 minutes to contest". (Also check the time left to CF 291; you can see the lag as well.)
Yeah, seems to be so.
I'll fix it after the contest.
Перевод документации алгоритмических языков на русский язык :
Valentine Algorithm cUp.
Документация алгоритмических языков.
Подготовлено: AmirMohammad Dehghan
[email protected]
Перевод : Баландин Илья
Внимание: каждый символ в вашем коде должен быть английской буквой, цифрой или один из символов: ~`!@#$%^&*()-_=+{}[]|;:”,’<>./? В каждой строке должно быть не более одной команды.
Autolan
Этот язык обрабатывает строку, используя автоматон.
Автоматон – это ориентированный граф, каждому ребру которого приписан символ. Вершины графа будем называть состояниями. Изначально вы находитесь в состоянии. Символы строки передаются вам один за другим, и для каждого символа c если вы находитесь в состоянии s и для него есть ребро в состояние t , которому приписан символ c, вы переходите в состояние t (если подходящего ребра нет, то ничего не происходит). Некоторые состояния вы объявляете допустимыми. После того, как символы выданы вам, если текущее состояние допустимо, то выданная строка приемлима, иначе она отвергнута.
Ваша задача – сконструировать автоматон.
Важные элементы: начальное состояние, допустимое состояние и рёбра.
Допустимые команды:
N n : данную команду рекомендуется использовать в первой строке кода. Она означает, что автоматон имеет n состояний (1<=n<=1000000). Order: w(n)
I x : данную команду рекомендуется использовать во второй строке кода. Она означает, что начальное состояние – x (1<=x<=n). Order: w(1)
A k v1 v2 … vk : эту команду рекомендуется использовать в третьей строке кода. Она означает, что допустимыми являются состояния v1 v2 … vk (1<=vi<=n, 1<=k<=n). Order: w(k).
Код должен содержать эти команды только один раз.
E s c t : это означает, что есть ребро из состояния s в состояние t , которому приписан символ c (1<=s,t<=n и в коде не должно быть команды типа E s c x). Order: w(1).
Cursle
Данный язык обрабатывает строку, используя указатель.
Изначально указатель находится на первом символе строки. Если в какой-то момент строка оказывается пустой, то выполнение программы на этом завершается.
Допустимые команды:
C x : если символ, на котором стоит указатель равен x, то перейти на следующую строчку, иначе перейти на строку, идущую после следующей. Имеется ввиду переход между строками кода. Order: w(1).
T d : перейти к строке с номером текущая_строка+d (d может быть отрицательным). Имеется ввиду переход между строками кода. Order: w(1).
A x : добавить символ x перед указателем. Order: w(1).
N : перевести указатель на следующий символ (если он не на последнем символе). Order: w(1).
P : перевести указатель на предыдущий символ (если он не первом символе). Order: w(1).
DIT
Язык работает с 4 хранилищами, пронумерованными от 1 до 4, каждое из которых содержит неотрицательное целое число.
Допустимые команды:
D x : если число в хранилище номер x равно нулю, то перейти к следующей строке, иначе уменьшить это число и перейти к строке, идущей после следующей строки. Order: w(1).
I x : увеличить число в хранилище номер x на 1 (1<=x<=4). Order: w(1).
T d : перейти к строке текущая_строка+d (d может быть отрицательным). Order: w(1).
IDXT
Этот язык такой же, как DIT, только в IDXT есть ещё одна допустимая команда:
X a b : сконструировать числа c,d : если a>0, то c=a, иначе c= число из хранилища с номером –a. Аналогично с d : если b>0, то d=b, иначе d= число из хранилища с номером –b. Затем проверить, является ли истиной d|c. Если да, то перейти к следующей строке, иначе перейти к строке, идущей после следующей. -4<=a,b<=1000000000, a,b≠0. Order: w(1).
Prolan
Этот язык работает со строкой s.
В этом языке есть только одна команда:
(x,y) : проверяет, является ли x подстрокой s , затем заменяет первые включения x в s на y и переходит к первой строке (в коде). Если x не является подстрокой s, то переходит к следующей строке (в коде). Order: w(|s|+|x|+|y|) (результат проверки на него не влияет).
x и y не должны содержать символов (), а так же пробелов. y может быть пустой, а x — нет.
This was fun.. Thanks :)
I have a question in problem F.. It's to be solved using Prolan language and the max. order is 10^7. The order of the single valid command in Prolan is w(|s| + |x| + |y|)... If |s| = 2*10^100+1... How can we pass the given order or did I understand something wrong?
|s| = 2 * 100 + 1.
oh... I can't believe I thought about it like that... Feeling very stupid now. Thanks :)
the most dedicated candidate of today to get his valentine: ;)
Just because I'm bored, here's an incomplete, rough editorial, based on my solutions. I didn't solve C and F, and thus I don't have the solutions. Resemblance to the Codeforces platform is purely coincidental.
Problem A
The states are the number processed mod 31, plus 1 (because states begin with 1). For example, while processing 1234, you will come to state 2 (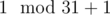 ), 13 (
), 13 (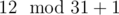 ), 31 (
), 31 (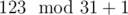 ), and 26 (
), and 26 (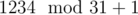 ). Accept if you end up on state 1. From state i, make an edge
). Accept if you end up on state 1. From state i, make an edge 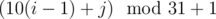 for each j = 0, 1, ..., 9. I can score a 2-minute submission here just because I remembered how to do one with modulo 3.
for each j = 0, 1, ..., 9. I can score a 2-minute submission here just because I remembered how to do one with modulo 3.
Problem B
Note that we're basically counting the number of brackets at the outermost level. One approach to eliminate all inner brackets is
([[],[); remove the leftmost leaf at each time. Now we're left with several[], we can assume each[]increments the digit right before it:This is very similar to a former Codeforces Round problem.
Problem D
This is just finding GCD, which can be done by Euclidean algorithm. From a, b, 0, 0, we compute a - b, 0, b, 0 if b < a, otherwise 0, b - a, a, 0. (Possible by simply incrementing storage 3 and decrementing storage 1 and 2; whichever reaches zero faster is the smaller value.) Afterwards, move storage 3 to the empty location, giving a - b, b, 0, 0 or a, b - a, 0, 0. Repeating enough times, we will be left with a single number that is the GCD; move it to storage 1.
Problem E
We need to know how to divide two numbers. Given a and b, with an empty storage c, we can compute a / b and store it to c: decrement a until b|a, then increment c; rinse and repeat until a = 0.
Now label the storage a, b, c, d; we start with n on a and 0 on b, c, d. We will use d as the counter for final answer. Begin with taking b = 2, and test b|a; if that's the case, divide a by b to c, move c back to a, and increment d. Repeat until b doesn't divide a, in which we increment b. Repeat until a = 1 (can be tested by decrementing a twice), where we move d to a.
To see that this is correct, simply note that if b|a, b must be prime; if it's composite, then b = pq for some p, q ≥ 2, and we must have already divided a by p and q before as 2 ≤ p, q < b.
My solution is not that efficient, given that I actually tested whether b is prime first before trying to divide. (The above has omitted this step.) But hey, still works.
Aww, I read "are multiplies of" as "are multiples of" and didn't notice "greatest". So I was trying to compute LCM, and I'm not sure that's possible with just 4 registers. :(
My A and E are exactly the same (up to permutations).
Here is my B (yeah, I know, it's ugly): ([],X) (X],]) (XXXXXXXXXXX,YX) (XXXXXXXXXX,Y0) (XXXXXXXXX,9) (XXXXXXXX,8) (XXXXXXX,7) (XXXXXX,6) (XXXXX,5) (XXXX,4) (XXX,3) (XX,2) (X,1) (YYYYYYYYYYY,ZY) (YYYYYYYYYY,Z0) (YYYYYYYYY,9) (YYYYYYYY,8) (YYYYYYY,7) (YYYYYY,6) (YYYYY,5) (YYYY,4) (YYY,3) (YY,2) (Y,1) (ZZZZZZZZZ,9) (ZZZZZZZZ,8) (ZZZZZZZ,7) (ZZZZZZ,6) (ZZZZZ,5) (ZZZZ,4) (ZZZ,3) (ZZ,2) (Z,1)
Well, there's the sample tests. I also initially thought of LCM until I read the samples.
I'll go ahead and post my solution for C.
Problem C
This problem is just addition using Cursle. You can solve it by long addition. Keep track of a carry field at the end of the string, along with the answer you are building (Baaa+bbbEcCoooX, c: carry bit, o: out) Look at the carry bit, then check the last digit of b (call it i). Go to "state" b[i+c]. In each state b[i], check the last digit of a (call it j) and go to state a[i+j]. In state a[i], prepend i%10 to out, and set c = i/10. You also have to be aware when a and b become empty. Once both a and b are empty, delete the extra characters. Rather than keeping track of numerical offsets to hop around my states, I used assembly style labels, and wrote a short resolver to calculate the offsets.I also used long addition. Instead of putting the output after everything, I modify the value of
ato be the output. Something likeBaaaaC?oooo+bbbbE, whereois the output,bis what remains of the original after consuming the last few digits for output, andCis the carry. For some reason I failed in test 5; probably OLE but I'm not sure.Thank you for very interesting problems! :) I participated in your previous round too and I have to say that I am looking forward to seeing more contests from you.