Suppose you have a set of lattice points each of whose coordinates lie in the interval [0, N]. I've heard that the number of points on the convex hull is O(N2 / 3). However, I cannot seem to be able to prove this. How can this be proven?
Also, how to generate testcases such that the convex hull contains as many points as possible?











I might have misunderstood, but if we take the 4 corner points (and have the remaining N-4 points inside), then their convex hull is a square with O(N) lattice points on every edge...
No, I mean the number of vertices of the convex hull. So, a square would only have four vertices.
A heuristic approach: take all the irreducible lattice vectors in [0, a]2 for some a, and sort them by the angle. Now construct the lower right envelope by taking prefix sums of the sorted list of those vectors. Expected gain in both x and y coordinate per point is Θ(a), and the number of vectors should be Θ(a2). If you plug in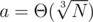 , the last prefix sum is (Θ(N), Θ(N)), and the lower right envelope contains
, the last prefix sum is (Θ(N), Θ(N)), and the lower right envelope contains 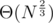 points.
points.
As for the other direction, it seems hard. I couldn't find a coherent proof for the 2-dimensional case on the Internet.
Nice, this allows us to construct testcases with O(N2 / 3) points on the hull.
There's a paper in German ("Über die Gitterpunke auf konvexen Kurven" by Vojtěch Jarník) that proves a Θ(l2 / 3) bound for convex C1 curves F of length l with 0 ≤ F' ≤ 1.
If we have a convex polygon, we can draw a convex C1 curve through all its vertices and apply his result to each octant. (The length of the curve is O(N).) This gives a O(N2 / 3) bound for convex polygons.
Edit: The paper also talks about convex polygons. One result is that the maximum number of vertices a convex polygon with integer coordinates and circumference x can have is
Nice to see a paper by Jarník cited, as someone whose head managed to collide with his books.
A simplified proof for the fact that a convex lattice polygon with coordinates in [0, N] has at most O(N2 / 3) vertices:
Let (x0, y0), ..., (xn, yn) be the vertices with (x0, y0) = (xn, yn). Let (ai, bi) = (xi + 1 - xi, yi + 1 - yi) be the i-th line segment. W.l.o.g. let (a0, b0), ..., (ak, bk) be the line segments with 0 ≤ ai ≤ bi (the ones in one octant). We'll only look at these segments. Note that
so there are at most N2 / 3 indices i with bi ≥ N1 / 3. Let's call those segments long and the other ones short. Let m + 1 be the number of short segments and (asj, bsj) be the j-th short segment. Then
so
On the other hand, by restriction on the octant and convexity of the polygon, the sequence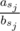 is sorted, so using ai ≤ bi we get
is sorted, so using ai ≤ bi we get
so m ≤ 2N2 / 3 hence k ≤ 3N2 / 3. Summing up over all 8 octants, we get an upper bound of 24N2 / 3 for the number of vertices.
Just FYI, in your first summation you probably want yk + 1 - yk.
I assume you meant replacing bk by bi and made the same error in your comment. That's correct. Thanks.
Nice proof. But I think the sequence $$$a_{s_j} / b_{s_j}$$$ could always be sorted, which is independent of the restriction on the octant and convexity of the polygan?
If the polygon is not convex, then there can be duplicate $$$\frac{a_{s_j}}{b_{s_j}}$$$ and the proof falls apart.
If the polygon is not convex but you assume that no two sides are parallel, then yes, you can sort and do the same proof. Geometrically this corresponds to constructing a convex polygons with the same "side vectors". (The same idea applies if there is a constant $$$c$$$ such that every side is parallel to at most $$$c$$$ other sides.)