Разбор
Tutorial is loading...
Решение (Vovuh)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
#ifdef _DEBUG
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int x;
cin >> x;
cout << x - !(x & 1) << " ";
}
return 0;
}
Разбор
Tutorial is loading...
Решение (Vovuh)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
#ifdef _DEBUG
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
vector<pair<int, int>> res(n);
vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> res[i].first;
a[i] = res[i].first;
res[i].second = i + 1;
}
sort(res.begin(), res.end());
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
sort(res.begin(), res.begin() + k, [&](pair<int, int> a, pair<int, int> b) { return a.second < b.second; });
int lst = 0, sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; ++i) {
sum += *max_element(a.begin() + lst, a.begin() + res[i].second);
lst = res[i].second;
}
sum += *max_element(a.begin() + lst, a.end());
cout << sum << endl;
lst = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; ++i) {
cout << res[i].second - lst << " ";
lst = res[i].second;
}
cout << n - lst << endl;
return 0;
}
1006C - Three Parts of the Array
Разбор
Tutorial is loading...
Решение (Vovuh, set)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
#ifdef _DEBUG
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
cin >> a[i];
set<long long> sum;
long long l = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
l += a[i];
sum.insert(l);
}
long long ans = 0;
long long r = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
sum.erase(l);
l -= a[i];
r += a[i];
if (sum.count(r))
ans = max(ans, r);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
Решение (ivan100sic, two pointers)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef long double ld;
int n;
int a[200005];
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
cerr.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n;
for (int i=1; i<=n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
int i = 0, j = n+1;
ll zi = 0, zj = 0, solidx = 0;
while (i < j) {
if (zi < zj)
zi += a[++i];
else if (zi > zj)
zj += a[--j];
else {
solidx = i;
zi += a[++i];
zj += a[--j];
}
}
cout << accumulate(a+1, a+solidx+1, 0ll); // here
}
Разбор
Tutorial is loading...
Решение (Ne0n25)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
#define mp make_pair
#define pb push_back
#define sqr(a) ((a) * (a))
#define sz(a) int(a.size())
#define all(a) a.begin(), a.end()
#define forn(i, n) for(int i = 0; i < int(n); i++)
#define fore(i, l, r) for(int i = int(l); i < int(r); i++)
typedef long long li;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<int, int> pt;
template <class A, class B> ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const pair<A, B> &a) {
return out << "(" << a.x << ", " << a.y << ")";
}
template <class A> ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const vector<A> &v) {
out << "[";
forn(i, sz(v)) {
if(i) out << ", ";
out << v[i];
}
return out << "]";
}
mt19937 rnd(time(NULL));
const int INF = int(1e9);
const li INF64 = li(1e18);
const int MOD = INF + 7;
const ld EPS = 1e-9;
const ld PI = acos(-1.0);
int n;
string s, t;
bool read() {
if (!(cin >> n >> s >> t))
return false;
return true;
}
void solve() {
int ans = 0;
forn(i, n / 2) {
map<char, int> a;
a[s[i]]++; a[s[n - i - 1]]++;
a[t[i]]++; a[t[n - i - 1]]++;
if (sz(a) == 4)
ans += 2;
else if (sz(a) == 3)
ans += 1 + (s[i] == s[n - i - 1]);
else if (sz(a) == 2)
ans += a[s[i]] != 2;
}
if (n % 2 == 1 && s[n / 2] != t[n / 2])
ans++;
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main() {
#ifdef _DEBUG
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
int tt = clock();
#endif
cerr.precision(15);
cout.precision(15);
cerr << fixed;
cout << fixed;
#ifdef _DEBUG
while (read()) {
#else
if (read()) {
#endif
solve();
#ifdef _DEBUG
cerr << "TIME = " << clock() - tt << endl;
tt = clock();
#endif
}
}
Разбор
Tutorial is loading...
Решение (mareksom)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, q;
vector<vector<int>> tree;
int current_preorder;
vector<int> preorder, max_preorder;
vector<int> sorted_by_preorder;
void Dfs(int w) {
sorted_by_preorder[current_preorder] = w;
preorder[w] = current_preorder++;
for (int c : tree[w]) {
Dfs(c);
}
max_preorder[w] = current_preorder - 1;
}
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> q;
assert(2 <= n);
assert(1 <= q);
tree.resize(n);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int p;
cin >> p;
p--;
assert(0 <= p and p < n);
tree[p].push_back(i);
}
preorder.resize(n);
max_preorder.resize(n);
sorted_by_preorder.resize(n);
current_preorder = 0;
Dfs(0);
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
int u, k;
cin >> u >> k;
u--; k--;
assert(0 <= u and u < n);
assert(0 <= k and k < n);
k += preorder[u];
int answer = -1;
if (k <= max_preorder[u]) {
answer = sorted_by_preorder[k] + 1;
assert(1 <= answer and answer <= n);
}
cout << answer << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
Разбор
Tutorial is loading...
Решение (Vovuh)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 20;
map<long long, int> v[N][N];
int n, m;
int half;
long long k;
long long a[N][N];
long long ans;
void calclf(int x, int y, long long val, int cnt) {
val ^= a[x][y];
if (cnt == half) {
++v[x][y][val];
return;
}
if (x + 1 < n)
calclf(x + 1, y, val, cnt + 1);
if (y + 1 < m)
calclf(x, y + 1, val, cnt + 1);
}
void calcrg(int x, int y, long long val, int cnt) {
if (cnt == n + m - 2 - half) {
if (v[x][y].count(k ^ val))
ans += v[x][y][k ^ val];
return;
}
if (x > 0)
calcrg(x - 1, y, val ^ a[x][y], cnt + 1);
if (y > 0)
calcrg(x, y - 1, val ^ a[x][y], cnt + 1);
}
int main() {
#ifdef _DEBUG
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
cin >> n >> m >> k;
half = (n + m - 2) / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
cin >> a[i][j];
}
}
calclf(0, 0, 0, 0);
calcrg(n - 1, m - 1, 0, 0);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}











I'm not sure why this hacking attempt was successful: http://codeforces.net/contest/1006/submission/40420960
Can someone please tell me what went wrong?
Try with this test case:
Your output
You have a problem with repeated numbers in this part of the code:
Good luck! :P
В задаче F можно было последовательно пройтись точкам (x, y) диагонали, начинающейся с левого нижнего угла и просуммировать произведения кол-ва путей из (1, 1) в (x, y) и из (x, y) в (n, m), так как все пути проходят через такую диагональ. http://codeforces.net/contest/1006/submission/40438712
Формально мое решение делает то же самое, только при помощи рекурсивного перебора.
То что вы описали и является основной идеей meet-in-the-middle. Второе название метода Bidirectional search. Заметьте что это метод или стратегия, а реализация в свою очередь может отличаться.
Please anyone explain the problem F. Thanks!!!
Read code :) that's easier to understand.
You use a structure, v[x][y][c] = number of way to go to cell x, y, have c at xor value. This is the key of solution.
Thanks, after viewing the code it becomes easier.
Спасибо за разбор! Скажите, пожалуйста, как правильно называется подход, примененный в задаче Е. В разборе задачи 877E - Данил и подработка автор называет его Эйлеровым обходом дерева, но это, как я понимаю, является лишь частным случаем деревьев Эйлерова обхода в задаче о динамической связности, и где можно почитать про этот частный случай, возможно, на английском. Приходилось применять уже четыре раза, четвертый был здесь, первый по ссылке выше, второй 375D - Дерево и запросы и третий 600E - Lomsat gelral.
Вообще, существует много моделей эйлерова обхода дерева. Например, в сведении задачи LCA к задаче RMQ также записывается эйлеров обход, но в немного другом виде. Также, насколько я помню, в задачах, в которых необходимы простые запросы на поддеревья (вроде += или что-то подобное), можно писать ДО опять же по эйлеровому обходу. Про сведение LCA к RMQ можно почитать на емаксе, а ДО по эйлеровому обходу... Вполне себе очевидная вещь, вроде бы как даже по эйлеровому обходу, примененному в этой задаче, можно построить дерево отрезков и делать запросы на поддеревьях как на подотрезках массива.
Большое спасибо за Ваш ответ! К слову, еще можно оффлайн запросы обратывать по Эйлеровому обходу при помощи алгоритма Мо, как в последних двух приведенных задачах, и еще вспомнил задачу 609E - Минимальное остовное дерево по каждому ребру, одним из способов решения которой было как раз сведение LCA к RMQ на Эйлеровом обходе остовного дерева
Но отвечая на то, как же все-таки называется этот подход... Я не знаю. Для меня это просто Эйлеров обход дерева. Эйлеровым обходом дерева в моем кругу называют выписывание вершин дерева в порядке дфса с некоторыми необходимыми дополнительными выписываниями (как в сведении LCA к RMQ).
Complexity of problem F: We run 2 recursive backtracking. So why is not it O( 2^((n+m-2)/2) ) instead of your complexity ?
Maybe because I don't understand how to complete path with 2 child-paths.
For everyone that has same question with me,
Because we use a map, complexity is O( n log n ) with n = number of recursion ( 2^((n+m-2)/2) ).
The complexity is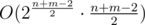 because each backtracking will made
because each backtracking will made 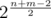 moves and summary size of maps will be
moves and summary size of maps will be 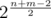 so if we take logarithm of this value we will obtain just
so if we take logarithm of this value we will obtain just  .
.
This is because n,m can take maximum value upto 20. So you have to compute all 2^20 paths. This will exceed the time limit because time limit is generally upto 2^12 . So it is wiser to break problems into two sets of 10, so computations will become 2^10+2^10= 2^11 which fits our time limit.
You can try this problem too Codechef Problem
I ask a question about the complexity. I don't think you answer right question. :)
In the problem F,because we can only move to the bottom or to the right,we don't need "cnt" to record the number of moves.x+y is just the "cnt";
vovuh In problem F:
meet in the middlewas used. Can you suggest any tutorials and problems for this technique? I don't really understand it. Thanks!In basis, instead of finding the solution to go from the initial state to the final state, you find the solution to go from each of those states to some mid-states (which has half the moves/resources required to be done). The final work will be merging path — one from the initial, one from the final, to get the answer.
You can search for problems with tags "meet-in-the-middle" on Codeforces problemsets. There are enough for you to practice, I suppose.
Thank you Akikaze. I have a small doubt, it may seem silly but anyway I ask, what are the main differences between this and divide and conquer technique? I went through this geeksforgeeks article, which says
What does it mean by — having the same structure as the original problem? And how to decide which one to use?
Well think of native algorithm for this task.
You would call (i+1,j) or (i,j+1) until you get to (n,m).
But let's see now meet in the middle approach: Go until (i+j)-1==(n+m)/2 (until you reach the middle). Store how many same results for coordinates (i,j) exist (use map because result may be 10^18). And after you went to middle, go backwards from (n,m) to middle and when you reach check if result is k.
All I'm saying is just to tell that when you come to middle, you store result count in map, and then you look for results going backwards. Storing result in map and searching answer in map means that don’t have the same structure as the original problem. At least I see it that way, maybe I'm wrong. Hope it helps :D
Let's take the classic merge sort algorithm as an example. The problem is to sort the array. If we cut the problem in half, our goal is still to sort the two halves of the array. So we can solve each half by dividing them into two more halves, again.
Another example would be the closest pair of points problem. If we divide the set of points in half, we would still need to find closest pair of points in each half. More dividing, yay.
Now, let's look at the xor-paths problem. Our original problem is to find a path from one corner to the opposite, with xor exactly k. When we divide the grid in half, our problem for each half is not limited to finding xor exactly k anymore, thus we can't solve each half in the same manner.
An easy (but I'm not sure if correct) way to distinguish them is that meet-in-the-middle is typically used to optimize a complete search. When you split the problem, ask yourself: "If the problem is the same for the two halves, and I can solve those halves by brute force, can I use those results to solve the full problem?". If the answer is yes, then it is DnC.
Thanks for the explanation with examples neko_nyaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa. It makes sense now :D
?detaR tI sI
I don't quite understand in D why in first example
abacaba
bacabaa
When we look at 3-rd line containing characters 'a','c','a','b' result is 2. Why can't we just turn 'c' to 'b', swap (a[3],b[3]) and then swap(a[3],a[5])?
You can only preprocess in the first string (in this case,
abacaba).Can someone help me debug this code.
Well,algorithm isn't good. You're going from beginning to end. It will give TLE. Read editorial or try to see how others managed to do meet in the middle.
You need meet in the middle to solve this problem, because your algorithm will cost too much time.
My submission for D: http://codeforces.net/contest/1006/submission/40508497 Can someone give me a small test case where this fails?
2 bc aa
А где можно найти побольше задач на meet-in-the-middle. Просто я впервые встречаю подобную идею, и хотел бы порешать такие задачи.
На Codeforces можно найти много задач с таким тегом в архиве, я думаю, но совсем учебных задач на meet-in-the-middle там нет. Задача с этого раунда одна из самых-самых учебных, но в раундах на Codeforces они обычно более идейные. Но можете попробовать
https://beta.atcoder.jp/contests/agc026/tasks/agc026_c
http://acm.timus.ru/problem.aspx?space=1&num=1863
http://acm.timus.ru/problem.aspx?space=1&num=1495
Огромное спасибо)
If F problem if n+m is not so small how to find the time complexity of the recursive solution. How it is O((n+m-2Cm-1)*(n+m-2))
About O(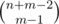 ·(n + m - 2)) — exists the method which allows us to iterate over all binary masks of length n with exactly k ones with the time complexity O(
·(n + m - 2)) — exists the method which allows us to iterate over all binary masks of length n with exactly k ones with the time complexity O(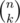 ). And, of course, for each mask we need to iterate over all its bits and spend n + m - 2 operations to do this
). And, of course, for each mask we need to iterate over all its bits and spend n + m - 2 operations to do this
But how the complexity is O((n+m-2)C(m-1)·(n + m - 2))?? because to iterate all mask of size n+m-2 you need a for loop which complexity is 2^(n+m-2)
Not necessary. In one of the previous comments I noticed that exists a method which allows us to iterate over all binary masks of length n with exactly k ones with the complexity written above. If you are very interested, there is a code on C++. Unfortunately, now I cannot describe how it works.
But with such a cycle we need to check where ones are placed in the current mask. So overall complexity is O(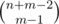 ·(n + m - 2)).
·(n + m - 2)).
My submission for E: http://codeforces.net/contest/1006/submission/40523424 Can someone help optimise this code? The logic seems simpler than the one in the editorial.
Well, for every vertex you are storing whole subtree. Off course it will give memory limit exceeded, because you are using O(n^2) memory. And your logic may be simpler, but that doesn't matter since solution is wrong — program:
int main { return 0; }
will be simpler than the one in tutorial, even simpler than yours, but it won't give correct answer either :)
If you want to get AC you have to understand what's going on in editorial, why it is done like that and then code it in similar way.
This is my submission for the Problem D : http://codeforces.net/contest/1006/submission/40525793
These are the steps that I followed while writing the solution :
1.segregate all the four characters, whose positions can be changed after the preprocess, I named them a , b (from the first string ) and c,d (from the second string)
2.i created a set to count the number of unique characters in these four elements.
3.If the set size is 4 , which means all the characters are unique , then ans = ans + 2;
4.If the set size is 3 , in this case there are two possible arrangements, either the ans = ans + 1 or ans = ans + 2 , if a==b or c==d ( the pair containing same character is present in the first string or in the second string )
5.If the set size is 2, then ans = ans + 1 , only if there are three same characters
6.If the string size is odd, check whether the middle element is equal in both the strings. Can you tell me what I am missing from this.
I got where I am mistaken , in the step 4 , if c==d , then ans = ans + 1 , instead of ans = ans + 2.
Correct solution : http://codeforces.net/contest/1006/submission/40542519
Polycarp sounds like poly-crap. I don't like these puns in problem statement.
why do you always give solutions in cpp . please try python for once .
C++ is more understandable for a lot of participants. My Python solutions are as short as possible and not so clear as C++ solutions. And one more reason is that for the last 2-3 problems we don't guarantee that Python solutions will pass.
this was the first editorial till now that i understood completely , i hope tutorials in future will also be so great , then only novice programmers can learn. thanks.
Can anyone explain problem B. The code in the editorial is confusing
Did you read explanation? What part in it you don't understand?
I cant understand solution of F, please explain me if n = 10 and m = 10? with O (2 ^ (n + m — 2))
understood...
Problem C — Three Parts of the Array Can someone find the problem here? http://codeforces.net/contest/1006/submission/40760589 I find it exactly the same as tutorial's solution with two pointers, but Test Case #12 fails. Thanks.
Test case on which your code is wrong:
3
2 1 3
Thanks mate.
Can anyone explain to me why my solution for problem C get's WA In testcase 13 ? 42740594
If someone want to try a variation of Problem F (n*n matrix rather than n*m matrix) go and solve https://www.codechef.com/problems/XORGRID
My code for problem F:https://codeforces.net/contest/1006/submission/53013382
What is wrong in this code? Is this an implementation problem or a logic problem?
I binary searched on indices such that we split the first part at mid, and then I ran a loop backwards finding whether a sum3 exists for the corresponding sum1 upto mid.
https://codeforces.net/contest/1006/submission/56046778
I am getting WA on test 6.
Your code has a wrong answer in this test case:
44 5 10 4Your output: 0 Answer : 4 Good luck!Still getting WA on test 6 :( https://codeforces.net/contest/1006/submission/56071670
tutorial for problem E, I forgot to mention the question.
The solution in the tutorial is based on dividing them into sub trees.For the given sample,from normal dfs traverse starting from source 1, we get, 1,2,3,5,6,8,7,9,4. We just need to divide this array into continuous sub arrays like [3,5,6,8,7,9] or [7,9] .
To make this happen,we just need to find, "after how many vertexes popped, the vertex pushed first was popped." Like, when '3' was pushed,then after pushing 5 vertex, '3' was popped. So this gives us the subarray from array1 which is from (index of 3) to ((index of 3)+5 which is the subarray [3,5,6,8,7,9].
So in the dfs code,we'll compute the array1 along with the index of the vertexes in array one and also the "after how many vertexes popped, the vertex pushed first was popped." Then we'll just simply calculate if the given K in query is smaller than that number or not and if smaller, we'll print array1[index+k-1] otherwise -1 .
Can someone explain me why this solution fail? Solution