| Codeforces Round 361 (Div. 2) |
|---|
| Finished |
Mike and !Mike are old childhood rivals, they are opposite in everything they do, except programming. Today they have a problem they cannot solve on their own, but together (with you) — who knows?
Every one of them has an integer sequences a and b of length n. Being given a query of the form of pair of integers (l, r), Mike can instantly tell the value of 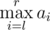 while !Mike can instantly tell the value of
while !Mike can instantly tell the value of 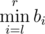 .
.
Now suppose a robot (you!) asks them all possible different queries of pairs of integers (l, r) (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n) (so he will make exactly n(n + 1) / 2 queries) and counts how many times their answers coincide, thus for how many pairs 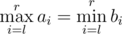 is satisfied.
is satisfied.
How many occasions will the robot count?
The first line contains only integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000).
The second line contains n integer numbers a1, a2, ..., an ( - 109 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the sequence a.
The third line contains n integer numbers b1, b2, ..., bn ( - 109 ≤ bi ≤ 109) — the sequence b.
Print the only integer number — the number of occasions the robot will count, thus for how many pairs 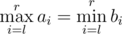 is satisfied.
is satisfied.
6
1 2 3 2 1 4
6 7 1 2 3 2
2
3
3 3 3
1 1 1
0
The occasions in the first sample case are:
1.l = 4,r = 4 since max{2} = min{2}.
2.l = 4,r = 5 since max{2, 1} = min{2, 3}.
There are no occasions in the second sample case since Mike will answer 3 to any query pair, but !Mike will always answer 1.
| Name |
|---|




