| Codeforces Round 211 (Div. 2) |
|---|
| Finished |
You know that Japan is the country with almost the largest 'electronic devices per person' ratio. So you might be quite surprised to find out that the primary school in Japan teaches to count using a Soroban — an abacus developed in Japan. This phenomenon has its reasons, of course, but we are not going to speak about them. Let's have a look at the Soroban's construction.
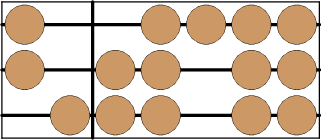
Soroban consists of some number of rods, each rod contains five beads. We will assume that the rods are horizontal lines. One bead on each rod (the leftmost one) is divided from the others by a bar (the reckoning bar). This single bead is called go-dama and four others are ichi-damas. Each rod is responsible for representing a single digit from 0 to 9. We can obtain the value of a digit by following simple algorithm:
- Set the value of a digit equal to 0.
- If the go-dama is shifted to the right, add 5.
- Add the number of ichi-damas shifted to the left.
Thus, the upper rod on the picture shows digit 0, the middle one shows digit 2 and the lower one shows 7. We will consider the top rod to represent the last decimal digit of a number, so the picture shows number 720.
Write the program that prints the way Soroban shows the given number n.
The first line contains a single integer n (0 ≤ n < 109).
Print the description of the decimal digits of number n from the last one to the first one (as mentioned on the picture in the statement), one per line. Print the beads as large English letters 'O', rod pieces as character '-' and the reckoning bar as '|'. Print as many rods, as many digits are in the decimal representation of number n without leading zeroes. We can assume that number 0 has no leading zeroes.
2
O-|OO-OO
13
O-|OOO-O
O-|O-OOO
720
O-|-OOOO
O-|OO-OO
-O|OO-OO
| Name |
|---|




