Viscious Keyboard
Tutorial is loading...
example code 1
print (lambda s: max((s[:i] + x + s[i+1:]).count("VK") for x in "VK" for i in range(len(s))))(raw_input())
example code 2
print (lambda s: s.count("VK") + int(any(x*3 in "K" + s + "V" for x in "VK")))(raw_input())
Valued Keys
Tutorial is loading...
example code
x,y = raw_input(), raw_input()
print all(a>=b for a,b in zip(x,y)) * y or "-1"
Voltage Keepsake
Tutorial is loading...
example code (c++)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
// Adjust MAXN for bounds
const ll MAXN=1e5+4;
// MAXV is the max amount of time we can take
const ld MAXV=1e18;
ll a[MAXN],b[MAXN];
ld exhaust[MAXN];
int n;
ll P;
bool f(ld imid) {
ld needsum=0;
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) {
ld need=max(0.0L, (imid-exhaust[i])*a[i]);
needsum+=need;
}
ld supply=imid*P;
return supply>=needsum;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%lld",&n,&P);
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) {
scanf("%lld%lld",&a[i],&b[i]);
}
ll suma=0;
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) {
suma+=a[i];
}
if (P>=suma) {
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) {
exhaust[i]=((ld)b[i])/((ld)a[i]);
}
ld imin=0,imax=MAXV;
for (ll iter=0;iter<220;iter++) {
ld imid=(imin+imax)/2;
if (f(imid)) imin=imid;
else imax=imid;
}
if (imax>MAXV-100) printf("-1\n");
else printf("%.9f\n",(double)imin);
}
Volatile Kite
Tutorial is loading...
example code (c++)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define sim template < class c
#define ris return * this
#define dor > debug & operator <<
#define eni(x) sim > typename \
enable_if<sizeof dud<c>(0) x 1, debug&>::type operator<<(c i) {
sim > struct rge {c b, e; };
sim > rge<c> range(c i, c j) { return rge<c>{i, j}; }
sim > auto dud(c* x) -> decltype(cerr << *x, 0);
sim > char dud(...);
struct debug {
#ifdef LOCAL
~debug() { cerr << endl; }
eni(!=) cerr << boolalpha << i; ris; }
eni(==) ris << range(begin(i), end(i)); }
sim, class b dor(pair < b, c > d) {
ris << "(" << d.first << ", " << d.second << ")";
}
sim dor(rge<c> d) {
*this << "[";
for (auto it = d.b; it != d.e; ++it)
*this << ", " + 2 * (it == d.b) << *it;
ris << "]";
}
#else
sim dor(const c&) { ris; }
#endif
};
#define imie(...) " [" << #__VA_ARGS__ ": " << (__VA_ARGS__) << "] "
typedef long double ld;
typedef long double ll;
ld K(ld a) { return a * a; }
struct P {
ll x, y;
void read() { cin >> x >> y; }
P operator + (P b) { return P{x + b.x, y + b.y}; }
P operator - (P b) { return P{x - b.x, y - b.y}; }
P operator * (ld/*ll*/ mul) { return P{x * mul, y * mul}; }
ll operator * (P b) { return x * b.y - y * b.x; }
ll dot(P b) { return x * b.x + y * b.y; }
ld len() { return sqrt(K(x) + K(y)); }
P lenTo(ld to) { return *this * (to / len()); }
ld dist(P & b) { return (*this - b).len(); }
};
struct L2 {
P one, two;
ld dist(P he) {
return abs((he - one) * (he - two)) / one.dist(two);
}
};
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<P> points(n);
for(P & p : points)
p.read();
ld answer = 1e15;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < 2 * n; ++j)
if(abs(i - j) <= 2)
for(int k = 0; k < 2 * n; ++k)
if(abs(i - k) <= 2 && (int) set<int>{i % n, j % n, k % n}.size() == 3)
answer = min(answer, L2{points[i%n], points[j%n]}.dist(points[k%n]));
printf("%.10lf\n", (double) answer / 2);
}
example code (java)
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.Writer;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* Built using CHelper plug-in
* Actual solution is at the top
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream inputStream = System.in;
OutputStream outputStream = System.out;
InputReader in = new InputReader(inputStream);
OutputWriter out = new OutputWriter(outputStream);
NonConvexPolygon solver = new NonConvexPolygon();
solver.solve(1, in, out);
out.close();
}
static class NonConvexPolygon {
public void solve(int testNumber, InputReader in, OutputWriter out) {
int n = in.nextInt();
long[][] p = new long[n][2];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
p[i][0] = in.nextInt();
p[i][1] = in.nextInt();
}
double ans = 1L << 60;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int prev = (i + n - 1) % n, next = (i + 1) % n;
ans = Math.min(ans, PointToSegmentDistance.pointToLineThroughTwoPointsDistance(
p[i][0], p[i][1], p[prev][0], p[prev][1], p[next][0], p[next][1]
) / 2.0);
}
out.printf("%.10f\n", ans);
}
}
static class Utils {
public static double cross(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
Point ab = new Point(b.x - a.x, b.y - a.y);
Point ac = new Point(c.x - a.x, c.y - a.y);
return ab.x * ac.y - ab.y * ac.x;
}
}
static class PointToSegmentDistance {
static double fastHypot(double x, double y) {
return Math.sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
public static double pointToLineThroughTwoPointsDistance(long x, long y, long ax, long ay, long bx, long by) {
double t = Utils.cross(new Point(ax, ay), new Point(bx, by), new Point(x, y));
return Math.abs(t / fastHypot(ax - bx, ay - by));
}
}
static class Point implements Comparable<Point> {
public double x;
public double y;
public double angle;
public int idx;
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
angle = 0;
}
public Point(double x, double y, int idx) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.idx = idx;
}
public int compareTo(Point other) {
return x == other.x ? (int) Math.signum(y - other.y) : (int) Math.signum(x - other.x);
}
}
static class OutputWriter {
private final PrintWriter writer;
public OutputWriter(OutputStream outputStream) {
writer = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream)));
}
public OutputWriter(Writer writer) {
this.writer = new PrintWriter(writer);
}
public void printf(String format, Object... objects) {
writer.printf(format, objects);
}
public void close() {
writer.close();
}
}
static class InputReader {
private InputStream stream;
private byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
private int curChar;
private int numChars;
public InputReader(InputStream stream) {
this.stream = stream;
}
public int read() {
if (this.numChars == -1) {
throw new InputMismatchException();
} else {
if (this.curChar >= this.numChars) {
this.curChar = 0;
try {
this.numChars = this.stream.read(this.buf);
} catch (IOException var2) {
throw new InputMismatchException();
}
if (this.numChars <= 0) {
return -1;
}
}
return this.buf[this.curChar++];
}
}
public int nextInt() {
int c;
for (c = this.read(); isSpaceChar(c); c = this.read()) {
;
}
byte sgn = 1;
if (c == 45) {
sgn = -1;
c = this.read();
}
int res = 0;
while (c >= 48 && c <= 57) {
res *= 10;
res += c - 48;
c = this.read();
if (isSpaceChar(c)) {
return res * sgn;
}
}
throw new InputMismatchException();
}
public static boolean isSpaceChar(int c) {
return c == 32 || c == 10 || c == 13 || c == 9 || c == -1;
}
}
}
Vulnerable Kerbals
Tutorial is loading...
example code (c++)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define sim template < class c
#define ris return * this
#define dor > debug & operator <<
#define eni(x) sim > typename \
enable_if<sizeof dud<c>(0) x 1, debug&>::type operator<<(c i) {
sim > struct rge {c b, e; };
sim > rge<c> range(c i, c j) { return rge<c>{i, j}; }
sim > auto dud(c* x) -> decltype(cerr << *x, 0);
sim > char dud(...);
struct debug {
#ifdef LOCAL
~debug() { cerr << endl; }
eni(!=) cerr << boolalpha << i; ris; }
eni(==) ris << range(begin(i), end(i)); }
sim, class b dor(pair < b, c > d) {
ris << "(" << d.first << ", " << d.second << ")";
}
sim dor(rge<c> d) {
*this << "[";
for (auto it = d.b; it != d.e; ++it)
*this << ", " + 2 * (it == d.b) << *it;
ris << "]";
}
#else
sim dor(const c&) { ris; }
#endif
};
#define imie(...) " [" << #__VA_ARGS__ ": " << (__VA_ARGS__) << "] "
const int nax = 2e5 + 5;
bool forbidden[nax];
int my_gcd(int a, int b) {
if(a == 0 || b == 0) return max(a, b); // return m
return __gcd(a, b);
}
#define __gcd use____my_gcd
vector<int> which[nax];
pair<int,int> dp[nax];
int my_pow(int a, int b, int m) {
int r = 1;
while(b) {
if(b % 2) r = (long long) r * a % m;
a = (long long) a * a % m;
b /= 2;
}
return r;
}
int main() {
int n, m;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
while(n--) {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
forbidden[x] = true;
}
#define n use_____m
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
if(!forbidden[i])
which[my_gcd(i, m)].push_back(i);
if(forbidden[0])
which[m].push_back(0); // hack
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
if(!which[i].empty()) {
dp[i] = {0, 0};
for(int j = 1; j < i; ++j)
if(i % j == 0 && dp[j].first > 0)
dp[i] = max(dp[i], make_pair(dp[j].first, j));
dp[i].first += which[i].size();
}
vector<int> ans;
int x = m;
while(!which[x].empty()) {
for(int y : which[x])
ans.push_back(y);
x = dp[x].second;
}
reverse(ans.begin(), ans.end());
if(forbidden[0]) {
assert(!ans.empty());
ans.pop_back();
}
debug() << imie(ans);
int previous = 1;
printf("%d\n", (int) ans.size());
int cnt_coprime = 0;
for(int i = 2; i < m; ++i)
if(my_gcd(i, m) == 1)
++cnt_coprime;
for(int nxt : ans) {
if(nxt == 0) {
printf("0");
continue;
}
int a = previous / my_gcd(m, previous);
int b = nxt / my_gcd(m, nxt);
int print = (long long) b * my_pow(a, cnt_coprime, m) % m;
print = (long long) print * my_gcd(m, nxt) / my_gcd(m, previous) % m;
printf("%d ", print);
previous = nxt;
}
puts("");
}
example code (java)
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.Writer;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* Built using CHelper plug-in
* Actual solution is at the top
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream inputStream = System.in;
OutputStream outputStream = System.out;
InputReader in = new InputReader(inputStream);
OutputWriter out = new OutputWriter(outputStream);
PrefixProductSequence solver = new PrefixProductSequence();
solver.solve(1, in, out);
out.close();
}
static class PrefixProductSequence {
public int[] div;
public boolean[] forbidden;
public ArrayList<Long> ans;
public int n;
public int m;
public void solve(int testNumber, InputReader in, OutputWriter out) {
n = in.nextInt();
m = in.nextInt();
forbidden = new boolean[m + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
forbidden[in.nextInt()] = true;
}
int[] add = new int[m + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (!forbidden[i]) {
int g = Utils.gcd(i, m);
add[m / g]++;
}
}
int[] arr = new int[m + 1];
div = new int[m + 1];
Arrays.fill(arr, 1);
Arrays.setAll(div, x -> x);
for (int i = 2; i <= m; i++) {
arr[i] += add[i];
for (int j = i + i; j <= m; j += i) {
if (arr[i] > arr[j]) {
arr[j] = arr[i];
div[j] = j / i;
}
}
}
ans = new ArrayList<>();
solve(1, 1);
out.println(ans.size());
boolean first = true;
for (long x : ans) {
if (!first) out.print(" ");
out.print(x);
first = false;
}
out.println();
}
public void solve(int cmult, long mm) {
if (cmult == m) {
if (!forbidden[0]) {
ans.add(0L);
}
return;
}
int prev = 1;
boolean has = false;
for (int i = 1; i < m / cmult; i++) {
if (!forbidden[i * cmult] && Utils.gcd(m / cmult, i) == 1) {
long x = Utils.inv(prev, m / cmult) * i % m;
if (!has) {
has = true;
x = x * mm % m;
}
ans.add(x);
prev = i;
}
}
long nmm = Utils.inv(prev, m / cmult) * div[m / cmult] % m;
if (!has) nmm = nmm * mm % m;
solve(cmult * div[m / cmult], nmm);
}
}
static class OutputWriter {
private final PrintWriter writer;
public OutputWriter(OutputStream outputStream) {
writer = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream)));
}
public OutputWriter(Writer writer) {
this.writer = new PrintWriter(writer);
}
public void print(Object... objects) {
for (int i = 0; i < objects.length; i++) {
if (i != 0) {
writer.print(' ');
}
writer.print(objects[i]);
}
}
public void println() {
writer.println();
}
public void close() {
writer.close();
}
public void print(long i) {
writer.print(i);
}
public void println(int i) {
writer.println(i);
}
}
static class InputReader {
private InputStream stream;
private byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
private int curChar;
private int numChars;
public InputReader(InputStream stream) {
this.stream = stream;
}
public int read() {
if (this.numChars == -1) {
throw new InputMismatchException();
} else {
if (this.curChar >= this.numChars) {
this.curChar = 0;
try {
this.numChars = this.stream.read(this.buf);
} catch (IOException var2) {
throw new InputMismatchException();
}
if (this.numChars <= 0) {
return -1;
}
}
return this.buf[this.curChar++];
}
}
public int nextInt() {
int c;
for (c = this.read(); isSpaceChar(c); c = this.read()) {
;
}
byte sgn = 1;
if (c == 45) {
sgn = -1;
c = this.read();
}
int res = 0;
while (c >= 48 && c <= 57) {
res *= 10;
res += c - 48;
c = this.read();
if (isSpaceChar(c)) {
return res * sgn;
}
}
throw new InputMismatchException();
}
public static boolean isSpaceChar(int c) {
return c == 32 || c == 10 || c == 13 || c == 9 || c == -1;
}
}
static class Utils {
public static long inv(long N, long M) {
long x = 0, lastx = 1, y = 1, lasty = 0, q, t, a = N, b = M;
while (b != 0) {
q = a / b;
t = a % b;
a = b;
b = t;
t = x;
x = lastx - q * x;
lastx = t;
t = y;
y = lasty - q * y;
lasty = t;
}
return (lastx + M) % M;
}
public static int gcd(int a, int b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}
}
}
Varying Kibibits
Tutorial is loading...
example code (c++, inclusion/exclusion approach)
// vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv Library code start
#include <array>
#define NDEBUG
NDEBUG
#include <algorithm>
#include <cassert>
#include <cstring>
#include <functional>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <tuple>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
#include <queue>
#include <random>
#define forn(t, i, n) for (t i = 0; i < (n); ++i)
#define rforn(t, i, n) for (t i = (n) - 1; i >= 0; --i)
#define all(c) c.begin(), c.end()
using namespace std;
/// caide keep
bool __hack = std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
/// caide keep
auto __hack1 = cin.tie(nullptr);
// Section with adoption of array and vector algorithms.
// 32 bit ints (sum LSB + MSB == 32)
// TODO: Section with some container algorithms
#define ENABLE_IF(e) typename enable_if<e>::type* = nullptr
namespace template_util {
template<class T>
constexpr T min(T a, T b) {
return a < b ? a : b;
}
constexpr int bytecount(uint64_t x) {
return x ? 1 + bytecount(x >> 8) : 0;
}
/// caide keep
template<int N>
struct bytetype {
typedef uint64_t type;
};
/// caide keep
template<>
struct bytetype<4> {
typedef uint32_t type;
};
/// caide keep
template<>
struct bytetype<3> {
};
/// caide keep
template<>
struct bytetype<2> {
};
/// caide keep
template<>
struct bytetype<1> {
typedef uint8_t type;
};
/// caide keep
template<>
struct bytetype<0> {
typedef uint8_t type;
};
/// caide keep
template<uint64_t N>
struct minimal_uint : bytetype<bytecount(N)> {
};
}
template<class T>
T next(istream& in) {
T ret;
in >> ret;
return ret;
}
template<class T>
vector<T> next_vector(istream& in, size_t n) {
vector<T> ret(n);
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ret[i] = next<T>(in);
}
return ret;
}
#define dbg(...) ;
/*
TODOs:
cache invs
primitive root
discrete log
tests!!!
*/
namespace mod_impl {
/// caide keep
template <class T>
constexpr inline T mod(T MOD) {
return MOD;
}
/// caide keep
template <class T>
constexpr inline T mod(T* MOD) {
return *MOD;
}
/// caide keep
template <class T>
constexpr inline T max_mod(T MOD) {
return MOD - 1;
}
/// caide keep
template <class T>
constexpr inline T max_mod(T*) {
return numeric_limits<T>::max() - 1;
}
constexpr inline uint64_t combine_max_sum(uint64_t a, uint64_t b) {
return a > ~b ? 0 : a + b;
}
constexpr inline uint64_t combine_max_mul(uint64_t a, uint64_t b) {
return a > numeric_limits<uint64_t>::max() / b ? 0 : a * b;
}
/// caide keep
template <class T>
constexpr inline uint64_t next_divisible(T mod, uint64_t max) {
return max % mod == 0 ? max : combine_max_sum(max, mod - max % mod);
}
/// caide keep
template <class T>
constexpr inline uint64_t next_divisible(T*, uint64_t) {
return 0;
}
//caide keep
constexpr int IF_THRESHOLD = 2;
template <class T, T MOD_VALUE, uint64_t MAX,
class RET = typename template_util::minimal_uint<max_mod(MOD_VALUE)>::type,
ENABLE_IF(MAX <= max_mod(MOD_VALUE) && !is_pointer<T>::value)>
inline RET smart_mod(typename template_util::minimal_uint<MAX>::type value) {
return value;
}
template <class T, T MOD_VALUE, uint64_t MAX,
class RET = typename template_util::minimal_uint<max_mod(MOD_VALUE)>::type,
ENABLE_IF(max_mod(MOD_VALUE) < MAX && MAX <= IF_THRESHOLD * max_mod(MOD_VALUE) && !is_pointer<T>::value)>
inline RET smart_mod(typename template_util::minimal_uint<MAX>::type value) {
while (value >= mod(MOD_VALUE)) {
value -= mod(MOD_VALUE);
}
return (RET)value;
}
template <class T, T MOD_VALUE, uint64_t MAX,
class RET = typename template_util::minimal_uint<max_mod(MOD_VALUE)>::type,
ENABLE_IF(IF_THRESHOLD * max_mod(MOD_VALUE) < MAX || is_pointer<T>::value)>
inline RET smart_mod(typename template_util::minimal_uint<MAX>::type value) {
return (RET)(value % mod(MOD_VALUE));
}
}
#define MOD mod_impl::mod(MOD_VALUE)
#define MAX_MOD mod_impl::max_mod(MOD_VALUE)
struct DenormTag {};
template <class T, T MOD_VALUE, uint64_t MAX = MAX_MOD, ENABLE_IF(MAX_MOD >= 2)>
struct ModVal {
typedef typename template_util::minimal_uint<MAX>::type storage;
storage value;
/// caide keep
inline ModVal(): value(0) {
assert(MOD >= 2);
}
inline ModVal(storage v, DenormTag): value(v) {
assert(MOD >= 2);
assert(v <= MAX);
};
inline operator ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE>() {
return {v(), DenormTag()};
};
explicit inline operator uint64_t() const {
return v();
}
typename template_util::minimal_uint<mod_impl::max_mod(MOD_VALUE)>::type v() const {
return mod_impl::smart_mod<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX>(value);
}
};
template <class T, T MOD_VALUE, uint64_t MAX,
uint64_t NEW_MAX = mod_impl::next_divisible(MOD_VALUE, MAX),
ENABLE_IF(NEW_MAX != 0),
class Ret = ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, NEW_MAX>>
inline Ret operator-(const ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX>& o) {
static_assert(NEW_MAX <= numeric_limits<typename Ret::storage>::max(), "bad unary minus template");
assert(NEW_MAX % MOD == 0 && o.value <= NEW_MAX);
return {typename Ret::storage(NEW_MAX - o.value), DenormTag()};
}
template <class T, T MOD_VALUE, uint64_t MAX1, uint64_t MAX2,
uint64_t NEW_MAX = mod_impl::combine_max_sum(MAX1, MAX2),
ENABLE_IF(NEW_MAX != 0), class Ret = ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, NEW_MAX>>
inline Ret operator+(ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX1> o1, ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX2> o2) {
return {typename Ret::storage(typename Ret::storage() + o1.value + o2.value), DenormTag()};
}
template <class T, T MOD_VALUE, uint64_t MAX1, uint64_t MAX2,
uint64_t NEW_MAX = mod_impl::combine_max_mul(MAX1, MAX2),
ENABLE_IF(NEW_MAX != 0), class Ret = ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, NEW_MAX>>
inline Ret operator*(ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX1> o1, ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX2> o2) {
return {typename Ret::storage(typename Ret::storage(1) * o1.value * o2.value), DenormTag()};
}
template <class T, T MOD_VALUE, uint64_t MAX1, uint64_t MAX2,
uint64_t NEW_MAX = mod_impl::combine_max_mul(MAX1, MAX2),
uint64_t NEW_MAX1 = mod_impl::combine_max_mul(MAX_MOD, template_util::min(MAX1, MAX2)),
ENABLE_IF(NEW_MAX == 0 && NEW_MAX1 != 0 && MAX1 <= MAX2),
class Ret = ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, mod_impl::combine_max_mul(MAX1, MAX_MOD)>>
inline Ret operator*(const ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX1>& o1, const ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX2>& o2) {
return {typename Ret::storage(typename Ret::storage(1) * o1.value * o2.v()), DenormTag()};
}
template <class T, T MOD_VALUE, uint64_t MAX1, uint64_t MAX2,
uint64_t NEW_MAX = mod_impl::combine_max_mul(MAX1, MAX2),
uint64_t NEW_MAX1 = mod_impl::combine_max_mul(MAX_MOD, template_util::min(MAX1, MAX2)),
ENABLE_IF(NEW_MAX == 0 && NEW_MAX1 != 0 && MAX2 < MAX1),
class Ret = ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, mod_impl::combine_max_mul(MAX_MOD, MAX2)>>
inline Ret operator*(const ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX1>& o1, const ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX2>& o2) {
return {typename Ret::storage(typename Ret::storage(1) * o1.v() * o2.value), DenormTag()};
}
template <class T, T MOD_VALUE, uint64_t MAX1, uint64_t MAX2>
inline auto operator-(const ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX1>& lhs, const ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX2>& rhs) -> decltype(lhs + (-rhs)) {
return lhs + (-rhs);
}
template <class T, T MOD_VALUE, uint64_t MAX>
inline ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE>& operator+=(ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE>& lhs, const ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX>& rhs) {
lhs = lhs + rhs;
return lhs;
}
template <class T, T MOD_VALUE, uint64_t MAX>
inline ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE>& operator-=(ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE>& lhs, const ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX>& rhs) {
lhs = lhs - rhs;
return lhs;
}
template <class T, T MOD_VALUE, uint64_t MAX1, uint64_t MAX2>
inline bool operator!=(const ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX1>& lhs, const ModVal<T, MOD_VALUE, MAX2>& rhs) {
return lhs.v() != rhs.v();
}
template <class T, T MOD_VALUE, class MOD_TYPE>
struct ModCompanion {
typedef MOD_TYPE mod_type;
typedef ModVal<mod_type, MOD_VALUE> type;
template <uint64_t C>
inline static constexpr ModVal<mod_type, MOD_VALUE, C> c() {
return {C, DenormTag()};
};
template <uint64_t MAX = numeric_limits<uint64_t>::max()>
inline static ModVal<mod_type, MOD_VALUE, MAX> wrap(uint64_t x) {
assert(x <= MAX);
return {typename ModVal<mod_type, MOD_VALUE, MAX>::storage(x), DenormTag()};
};
template <uint64_t MAX, ENABLE_IF(!is_pointer<T>::value && MAX <= MAX_MOD)>
inline static ModVal<mod_type, MOD_VALUE> inv(const ModVal<mod_type, MOD_VALUE, MAX>& x) {
if (x.value == 1) {
return c<1>();
}
return -(wrap<MAX_MOD / 2>(MOD / x.value) * inv(wrap<MAX>(MOD % x.value)));
};
};
#undef MOD
#undef MAX_MOD
template <uint64_t MOD_VALUE>
struct Mod : ModCompanion<uint64_t, MOD_VALUE, typename template_util::minimal_uint<MOD_VALUE>::type> {
template<uint64_t VAL>
static constexpr uint64_t literal_builder() {
return VAL;
}
template<uint64_t VAL, char DIGIT, char... REST>
static constexpr uint64_t literal_builder() {
return literal_builder<(10 * VAL + DIGIT - '0') % MOD_VALUE, REST...>();
}
};
#define REGISTER_MOD_LITERAL(mod, suffix) \
template <char... DIGITS> mod::type operator "" _##suffix() { \
return mod::c<mod::literal_builder<0, DIGITS...>()>(); \
}
// ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ Library code end
using md = Mod<1000000007>;
using mt = md::type;
REGISTER_MOD_LITERAL(md, mod)
using Val = tuple<int, mt, mt>;
mt pow2s[1000001], powInv2s[1000001];
mt pow2(int p) {
return p < 0 ? powInv2s[-p] : pow2s[p];
}
Val mul(Val a, Val b) {
const mt p2a = pow2(get<0>(a));
const mt p2b = pow2(get<0>(b));
return Val{get<0>(a) + get<0>(b), p2a * get<1>(b) + get<1>(a) * p2b, p2a * get<2>(b) + 2_mod * get<1>(a) * get<1>(b) + get<2>(a) * p2b};
}
Val inv(Val a) {
Val b;
get<0>(b) = -get<0>(a);
const mt p2b = pow2(get<0>(b));
get<1>(b) = -p2b * (get<1>(a) * p2b);
get<2>(b) = -p2b * (2_mod * get<1>(a) * get<1>(b) + get<2>(a) * p2b);
return b;
}
Val d[1000000][7];
mt dSum[1000000][7];
void solve(istream& in, ostream& out) {
pow2s[0] = powInv2s[0] = 1_mod;
mt inv2 = md::inv(2_mod);
forn (int, i, 1000000) {
pow2s[i + 1] = pow2s[i] * 2_mod;
powInv2s[i + 1] = powInv2s[i] * inv2;
}
int n = next<int>(in);
auto as = next_vector<int>(in, n);
sort(all(as));
uint64_t ans = 0;
int add[1 << 6];
forn (int, mask, 1 << 6) {
add[mask] = 0;
int mask1 = mask;
forn (int, it, 6) {
add[mask] = add[mask] * 10 + (mask1 & 1);
mask1 /= 2;
}
}
int asIt = n - 1;
rforn (int, x, 1000000) {
int badMask = 0;
int x1 = x;
forn (int, it, 6) {
badMask = 2 * badMask + (x1 % 10 == 9 ? 1 : 0);
x1 /= 10;
}
d[x][0] = Val{0, 0_mod, 0_mod};
dSum[x][0] = 0_mod;
forn (int, bit, 6) {
d[x][bit + 1] = d[x][bit];
dSum[x][bit + 1] = dSum[x][bit];
if (!(badMask & (1 << bit))) {
d[x][bit + 1] = mul(d[x][bit + 1], inv(d[x + add[1 << bit]][bit]));
dSum[x][bit + 1] -= dSum[x + add[1 << bit]][bit];
}
}
auto val = inv(d[x][6]);
while (asIt >= 0 && as[asIt] == x) {
--asIt;
val = mul(val, Val{1, md::wrap(x), md::wrap(1ULL * x * x)});
}
auto sum = get<2>(val) + dSum[x][6];
forn (int, bit, 6) {
d[x][bit] = mul(d[x][bit], val);
dSum[x][bit] += get<2>(val);
}
if (sum != 0_mod) {
dbg(x, sum, x * uint64_t(sum));
ans ^= x * uint64_t(sum);
}
}
out << ans << endl;
}
int main() {
solve(cin, cout);
return 0;
}
example code (java, FWHT approach)
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.Writer;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* Built using CHelper plug-in
* Actual solution is at the top
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream inputStream = System.in;
OutputStream outputStream = System.out;
InputReader in = new InputReader(inputStream);
OutputWriter out = new OutputWriter(outputStream);
MinAddition solver = new MinAddition();
solver.solve(1, in, out);
out.close();
}
static class MinAddition {
public int[] pow10 = {1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000, 1000000};
public int MAXN = 1000000;
public int LOG = 6;
public int mod = 1000000007;
public void solve(int testNumber, InputReader in, OutputWriter out) {
int n = in.nextInt();
int[] freq = new int[MAXN];
int[] sum = new int[MAXN];
int[] sum2 = new int[MAXN];
int[] pow2 = new int[n + 1];
pow2[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) pow2[i] = (pow2[i - 1] << 1) % mod;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int a = in.nextInt();
freq[a]++;
sum[a] += a;
if (sum[a] >= mod) sum[a] -= mod;
int x = (int) (1L * a * a % mod);
sum2[a] += x;
if (sum2[a] >= mod) sum2[a] -= mod;
}
int[] mod10 = new int[MAXN];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) mod10[i] = i;
for (int i = 10; i < MAXN; i++) mod10[i] = mod10[i - 10];
for (int level = LOG - 1; level >= 0; level--) {
for (int i = MAXN - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int d = mod10[i / pow10[level]];
if (d > 0) {
int p = i - pow10[level];
freq[p] += freq[i];
sum[p] += sum[i];
if (sum[p] >= mod) sum[p] -= mod;
sum2[p] += sum2[i];
if (sum2[p] >= mod) sum2[p] -= mod;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAXN; i++) {
int sdiff = (int) ((1L * sum[i] * sum[i] + mod - sum2[i]) % mod);
int ssame = sum2[i];
int g = 0;
if (freq[i] >= 1)
g += (int) (1L * ssame * pow2[freq[i] - 1] % mod);
if (freq[i] >= 2)
g += (int) (1L * sdiff * pow2[freq[i] - 2] % mod);
while (g >= mod) g -= mod;
freq[i] = g;
}
for (int level = 0; level < LOG; level++) {
for (int i = 0; i < MAXN; i++) {
int d = mod10[i / pow10[level]];
if (d + 1 < 10) {
int p = i + pow10[level];
freq[i] -= freq[p];
if (freq[i] < 0) freq[i] += mod;
}
}
}
long s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < MAXN; i++) {
s ^= 1L * i * freq[i];
}
out.println(s);
}
}
static class OutputWriter {
private final PrintWriter writer;
public OutputWriter(OutputStream outputStream) {
writer = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream)));
}
public OutputWriter(Writer writer) {
this.writer = new PrintWriter(writer);
}
public void close() {
writer.close();
}
public void println(long i) {
writer.println(i);
}
}
static class InputReader {
private InputStream stream;
private byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
private int curChar;
private int numChars;
public InputReader(InputStream stream) {
this.stream = stream;
}
public int read() {
if (this.numChars == -1) {
throw new InputMismatchException();
} else {
if (this.curChar >= this.numChars) {
this.curChar = 0;
try {
this.numChars = this.stream.read(this.buf);
} catch (IOException var2) {
throw new InputMismatchException();
}
if (this.numChars <= 0) {
return -1;
}
}
return this.buf[this.curChar++];
}
}
public int nextInt() {
int c;
for (c = this.read(); isSpaceChar(c); c = this.read()) {
;
}
byte sgn = 1;
if (c == 45) {
sgn = -1;
c = this.read();
}
int res = 0;
while (c >= 48 && c <= 57) {
res *= 10;
res += c - 48;
c = this.read();
if (isSpaceChar(c)) {
return res * sgn;
}
}
throw new InputMismatchException();
}
public static boolean isSpaceChar(int c) {
return c == 32 || c == 10 || c == 13 || c == 9 || c == -1;
}
}
}
Verifying Kingdom
Tutorial is loading...
example code (c++)
// vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv Library code start
#define NDEBUG
NDEBUG
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
#include <cassert>
#include <cstring>
#include <functional>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <tuple>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
#include <queue>
#include <random>
#define forn(t, i, n) for (t i = 0; i < (n); ++i)
#define foran(t, i, a, n) for (t i = (a); i < (n); ++i)
using namespace std;
/// caide keep
bool __hack = std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
/// caide keep
auto __hack1 = cin.tie(nullptr);
template<class T>
inline T mn(T arg) {
return arg;
}
template<class T, class... Args>
inline bool rmx(T &to, Args... args) {
auto v = mn(args...);
if (to < v) {
to = v;
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Section with adoption of array and vector algorithms.
// 32 bit ints (sum LSB + MSB == 32)
// TODO: Section with some container algorithms
namespace template_util {
constexpr int bytecount(uint64_t x) {
return x ? 1 + bytecount(x >> 8) : 0;
}
/// caide keep
template<int N>
struct bytetype {
};
/// caide keep
template<>
struct bytetype<4> {
};
/// caide keep
template<>
struct bytetype<3> {
};
/// caide keep
template<>
struct bytetype<2> {
};
/// caide keep
template<>
struct bytetype<1> {
};
/// caide keep
template<>
struct bytetype<0> {
};
/// caide keep
template<uint64_t N>
struct minimal_uint : bytetype<bytecount(N)> {
};
}
template<class T>
T next(istream& in) {
T ret;
in >> ret;
return ret;
}
// ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ Library code end
int tr[1000][3];
int l[1000], r[1000];
bool col[1000];
int ans[2000];
tuple<int, int, int> chooseDfs(int total, int i, int p = -1) {
int size = 1, best = -1, bestSize = 1000000000, maxSize = 0;
forn (int, e, 3) {
int j = tr[i][e];
if (j != p && j >= 0 && !col[j]) {
auto r1 = chooseDfs(total, j, i);
if (get<1>(r1) < bestSize) {
best = get<0>(r1);
bestSize = get<1>(r1);
}
size += get<2>(r1);
rmx(maxSize, get<2>(r1));
}
}
rmx(maxSize, total - size);
if (maxSize < bestSize) {
best = i;
bestSize = maxSize;
}
return tuple<int, int, int>{best, bestSize, size};
}
int sizeDfs(int i, int p = -1) {
auto r = 1;
forn (int, e, 3) {
int j = tr[i][e];
if (j != p && j >= 0 && !col[j]) {
r += sizeDfs(j, i);
}
}
return r;
}
void ansDfs(int n, int i) {
forn (int, e, 2) {
if (tr[i][e] >= 0) {
ansDfs(n, tr[i][e]);
}
ans[tr[i][e] < 0 ? -2 - tr[i][e] : n + tr[i][e]] = n + i + 1;
}
}
void solve(istream& in, ostream& out) {
auto q = [&](int a, int b, int c) {
out << a + 1 << " " << b + 1 << " " << c + 1 << endl;
string s = next<string>(in);
if (s == "X") {
return 2;
} else if (s == "Y") {
return 1;
} else if (s == "Z") {
return 0;
} else {
throw 42;
}
};
int n = next<int>(in);
memset(tr, -1, sizeof(tr));
tr[0][0] = -2;
tr[0][1] = -3;
l[0] = 0;
r[0] = 1;
foran (int, i, 2, n) {
memset(col, 0, sizeof(col));
int x = 0;
while (true) {
x = get<0>(chooseDfs(sizeDfs(x), x));
int e = q(l[x], r[x], i);
if (tr[x][e] < 0 || col[tr[x][e]]) {
if (tr[x][e] >= 0) {
forn (int, e1, 3) {
if (tr[tr[x][e]][e1] == x) {
tr[tr[x][e]][e1] = i - 1;
}
}
}
tr[i - 1][e] = tr[x][e];
tr[x][e] = i - 1;
tr[i - 1][e == 0 ? 1 : 0] = -2 - i;
tr[i - 1][e == 2 ? 1 : 2] = x;
l[i - 1] = tr[i - 1][0] < 0 ? -2 - tr[i - 1][0] : l[tr[i - 1][0]];
r[i - 1] = tr[i - 1][1] < 0 ? -2 - tr[i - 1][1] : r[tr[i - 1][1]];
break;
}
col[x] = true;
x = tr[x][e];
}
}
int r = 0;
while (tr[r][2] != -1) {
r = tr[r][2];
}
ans[n + r] = -1;
ansDfs(n, r);
out << "-1\n";
forn (int, i, 2 * n - 1) {
out << ans[i] << " ";
}
out << "\n";
}
int main() {
solve(cin, cout);
return 0;
}
example code (java)
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.Writer;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* Built using CHelper plug-in
* Actual solution is at the top
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream inputStream = System.in;
OutputStream outputStream = System.out;
InputReader in = new InputReader(inputStream);
OutputWriter out = new OutputWriter(outputStream);
ForgottenTree solver = new ForgottenTree();
solver.solve(1, in, out);
out.close();
}
static class ForgottenTree {
public InputReader in;
public OutputWriter out;
public int nidx;
public int n;
public int[] par;
public void solve(int testNumber, InputReader in, OutputWriter out) {
this.in = in;
this.out = out;
n = in.nextInt();
nidx = n;
ForgottenTree.Node root = new ForgottenTree.Node(0);
ForgottenTree.Node.cgen = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
ForgottenTree.Node.cgen++;
root.getLeaves();
root = insert(root, i);
}
out.println(-1);
par = new int[2 * n - 1];
dfs(root, -2);
out.println(par);
}
public String ask(int a, int b, int c) {
out.println((a + 1) + " " + (b + 1) + " " + (c + 1));
out.flush();
String ret = in.next();
if (ret.equals("-1")) System.exit(0);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(ForgottenTree.Node root, int p) {
par[root.label] = p + 1;
if (root.lchild != null) {
dfs(root.lchild, root.label);
dfs(root.rchild, root.label);
}
}
public ForgottenTree.Node insert(ForgottenTree.Node root, int label) {
if (!root.active()) {
return add(root, label);
}
root.dfs();
if (root.lchild == null) {
return add(root, label);
}
int curleaves = root.nleaves;
if (curleaves <= 1) {
int nnodes = 0;
ForgottenTree.Node cur = root;
while (!cur.isLeaf()) {
nnodes++;
if (cur.lchild.active()) cur = cur.lchild;
else cur = cur.rchild;
}
cur = root;
int depth = 0;
while (2 * (depth + 1) < nnodes) {
if (cur.lchild.active()) cur = cur.lchild;
else cur = cur.rchild;
depth++;
}
return process(root, cur, label);
}
ForgottenTree.Node cur = root;
while (true) {
if (cur.lchild == null) {
if (cur.par == null) {
return add(cur, label);
}
if (cur.which == 0) {
cur.par.setChild(0, add(cur, label));
return root;
} else {
cur.par.setChild(1, add(cur, label));
return root;
}
}
int x1 = cur.lchild.active() ? cur.lchild.nleaves : 0;
int x2 = cur.rchild.active() ? cur.rchild.nleaves : 0;
if (x1 * 2 > curleaves) {
cur = cur.lchild;
continue;
}
if (x2 * 2 > curleaves) {
cur = cur.rchild;
continue;
}
return process(root, cur, label);
}
}
public ForgottenTree.Node process(ForgottenTree.Node root, ForgottenTree.Node cur, int label) {
String s = ask(cur.x, cur.y, label);
switch (s) {
case "X":
if (cur.par == null) {
return add(cur, label);
}
cur.disable();
return insert(root, label);
case "Y":
cur.setChild(1, insert(cur.rchild, label));
return root;
case "Z":
cur.setChild(0, insert(cur.lchild, label));
return root;
default:
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
public ForgottenTree.Node add(ForgottenTree.Node cnode, int label) {
ForgottenTree.Node add = new ForgottenTree.Node(nidx++);
add.setChild(0, cnode);
add.setChild(1, new ForgottenTree.Node(label));
return add;
}
static class Node {
public static int cgen;
public int x;
public int y;
public int label;
public int gen;
public int nleaves;
public int which;
public ForgottenTree.Node lchild;
public ForgottenTree.Node rchild;
public ForgottenTree.Node par;
public Node(int label) {
this.lchild = null;
this.rchild = null;
this.par = null;
this.which = 0;
this.label = label;
this.gen = 0;
this.nleaves = 1;
}
public boolean active() {
return gen < cgen;
}
public void disable() {
this.gen = cgen;
}
public boolean isLeaf() {
return lchild == null || (!lchild.active() && !rchild.active());
}
public void setChild(int which, ForgottenTree.Node x) {
if (which == 0) {
this.lchild = x;
} else {
this.rchild = x;
}
x.par = this;
x.which = which;
}
public void dfs() {
if (isLeaf()) {
this.nleaves = 1;
return;
}
this.nleaves = 0;
if (lchild.active()) {
lchild.dfs();
this.nleaves += lchild.nleaves;
}
if (rchild.active()) {
rchild.dfs();
this.nleaves += rchild.nleaves;
}
}
public void getLeaves() {
if (lchild == null) {
this.x = this.y = label;
return;
}
lchild.getLeaves();
rchild.getLeaves();
this.x = lchild.x;
this.y = rchild.x;
}
}
}
static class InputReader {
private InputStream stream;
private byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
private int curChar;
private int numChars;
public InputReader(InputStream stream) {
this.stream = stream;
}
public int read() {
if (this.numChars == -1) {
throw new InputMismatchException();
} else {
if (this.curChar >= this.numChars) {
this.curChar = 0;
try {
this.numChars = this.stream.read(this.buf);
} catch (IOException var2) {
throw new InputMismatchException();
}
if (this.numChars <= 0) {
return -1;
}
}
return this.buf[this.curChar++];
}
}
public int nextInt() {
int c;
for (c = this.read(); isSpaceChar(c); c = this.read()) {
;
}
byte sgn = 1;
if (c == 45) {
sgn = -1;
c = this.read();
}
int res = 0;
while (c >= 48 && c <= 57) {
res *= 10;
res += c - 48;
c = this.read();
if (isSpaceChar(c)) {
return res * sgn;
}
}
throw new InputMismatchException();
}
public String next() {
int c;
while (isSpaceChar(c = this.read())) {
;
}
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
result.appendCodePoint(c);
while (!isSpaceChar(c = this.read())) {
result.appendCodePoint(c);
}
return result.toString();
}
public static boolean isSpaceChar(int c) {
return c == 32 || c == 10 || c == 13 || c == 9 || c == -1;
}
}
static class OutputWriter {
private final PrintWriter writer;
public OutputWriter(OutputStream outputStream) {
writer = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream)));
}
public OutputWriter(Writer writer) {
this.writer = new PrintWriter(writer);
}
public void print(Object... objects) {
for (int i = 0; i < objects.length; i++) {
if (i != 0) {
writer.print(' ');
}
writer.print(objects[i]);
}
}
public void print(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (i != 0) {
writer.print(' ');
}
writer.print(array[i]);
}
}
public void println(int[] array) {
print(array);
writer.println();
}
public void println(Object... objects) {
print(objects);
writer.println();
}
public void close() {
writer.close();
}
public void flush() {
writer.flush();
}
public void println(int i) {
writer.println(i);
}
}
}











Fast editorial! Great!
I think Lewin is fastest among problemsetters to put editorial :) .BTW I love the format too :)
Div1B can be solved in O(n*log(D)) by binary searching on d. For a particular d if a line passes through the circles with centre i,i+1,i+2 and radius d then concave polygon can be formed. My submission
"First, we can make only one angle of the polygon nonconvex." Why?
We dont need more.
If we can find 3 non-consecutive vertices of polygon moved for some D so that it becomes nonconvex, we can find 3 consecutive vertices of this polygon that being moved for the same D also make it nonconvex. If some vertex can become unconvex with some other vertex after moving them, it will also become unconvex with all of the vertices that are between them after moving these vertices for the same or lower D.
nice
In my impression, Div1 A is tough to solve in some language such as Java and C#. See this (26436569). It is almost same as expected solution. However, it failed at case 71.
I want to know whether this problem can be solved or not.
I got the same error so that means...probably not. Maybe test case 71 should not be counted for some languages?
Hi guys, quickly check out accepted solutions here http://codeforces.net/contest/801/status
and filter by Java | accepted | Problem C
we can learn something from how accepted Java solutions solved it.
Take care
After looking through different solutions, they all look identical to mine besides some names, nothing big.
After slowly making changes in my code until it works, this is what I came to:
I was calculating the amount of time a device would need the charger for to stay alive , so I was using Math.max(0, (b[i] — a[i] * time)/p) and compared the total to time.
What you were doing was using the required power as in the amount of energy per second the charger would need to have all of the devices living a.k.a. using Math.max(0, (a[i] — b[i]/time)) and comparing that to p.
There are also other people who calculate the overall energy with Math.max(0,a[i]*time-b) and comparing that to time*P. This is what the editorial used.
The only difference that caused power to work is that the numbers that are being worked with are smaller, meaning no calculation error. Thinking purely mathematically, all three way would work, but since the computer is not perfect at math, only one way works in practice.
To get rid of the errors in calculations with fractional numbers, try to avoid multiplications/divisions with double values. Instead do the mul/div operations with integers and leave only comparisons to doubles. In my solution, I check only
t <= sumB/ (sumA - p). sumA and sumB are the sums of those a[i] and b[i] for which t > b[i]/a[i]. Therefore all multiplication and division occurs with integers.Second thing worth-mentioning is that you can take high value in binary search to be a power of two. That would help to get integer values for t, most of the time.
Hope, this helps.
I had the same problem. setting the high value in binary search to 1e10 + 10 passes Test #71, but fails in Test #73. Setting it to 1e10 + 20, passes #73 but fails in #80 in my solution. Can't get further than that.
Judges should clarify this issue.
Cool)) All the titles of the problems are "V... K..."
P.S. Ранее условия и названия, в частности, были прочитаны на русском языке.
In D we shouldn't consider f(S) >= x as numbers, but rather as a vector of digits (what is currently not specified).
In div2C, I think the max answer can be at most around 10^10... The max answer will be generated by a case like:
100000 99999
1 100000
1 100000
........
........
1 100000
Could you verify?
Yes. It can be proved in this manner. Since p & a(i)'s are integers, this essentially means the sum of a(i)'s at t = 2sec < sum of a(i)'s at t = 1sec because p < sum of a(i)'s. This means sum of a(i)'s will decrease by atleast 1 after each second.
Therfore maximum answere possible = sum of all a(i)'s in the start which is nothing but (10 ^ 5) * (10 ^ 5).
I have a question concerning problem Div.2 C:
Why is the maximum answer 1e14?
I had trouble finding the upper limit in the contest so I ended up putting it 1e20 or more, I solved it.
Any help is appreciated.
in the worst case, p + 1 = sum of all a[i]. In that case, you need sum of all b[i] seconds to run out of energy
In that case, the maximum answer is less than 1e14.
Sum of all b[i] is 1e10. Therefore if the upper bound for binary search was 1e10, it would be fairly enough to solve the problem.
Please correct me if I'm wrong.
yes of course it's 10^10. My solution has it's upper bound at 1e11 and still pass the system test
I didn't participe but I read tasks...
I have questions for both A and B div 1. I would submit same solutions as written in editorial but some parts are not clear at all to me — they are intuitive but again I would like to hear proof.
1.In A task when time needed to charge all devices is smaller than searched time — can you show construcktive algorithm of charging everything on way that none of devices will be empty during this period ?
2.For B task. Why are we making always non-convex polygon, maybe sometime is more optimal to make polygon with edge intersections ?
If sum of demands <= p then this means you can come back to charge the same device after 1 second and it wouldn't have lost all of the charge.
Let's suppose it the device starts charging from device 1 then device 2 .... device n and repeat. For each device i it gives it a(i) charge i.e. which can support it for 1 second
Now since p > sum of all a(i)'s this essentially means it will be back at device 1 for the same charging cycle in <= 1sec and will re charge each device before it has fully drained all of it's charge of previous cycle.
Hey I didn't get it completely what you are saying! Can you explain in a bit detail ?
What part you didn't understand?
How much time do you spend supplying i'th device?
The time sufficient such that ith device garners a(i) amount of charge. SO the time in seconds will be a(i) / p seconds.
But this way of charging devices is not working on this testcase
3 15
2 1
5 1
8 1
You charge a first device 2/15 seconds. While you're charging amount of energy of the third device will be negative because 2*8/15 is bigger than 1
I have similar doubts on problem A. Here are my thoughts. You don't really need a constructive algorithm to prove that the devices are alive. If you think of it like conservation of energy (charge) — As long as the charger can supply energy of P*T which is greater or equal to the charge required by all devices, an infinitesimally small charge persists on each device.
I don't know if this is right. Any help is appreciated. Thanks!
In div2 C , what happens wrong when I compare the answer to the upper bound used in binary search for the infinity case? WA : 26437983 AC : 26438358
Easy ac with long double on cpp. Easy tl/wa with bigdecimal/double on java. Nice ;)
Someone please help me out in Div2 C problem. I don't know why i keep getting WA on test 31. I guess the problem might be lying in the error bound. Code: 26438641
The answer for 31 is -1. Don't use a certain time to determine if it is going on forever. Just check if the sum of the power usages is less than or equal to P.
For Division 2 C, I did everything the editorial said and even now, I am getting a .0003 error on test case 71. I can't seem to do better no matter what. Does anyone know why? Code: 26438965
Also, when I used BigDecimal, I got runtime error on testcase 10.
Crisp and clear explanations in the editorial.
In div1a (772A - Voltage Keepsake), you can use fewer runs of binary search by using the trick described by Um_nik in his blog: http://codeforces.net/blog/entry/49189?locale=en. It wasn't necessary today but it allowed making a program much faster (/ more precise). But please note that this thing has nothing to do with Java issues in this particular problem.
why there is not a fixed value for infinity .. like 1e10 or anything else (limits) in problem C
If you are asking why there isn't a value where you can safely say that the power will last forever, then their actually is, 1e14 + 1
can you please elaborate on why the upper limit is 1e14 + 1?
For 772A Voltage Keepsake, isn't Xi = max(0,T*ai — bi)?
I think you're right, because we want the power to be charged, so Xi = max(0, T * a — b) seems just what we need.
P.S.: it must be a mistake, the author's code uses Xi = max(0, T * a — b).
Hello:
In 772A - Voltage Keepsake how are you able to assume that the maximum for binary search is 1014? Where does this maximum come from?
Also in the tutorial for 772A - Voltage Keepsake, you say Xi = max(0, bi - T * ai), however in your example code you write:
ld need=max(0.0L, (imid-exhaust[i])*a[i]);Upon my own testing, I believe the condition in the code is right, and it should be updated to Xi = max(0, T * ai - bi).Thanks
Hello, I think I just (partially) figured out the answer to my question #1 (why is the maximum 1014). Feel free to correct me if I am wrong.
The largest time is produced if the power of the charger is one less than the sum of all the charges needed by the devices (if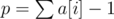 ).
).
EDIT: It does not seem that 1e14 is the lowest possible upper bound though... I'm not sure why it was chosen... see my other comment below for more info
can you elaborate on why we multiply those two numbers 1e9 * 1e5 ? it is the maximum TIME we seek after all.
In Div1-D, the inclusion-exclusion approach, how to calculate the modified f(x) function?
I have a solution with inclusion-exclusion .
You can see details Here ! 26449626
What do these array mean in your solution: cnt, sum, sq, g?
let S[i] : be the multiset of numbers which all of them has following condition :
for every x in S[i]:
for every k , kth digit of x is greater or equal than kth digit of i.
now :
sum[i] is equal to sum of these elements.
sq[i] is equal to sum of squares of this elements.
g[i] is equal to the answer(the thing that question want!) for all of the subset of S[i]
Can anyone please describe the solution of Div1 C with more details .
In div 1 C how do we create the edges in a suitable time?
the condition that we have an edge(directed) (u, v) :
gcd(u, m) | v , that's equal to gcd(u, m) | gcd(v, m)
so , replace each i , with gcd(i ,m),
now you want a path that each number is divisor of the next number .
you can do it with a simple dp .
see this solution for more details ! 26435471
Thx man that helped! :)
Your Welcome :))
Can you explain for me why gcd(u, m) | v, that's equal to gcd(u, m) | gcd(v, m) ?
suppose that d = (u, m), d|v
so d|u, d|m, d|v
so d|m, d|v
so d|(v, m)
Oh I see. Thank you for help
In problem E/div2:
there are two directed edges between two nodes i and j if and only if gcd(n, i) = gcd(n, j). Can anyone give a proof of this?Any help is appreciated.
Sory for my poor English.
we can prove that, exist x make ix ≡ j modn if and only if gcd(n, i)|gcd(n, j)
if ix ≡ j modn, gcd(n, j) = gcd(n, kn + ix) = gcd(n, ix). apparently, gcd(n, i)|gcd(n, j);
the other way, if gcd(n, i)|gcd(n, j), then exist x make gcd(n, ix) = gcd(n, j), and j = ix + kn, too.
so if there are two directed edges between i and j, and then gcd(n, i)|gcd(n, j) and gcd(n, j)|gcd(n, i), so, gcd(n, i) = gcd(n, j);
Thank you! techay
In problem B, why do we only need to consider every 3 consecutive points? What I did was that, for each point, I took its distance from all line segments such that atleast one endpoint of that segment is adjacent to the given point.
eg. A=(0,0), B=(1000,500), C=(1001,500), D=(1000,-500)
Here, distance from A to line BC is less than distance from A to line BD.
I am also having difficulty with the proof of correctness.
In this case, the optimal answer is actually the distance from point B to line AC.
I guess the difficulty may be when the projection of the point doesn't lie in the segment. In that case, I think we can claim that's never an optimal solution, and doesn't need to be considered.
Yes, in this case, that is true. But in general, can we say that given three consecutive vertices A, B and C, there can never exist some vertex D such that distance from B to line AD is less than distance from B to line AC and that this is the final answer?
in div1E , how does the checker check if the tree in output is isomorphic to the tree in input?
Tree hashing. For example computing the centroid of the tree, then we can hash the subtrees by imagining the subtree as a bracket subsequence, and for each internal node, we sort the subtrees oriented from it by hash value.
Here's my checker implementation: https://pastebin.com/N5nLQUrH
I just compute the bracket sequence, and don't do any hashing.
My dear!I have got at least 15 WA on div2 C!!!it's on the test 71 or 74 ,Could you please give me some suggestions?
cause it's a valid point of time to make all devices alive with 0 units of power, you didn't consider that.
thanks Lewin for that fast and well prepared tutorial, nice contest BTW.
801C - Voltage Keepsake why the max answer is 1e14 ?
It's not. The maximum answer is 1010.
Let's say I have 105 devices, each uses 1 unit of charge per second, and starts with 105 units of charge. The charger is p = 99999. The answer should be 1010.
Edit: this scenario is the same as test #66.
yeah I consider it as 1e10 as p has to be strictly less than the summation of the consumption and it's max val 1e5*1e5 ...but I got confused with 1e14 at the tutorial , thanks bro.
The problem C why the sum suply of these bi more than p ,than output -1?
It is if the sum of a[i]s is less than or equal to P, then the output is -1. The idea is that the total voltage will always increase through time.
OK,I have understand it.Thank you so much !
div 1 B can be solved in O(n): We can draw a line through the nearest two points with a given point, and it is easy to see that the answer is half the length of the perpendicular from the point to this line (and we have three options to draw a straight line through two of the three points). That is, the problem is reduced to the search for a minimum of three heights of triangles formed by every three neighboring points. /// Мы можем провести прямую через ближайшие с данной точкой две точки, и нетрудно убедиться, что ответом будет половина длины перпендикуляра от точки к этой прямой (причём у нас есть три варианта провести прямую через две из трех точек). То есть задача сводится к поиску минимума из трёх высот треугольников, образованных каждыми тремя соседними точками. /// http://codeforces.net/contest/772/submission/26468460
The upper bound is 1e10, not 1e14.
In div2-D, firstly I used Heron's formula to get triangular's area but repeatedly got wrong answer. After fixxing it by calculating with vector property, I got accepted.
Is it dangerous to use heron's formula in calculating triangular's area usually??
Same here, and I guess it is just the language precision in floating number that causes.
can anyone explain this line of the code given in the editorial for 772C — Vulnerable Kerbals:
Thanks in advance :)
UPD: DONE.
can anyone help explain in B. Volatile Kite if i am using int for coordinates of the vertex i am getting wrong answer but using double AC,in input they are integer