Tutorial is loading...
Solution
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define sd(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define slld(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define ss(x) scanf("%s",x)
#define ll long long
#define mod 1000000007
#define bitcount __builtin_popcountll
#define pb push_back
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mp make_pair
#define pi pair<int,int>
int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
//freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
int n,i,j;
string s[102];
sd(n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>s[i];
for(j=0;j<i;j++)
{
if(s[i]==s[j])
break;
}
if(j==i)
printf("NO\n");
else
printf("YES\n");
}
return 0;
}
Tutorial is loading...
DP solution 1
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define sd(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define slld(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define ss(x) scanf("%s",x)
#define ll long long
#define mod 1000000007
#define bitcount __builtin_popcountll
#define pb push_back
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mp make_pair
#define pi pair<int,int>
int a[100005];
ll dp[100005][3];
int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
//freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
int n,p,q,r,i;
sd(n);
sd(p);
sd(q);
sd(r);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
sd(a[i]);
dp[0][0]=1ll*p*a[0];
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
dp[i][0]=max(dp[i-1][0],1ll*p*a[i]);
dp[0][1]=dp[0][0]+1ll*q*a[0];
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
dp[i][1]=max(dp[i-1][1],dp[i][0]+1ll*q*a[i]);
dp[0][2]=dp[0][1]+1ll*r*a[0];
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
dp[i][2]=max(dp[i-1][2],dp[i][1]+1ll*r*a[i]);
printf("%lld\n",dp[n-1][2]);
return 0;
}
DP solution 2 with minimum and maximum computation
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define sd(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define slld(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define ss(x) scanf("%s",x)
#define mod 1000000007
#define bitcount __builtin_popcountll
#define ll long long
#define pb push_back
#define pi pair<int,int>
#define pii pair<pi,int>
#define mp make_pair
int minleft[100005],minright[100005],maxleft[100005],maxright[100005],a[100005];
int main()
{
int i,j,k;
int n,p,q,r;
cin>>n>>p>>q>>r;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
sd(a[i]);
minleft[1]=maxleft[1]=a[1];
minright[n]=maxright[n]=a[n];
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
minleft[i]=min(minleft[i-1],a[i]);
maxleft[i]=max(maxleft[i-1],a[i]);
}
for(i=n-1;i>=1;i--)
{
minright[i]=min(minright[i+1],a[i]);
maxright[i]=max(maxright[i+1],a[i]);
}
ll ans=-3e18;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
ll leftval = (p<0) ? 1ll*minleft[i]*p : 1ll*maxleft[i]*p;
ll rightval = (r<0) ? 1ll*minright[i]*r : 1ll*maxright[i]*r;
ans=max(ans,leftval+rightval+1ll*q*a[i]);
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
Tutorial is loading...
Solution
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define sd(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define slld(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define ss(x) scanf("%s",x)
#define ll long long
#define mod 1000000007
#define bitcount __builtin_popcountll
#define pb push_back
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mp make_pair
#define pi pair<int,int>
int dp[100005][3][12],x,k,m;
int a[3][12],b[3][12];
vector <int> q[100005];
void dfs(int cur,int par)
{
int i,j=0,l,r,temp;
for(i=0;i<q[cur].size();i++)
{
if(q[cur][i]==par)
continue;
j=1;
dfs(q[cur][i],cur);
}
if(!j)
{
dp[cur][0][0]=k-1;
dp[cur][1][1]=1;
dp[cur][2][0]=m-k;
return;
}
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<=x;j++)
{
a[i][j]=0;
b[i][j]=0;
}
}
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
a[i][0]=1;
for(i=0;i<q[cur].size();i++)
{
if(q[cur][i]==par)
continue;
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
for(l=0;l<=x;l++)
{
for(r=0;r<=x;r++)
{
if(l+r>x)
continue;
if(j==0)
{
temp=dp[q[cur][i]][0][r]+dp[q[cur][i]][1][r];
if(temp>=mod)
temp-=mod;
temp+=dp[q[cur][i]][2][r];
if(temp>=mod)
temp-=mod;
b[j][l+r]+=(1ll*a[j][l]*temp)%mod;
if(b[j][l+r]>=mod)
b[j][l+r]-=mod;
}
else if(j==1)
{
b[j][l+r]+=(1ll*a[j][l]*(dp[q[cur][i]][0][r]))%mod;
if(b[j][l+r]>=mod)
b[j][l+r]-=mod;
}
else
{
temp=dp[q[cur][i]][0][r]+dp[q[cur][i]][2][r];
if(temp>=mod)
temp-=mod;
b[j][l+r]+=(1ll*a[j][l]*temp)%mod;
if(b[j][l+r]>=mod)
b[j][l+r]-=mod;
}
}
}
}
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
for(l=0;l<=x;l++)
{
a[j][l]=b[j][l];
b[j][l]=0;
}
}
}
for(l=0;l<=x;l++)
{
dp[cur][0][l]=(1ll*a[0][l]*(k-1))%mod;
if(l>=1)
dp[cur][1][l]=a[1][l-1];
dp[cur][2][l]=(1ll*a[2][l]*(m-k))%mod;
}
}
int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
//freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
int n,i,j,ans;
sd(n);
sd(m);
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
sd(j);
sd(k);
q[j].pb(k);
q[k].pb(j);
}
sd(k);
sd(x);
dfs(1,0);
ans=0;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<=x;j++)
{
//printf("%d %d %d\n",i,j,dp[1][i][j]);
ans+=dp[1][i][j];
if(ans>=mod)
ans-=mod;
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}
Tutorial is loading...
Solution
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define sd(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define slld(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define ss(x) scanf("%s",x)
#define mod 1000000007
#define bitcount __builtin_popcountll
#define ll long long
#define pb push_back
#define pi pair<int,int>
#define pii pair<pi,int>
#define mp make_pair
vector<int>v[100005],v2[100005];
int inherit[100005],comp[100005],parent[100005][25],height[100005];
int parr[100005];
int findpar(int node)
{
return parr[node]==node ? node : parr[node]=findpar(parr[node]);
}
void dfs(int node, int par, int inh, int com)
{
parent[node][0]=par;
inherit[node]=inh;
comp[node]=com;
height[node]=height[par]+1;
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++)
{
parent[node][i]=parent[parent[node][i-1]][i-1];
}
for(int i=0;i<v[node].size();i++)
{
if(v[node][i]==par)
continue;
if(v2[node][i]==0)
dfs(v[node][i],node,inh+1,com);
else
dfs(v[node][i],node,inh,com+1);
}
}
int findlca(int u, int v)
{
if(height[u]>height[v])
swap(u,v);
for(int i=20;i>=0;i--)
{
if(height[parent[v][i]]>=height[u])
{
v=parent[v][i];
}
}
if(u!=v)
{
for(int i=20;i>=0;i--)
{
if(parent[u][i]!=parent[v][i])
{
u=parent[u][i];
v=parent[v][i];
}
}
u=parent[u][0];
v=parent[v][0];
}
return u;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,k;
int n,q;
sd(n);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
parr[i]=i;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
sd(j);
sd(k);
if(j==-1 && k==-1)
continue;
v[i].pb(j);
v[j].pb(i);
v2[i].pb(k);
v2[j].pb(k);
int x=findpar(i);
int y=findpar(j);
if(x!=y)
parr[x]=y;
}
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(parent[i][0]==0)
{
dfs(i,i,0,0);
}
}
sd(q);
while(q--)
{
sd(i);
sd(j);
sd(k);
int x=findpar(j);
int y=findpar(k);
if(x!=y)
{
printf("NO\n");
continue;
}
x=findlca(j,k);
if(i==1)
{
if(x!=j || comp[k]-comp[x]!=0 || j==k)
{
printf("NO\n");
}
else
printf("YES\n");
}
else
{
if(inherit[k]-inherit[x]!=0 || comp[j]-comp[x]!=0 || x==k)
printf("NO\n");
else
printf("YES\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
Tutorial is loading...
Solution
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define sd(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define slld(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define ss(x) scanf("%s",x)
#define ll long long
#define mod 1000000007
#define bitcount __builtin_popcountll
#define pb push_back
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mp make_pair
#define pi pair<int,int>
ll dp[11][2][1030][70];
ll len[12],a[100];
ll f(ll b,ll in,ll m,ll pos)
{
if(dp[b][in][m][pos]!=-1)
return dp[b][in][m][pos];
if(pos==0)
{
if(in!=0&&m==0)
return dp[b][in][m][pos]=1;
else
return dp[b][in][m][pos]=0;
return dp[b][in][m][pos];
}
ll j=0;
if(in==0)
j+=f(b,0,m,pos-1);
else
j+=f(b,1,(m^1),pos-1);
for(ll i=1;i<b;i++)
j+=f(b,1,(m^(1<<i)),pos-1);
dp[b][in][m][pos]=j;
return j;
}
int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
//freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
ll n,i,j,k,in;
ll ans,l,r,m,q,b;
k=1e18;
memset(dp,-1,sizeof dp);
for(i=2;i<=10;i++)
{
len[i]=1;
j=i;
while(j<k)
{
len[i]++;
j*=i;
}
f(i,0,0,len[i]+1);
}
sd(q);
while(q--)
{
sd(b);
sd(l);
sd(r);
ans=0;
l--;
if(l)
{
j=l;
i=0;
while(j)
{
a[i]=j%b;
j/=b;
i++;
}
m=0;
in=0;
for(j=i-1;j>=0;j--)
{
for(k=0;k<a[j];k++)
{
if(k!=0)
in=1;
if(in==0)
ans-=dp[b][0][m][j];
else
ans-=dp[b][1][(m^(1<<k))][j];
}
if(in|a[j])
{
in=1;
m=(m^(1<<a[j]));
}
}
ans-=dp[b][in][m][0];
}
j=r;
i=0;
while(j)
{
a[i]=j%b;
j/=b;
i++;
}
in=0;
m=0;
for(j=i-1;j>=0;j--)
{
for(k=0;k<a[j];k++)
{
if(k!=0)
in=1;
if(in==0)
ans+=dp[b][0][m][j];
else
ans+=dp[b][1][(m^(1<<k))][j];
}
if(in|a[j])
{
in=1;
m=(m^(1<<a[j]));
}
}
ans+=dp[b][in][m][0];
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
Tutorial is loading...
Solution
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define sd(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define slld(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define ss(x) scanf("%s",x)
#define mod 1000000007
#define bitcount __builtin_popcountll
#define ll long long
#define pb push_back
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pi pair<int,int>
#define pii pair<pi,int>
#define mp make_pair
ll ans[1000];
int upper[1000],lower[1000];
int block;
map <int,int> low[1000],up[1000];
map <int,int> vnotup[1000],vnotdown[1000];
int notboth[1000];
int minup[100005],mindown[100005];
void updateup(int i,int l,int r,int val)
{
if(upper[i]<=val)
return;
//map<int,int> m;
map<int,int> :: iterator it;
//m.clear();
for(int j=l;j<=r;j++)
{
if(minup[j]>val)
{
if(minup[j]==mod&&mindown[j]==mod&&upper[i]==mod&&lower[i]==mod)
{
notboth[i]--;
//notdown[i]++;
vnotdown[i][val]++;
//notdownsum[i]+=val;
}
else if(minup[j]==mod&&upper[i]==mod)
{
//notup[i]--;
int temp=min(lower[i],mindown[j]);
vnotup[i][temp]--;
if(vnotup[i][temp]==0)
vnotup[i].erase(temp);
//notupsum[i]-=min(lower[i],mindown[j]);
up[i][val]++;
low[i][temp]++;
ans[i]+=val;
ans[i]+=min(lower[i],mindown[j]);
}
else if(mindown[j]==mod&&lower[i]==mod)
{
int temp=min(upper[i],minup[j]);
vnotdown[i][temp]--;
if(vnotdown[i][temp]==0)
vnotdown[i].erase(temp);
vnotdown[i][val]++;
}
else
{
ans[i]+=val-min(upper[i],minup[j]);
up[i][min(minup[j],upper[i])]--;
up[i][val]++;
}
minup[j]=val;
}
}
}
void updatefullup(int i,int val)
{
if(val>=upper[i])
return;
map <int,int> :: iterator it;
int n=up[i].size();
n--;
ll sum=0;
int len2=0;
for(it=vnotup[i].begin();it!=vnotup[i].end();it++)
{
ans[i]+=1ll*(it->fi)*(it->se)+1ll*(it->se)*val;
len2+=it->se;
low[i][it->fi]+=it->se;
}
vnotup[i].clear();
it=vnotdown[i].upper_bound(val);
int temp=0;
for(it;it!=vnotdown[i].end();it++)
{
temp+=it->se;
}
it=vnotdown[i].upper_bound(val);
vnotdown[i].erase(it,vnotdown[i].end());
vnotdown[i][val]+=temp+notboth[i];
notboth[i]=0;
int len=0;
it=up[i].upper_bound(val);
for(it;it!=up[i].end();it++)
{
sum+=1ll*(it->fi)*(it->se);
len+=it->se;
}
it=up[i].upper_bound(val);
up[i].erase(it,up[i].end());
ans[i]+=1ll*len*val-sum;
up[i][val]+=len+len2;
upper[i]=val;
}
void updatedown(int i,int l,int r,int val)
{
if(lower[i]<=val)
return;
//map<int,int> m;
map<int,int> :: iterator it;
//m.clear();
for(int j=l;j<=r;j++)
{
if(mindown[j]>val)
{
if(mindown[j]==mod&&minup[j]==mod&&upper[i]==mod&&lower[i]==mod)
{
notboth[i]--;
//notup[i]++;
//notupsum[i]+=val;
vnotup[i][val]++;
}
else if(mindown[j]==mod&&lower[i]==mod)
{
//notdown[i]--;
int temp=min(upper[i],minup[j]);
vnotdown[i][temp]--;
if(vnotdown[i][temp]==0)
vnotdown[i].erase(temp);
low[i][val]++;
up[i][temp]++;
//notdownsum[i]-=min(upper[i],minup[j]);
ans[i]+=val;
ans[i]+=min(upper[i],minup[j]);
}
else if(minup[j]==mod&&upper[i]==mod)
{
int temp=min(lower[i],mindown[j]);
vnotup[i][temp]--;
if(vnotup[i][temp]==0)
vnotup[i].erase(temp);
vnotup[i][val]++;
}
else
{
ans[i]+=val-min(lower[i],mindown[j]);
low[i][min(mindown[j],lower[i])]--;
low[i][val]++;
}
mindown[j]=val;
}
}
}
void updatefulldown(int i,int val)
{
if(val>=lower[i])
return;
map <int,int> :: iterator it;
int n=low[i].size();
n--;
ll sum=0;
int len2=0;
for(it=vnotdown[i].begin();it!=vnotdown[i].end();it++)
{
ans[i]+=1ll*(it->fi)*(it->se)+1ll*(it->se)*val;
len2+=it->se;
up[i][it->fi]+=it->se;
}
vnotdown[i].clear();
it=vnotup[i].upper_bound(val);
int temp=0;
for(it;it!=vnotup[i].end();it++)
{
temp+=it->se;
}
it=vnotup[i].upper_bound(val);
vnotup[i].erase(it,vnotup[i].end());
vnotup[i][val]+=temp+notboth[i];
notboth[i]=0;
int len=0;
it=low[i].upper_bound(val);
for(it;it!=low[i].end();it++)
{
sum+=1ll*(it->fi)*(it->se);
len+=it->se;
}
it=low[i].upper_bound(val);
low[i].erase(it,low[i].end());
ans[i]+=1ll*len*val-sum;
low[i][val]+=len+len2;
lower[i]=val;
}
ll query(int i,int l,int r)
{
ll sum=0;
for(int j=l;j<=r;j++)
{
if(min(upper[i],minup[j])<mod&&min(lower[i],mindown[j])<mod)
sum+=min(upper[i],minup[j])+min(lower[i],mindown[j]);
}
return sum;
}
ll queryfull(int i)
{
return ans[i];
}
int main()
{
int i,j,k,q,n,t,l,r,val,block;
ll s;
n=100000;
for(i=0;i<1000;i++)
lower[i]=upper[i]=mod;
for(i=0;i<=100000;i++)
minup[i]=mindown[i]=mod;
block=300;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
j=i/block;
notboth[j]++;
}
sd(q);
while(q--)
{
sd(t);
sd(l);
sd(r);
r--;
if(t==1)
{
sd(val);
i=l/block;
j=r/block;
if(val>0)
{
if(i==j)
updateup(j,l,r,val);
else
{
updateup(i,l,(i+1)*block-1,val);
i++;
while(i<j)
{
// updateup(i,i*block,(i+1)*block-1,val);
updatefullup(i,val);
i++;
}
updateup(j,j*block,r,val);
}
}
else
{
if(i==j)
updatedown(j,l,r,-val);
else
{
updatedown(i,l,(i+1)*block-1,-val);
i++;
while(i<j)
{
// updatedown(i,i*block,(i+1)*block-1,-val);
updatefulldown(i,-val);
i++;
}
updatedown(j,j*block,r,-val);
}
}
}
else
{
s=0;
i=l/block;
j=r/block;
if(i==j)
s=query(j,l,r);
else
{
s=query(i,l,(i+1)*block-1);
i++;
while(i<j)
{
//s+=query(i,i*block,(i+1)*block-1);
s+=queryfull(i);
i++;
}
s+=query(j,j*block,r);
}
printf("%lld\n",s);
}
}
return 0;
}
Tutorial is loading...
Solution
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
using ld = long double;
using D = double;
using uint = unsigned int;
template<typename T>
using pair2 = pair<T, T>;
#ifdef WIN32
#define LLD "%I64d"
#else
#define LLD "%lld"
#endif
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define fi first
#define se second
const int maxn = 200005;
struct tpath
{
int rep, sz;
ll ansmiddle;
int edgeleft, edgeright;
};
int p[maxn], s[maxn];
int sz[maxn], down[maxn], up[maxn], top[maxn];
vector<tpath> path, path2;
vector<int> gr[maxn];
ll dp1[maxn], dp2[maxn], ansmiddle[maxn];
int n, m;
ll answer;
int tin[maxn], tout[maxn];
int timer;
inline int find(int a)
{
return (a == p[a] ? a : p[a] = find(p[a]));
}
inline bool isparent(int a, int b)
{
return tin[a] <= tin[b] && tout[a] >= tin[b];
}
void unite(int a, int b)
{
a = find(a);
b = find(b);
if (a == b) return;
if (s[a] > s[b]) swap(a, b);
p[a] = b;
if (s[a] == s[b]) s[b]++;
if (tin[top[a]] < tin[top[b]])
{
sz[top[a]] += sz[top[b]];
top[b] = top[a];
} else
{
sz[top[b]] += sz[top[a]];
}
}
void findpath(int a, int b)
{
a = top[find(a)];
b = top[find(b)];
// cout << "findpath " << a << ' ' << b << endl;
int lastdowna = 0;
while (!isparent(a, b))
{
path.pb({a, sz[a], ansmiddle[a], lastdowna, n - down[a]});
lastdowna = down[a];
a = top[find(up[a])];
}
path2.clear();
int lastdownb = 0;
while (a != b)
{
path2.pb({b, sz[b], ansmiddle[b], n - down[b], lastdownb});
lastdownb = down[b];
b = top[find(up[b])];
}
path.pb({a, sz[a], ansmiddle[a], lastdowna, lastdownb});
reverse(all(path2));
for (auto t : path2) path.pb(t);
}
void addedge(int a, int b)
{
if (find(a) == find(b)) return;
path.clear();
findpath(a, b);
// cout << "addedge " << a << ' ' << b << endl;
// for (auto t : path) cout << "(" << t.rep << ' ' << t.sz << ' ' << t.ansmiddle << ' ' << t.edgeleft << ' ' << t.edgeright << ")" << endl;
// 3
ll cnt0 = 1;
ll cnt1 = 0;
ll cnt2 = 0;
for (auto t : path)
{
answer -= t.sz * cnt2 * 2 + (ll)t.sz * (t.sz - 1) * cnt1 * 2 + (ll)t.sz * (t.sz - 1) * (t.sz - 2);
cnt2 += t.sz * cnt1 + (ll)t.sz * (t.sz - 1) * cnt0;
cnt1 += t.sz * cnt0;
}
ll sum = cnt1;
answer += ((ll)sum * (sum - 1) * (sum - 2));
// cout << "after 3: " << answer << endl;
// 2
cnt1 = 0;
for (auto t : path)
{
answer += cnt1 * (t.edgeleft - cnt1) * t.sz * 2;
cnt1 += t.sz;
}
cnt1 = 0;
for (int i = (int)path.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
auto &t = path[i];
answer += cnt1 * (t.edgeright - cnt1) * t.sz * 2;
cnt1 += t.sz;
}
// cout << "after 2: " << answer << endl;
// 1
cnt1 = 0;
cnt2 = 0;
for (auto t : path)
{
answer += cnt2 * t.sz * 2;
cnt2 += (n - t.edgeright - t.edgeleft - t.sz) * cnt1;
cnt1 += n - t.edgeright - t.edgeleft - t.sz;
}
cnt1 = 0;
cnt2 = 0;
for (int i = (int)path.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
auto &t = path[i];
answer += cnt2 * t.sz * 2;
cnt2 += (n - t.edgeleft - t.edgeright - t.sz) * cnt1;
cnt1 += n - t.edgeleft - t.edgeright - t.sz;
}
// cout << "after 1 old: " << answer << endl;
ll ttldown1 = 0;
ll ttldown2 = 0;
for (auto t : path)
{
ll curdown = n - t.edgeleft - t.edgeright - t.sz;
ll curdown2 = t.ansmiddle - curdown * (t.edgeleft + t.edgeright) * 2 - (ll)t.edgeleft * t.edgeright * 2;
answer += curdown2 * (sum - t.sz);
ttldown2 = ttldown2 + curdown2 + ttldown1 * curdown * 2;
ttldown1 += curdown;
}
// cout << "after 1: " << answer << endl;
for (int i = 1; i < (int)path.size(); i++) unite(path[i - 1].rep, path[i].rep);
ansmiddle[top[find(path[0].rep)]] = ttldown2;
}
int go(int cur, int pr)
{
down[cur] = 1;
up[cur] = pr;
dp1[cur] = 0;
ansmiddle[cur] = 0;
tin[cur] = timer++;
for (auto t : gr[cur]) if (t != pr)
{
down[cur] += go(t, cur);
answer += (ll)dp1[t] * dp1[cur] * 2;
answer += (ll)dp1[t] * dp2[cur] * 2 + dp2[t] * dp1[cur] * 2;
ansmiddle[cur] += (ll)dp1[t] * dp1[cur] * 2;
answer += dp2[t] * 2;
dp2[cur] += dp2[t];
dp1[cur] += dp1[t];
}
ansmiddle[cur] += (ll)(n - down[cur]) * dp1[cur] * 2;
dp2[cur] += dp1[cur];
dp1[cur] += 1;
tout[cur] = timer - 1;
// cout << "exit " << cur << ' ' << answer << ' ' << dp1[cur] << ' ' << dp2[cur] << endl;
return down[cur];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
a--, b--;
gr[a].pb(b);
gr[b].pb(a);
}
go(0, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
p[i] = i;
s[i] = 0;
top[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
printf("%lld\n", answer);
scanf("%d", &m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
a--, b--;
addedge(a, b);
printf("%lld\n", answer);
}
return 0;
}











Solutions (Code links) are not visible.
Updated!
In problem C, if we have node U and it has y children, we need to check every representation of x by y numbers, right? for example, in first childrens subtree we may put 0,1,2,..,x k-labeled nodes, second children can also have 1,2,..., x — a, where a is amount that we used for 1st children and so on. Is this right?
Not Necessary. I went into the same dead end during competition lol. From the tutorial, I just figured out we don't need to iterate through all the combinations but instead: Everytime combine the result of two children at a time. All the combinations of these two children are contained in the combined result (from 0 to x). Continue this process till all the children nodes are combined. By this way, it only takes x * x * (number of children) to have the result of all the combinations.
But if we visit all pairs of children isnt it num of children squared
see http://codeforces.net/blog/entry/54750?#comment-387718
Thank you so much! Only solution I could understood!
With problem D. Why does this hold? ~~~~~ For query 1 u v, answer will be "YES" iff u ≠ v (as u is not special case of itself) and lca(u, v) = u. ~~~~~ Should a special case of a part be a special case? Formally, b is a part of a, c is a special case of b, why do we need c to be a special case of a?
Sorry! There was a mistake in the editorial. All edges in the path from u to v should also be of type "is a special case of"
Third solution for problem B : Using segment tree
Make three arrays namely b, c, d.
b will store p * a[i] , c will store for q and d will store for r.
Make two segment trees (max query) for b and c namely tree1 for b and tree2 for c.
Start iterating array d.
For every di , find max in tree2 first from 0 to i range. Store it as a pair. This pair will store the max value of array c from range 0 to i and the position of that element (pos) in array c. After that, find max value of array b from 0 to pos.
For same di, find max now in tree1 first from 0 to i range. Store it as a pair (say R) again. This pair will store the same as above but now for array b first. Now, find the max value of element in array c from R.second to i.
Since now we are having two values for each di , keep taking max out of it from i = 0 to n.
The final result will be the answer.
For more details, here is my solution — http://codeforces.net/contest/855/submission/30682061
Fun linear solution for D: 30688152
Can you explain it in detail?
If you consider separate forests for type-1 and type-2 edges, you don't need LCA queries; only "is u ancestor of v" and "what is the root of v's tree". Those can easily be answered after some simple DFS precomputation.
For type-2 queries, it's enough to check whether u is an ancestor of v in the type-2 forest.
For type-1 queries, we need to check whether there is a vertex w, which is an ancestor of v in the type-1 forest, and an ancestor of u in the type-2 forest.
But w can have at most one parent, so it would have to be a root in either type-1 forest or type-2 forest. So, we can check whether type-1 root of v is an ancestor of u in the type-2 forest or the other way around.
you may have interchanged type 1 & 2.
In Problem C, can anyone provide me an explanation on this part?
Then, we can combine them two nodes at a time to form the dp array for the node curr.
let's say we want to calculate dp[v][j][x] (means the number of ways of getting
xnumber ofktype nodes in the subtree rooted at v, where type(v)=j) how to calculate this — let's assume f(v, j, x) has the same definition as dp[v][j][x].say we have
nchildren of node v. so essentially what we need to find is the number of ways to distributexamong these n children.here we can use a dp. (for convenience I'll call nodes of type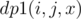 as the number of ways to choose a total of x special nodes from subtrees defined by v1, v2, ..., vi i.e. from first
as the number of ways to choose a total of x special nodes from subtrees defined by v1, v2, ..., vi i.e. from first 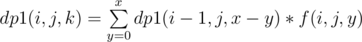 , i.e. we are iterating over y assuming that subtree of vi contributes y special nodes and rest x-y special nodes have been contributed by previous i-1 nodes. So, finally dp[v][j][x] = dp1(n, j, x)
, i.e. we are iterating over y assuming that subtree of vi contributes y special nodes and rest x-y special nodes have been contributed by previous i-1 nodes. So, finally dp[v][j][x] = dp1(n, j, x)
kas special node) Now, to do this computation at node v, we will form another DP dp1. We sayinodes. The recurrence can be defined asIn the editorial solution this dp1 is denoted by a and b array. you wont find i in the editorial's dp1 state, i can be avoided by using two arrays a and b. we store dp1(i, , ) in b array, and after its calculation it is added to a array, so this will become dp1(i - 1, , ) for the next iteration.
But in dp1 you dont memorise which node you are currently at, so values will always mix? I mean, first i childs of node u may mix with first i childs of some other node.
The graph is a tree. The graph has n-1 edges and is connected ,so every node can have at most 1 parent.
For every non leaf node v in the tree, we are doing this dp1() calculation locally for that node independent from others. see this part in the editorial's code -
see at the end we assign the a values to dp state of that node, for next node again a and b arrays will be assigned 0 values at the start in the dfs().
So doesn't this solution makes the complexity O(n*x) rather than O(x*x)? Because for each child node, we iterate through the number of special nodes from 0 to x.
while calculating dp1(i, 0, k) why don't we are considering the values at type 1 and type 2?
i have used similar approach but failed : http://codeforces.net/contest/855/submission/30802240
i know i am missing something please help me !
here dp1(i, 0, k) states node v is of 0 type. Doesn't make sense. Please read the comment carefully. or maybe I didn't get you?
" While assigning the value to dp[curr][1][cnt], we take into account only the values of dp[childofcurr][0][cnt - z]. Similarly for dp[curr][2][cnt], we take into account only dp[child of curr][0][cnt - z] and dp[child of curr][2][cnt - z]. "
I understand this as while calculating the value of type(0) we have to take the values of type(1) , type(0) and type(2) and for type(1) we take only of type(0) below it.
so, in your comment in the last part it is written that dp(i, j, k) = dp1(n, j, k) doesn't it include the value of type(1) ot type(2) if j = 0!
Can someone please explain C with more detail ?
I don't get how adding all the dp values of each pair would be the same as taking all combinations among children
In problem B , Why the below approach doesn't work? find min , max in array. ans = 0; If(p<0) ans += p * min else ans += p * max Repeat for q and r print ans.
I got this i<=j , j<=k
Why is the contest getting so much hate?
Because problem statements were garbage and problems are not interesting.
When the editorial of problem E and F will be updated? I am wating for those since yesterday. :(
Hello,
Can somebody explain for problem F (NAGINI) why my solution here receives a TLE for test case 30.
I have tried everything i could to optimise the code.
Thank You.
F can be solved by special segment tree, which is called Ji driver segment tree in China. You can see this code: http://codeforces.net/contest/855/submission/30680703
Where can I learn about it? Google search doesn't yield any similar result.
Sorry, I only have Chinese learning materials. Try to understand it by reading the code...My English is very poor, so I can't explain it in English.
Any online material? Then maybe google translate could help!!
Sorry, this code is not Ji driver segment tree, but you can learn it from: http://www.shuizilong.com/house/archives/hdu-5306-gorgeous-sequence/
And you can learn Ji driver segment tree from: http://www.doc88.com/p-6744902151779.html
Thanks. :)
Isn't this simply the trick to store in each node of the segment tree a flag if all elements/positions have the same value and then in the query and update we update only if the values of the whole segment are equal (else we just continue down)?
PS: example problem done with the same trick.
Looks like yes, in the tutorial in chinese they link this problem http://codeforces.net/contest/444/problem/C also, that can be solved with this trick
I haven't looked to provided links, but I can already say what you're saying is not true.
Consider following scenario: Firstly you set value of n on interval [1, n], then you use n/2 queries to set values of 0 in intervals [i, i] for odd i and then you make n queries with value of n-1, n-2, ... on interval [1, n]. All queries from last phase will update values in all even points, so if we use "typical lazy propagation" which you described we will end up having complexity O(n) per query.
Well, I didn't understand your case, so I will explain the main idea in this problem, first we reduce the problem to:
We have a array A of size N initially every element is equal to infinity and we can do:
Update in position: pos k, make A[pos] = k
Update in range: l r k, for every element i in the interval [l, r] make A[i] = min(A[i], k)
Query: l r, ask for the sum of every element different of infinity on the interval [l, r]
So, to solve this with the idea of the segment tree, we gonna keep for every segment what is the biggest element in that segment, how much times the biggest element appears on the segment , the second biggest segment on segment, the sum of the segment and a variable to indicate the lazy propagation
If we gonna do soma update in pos we just change the value of the biggest element, how many times appear and sum of the node in segment tree that represent this element.
When we gonna process some update we gonna do the recursive procedure of the segment tree:
if the current node is out of the interval of update, there is nothing to process in this node
if the max element in the range of current node is smaller than k, there is nothing to process in this node
if the range of current node is completely inside of the range of update and the second biggest element is smaller than k, we gonna process this node, the only thing that will change will be the sum of the interval and the biggest element element also we gonna sinalize the lazy propagation
Else we gonna recurse to the left son and right son, after this we gonna recalculate the value of the nodes where the recursion passed.
If we gonna query, we just do the normal of the segment tree, taking the sum value of each node
If I would say the complexity it would be in O(QN) in a trivial analise, but my intuition say that it's faster. My code is 30763830 . Can you say what is the complexity ?
What is this solution's complexity? It was kinda a big fuss in Polish community when Marcin_smu solved it faster than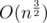 , namely in
, namely in 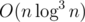 using some mergeable leftist tree.
using some mergeable leftist tree.
EDIT: Ok, Google translate told me that it is written that it is n log n. If that's true then it is very impressive
Well, I'll write a blog about this trick of segment tree later.
It can change the operation "range max/min" into the trivial operation "range add/minus" in extra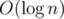 time complexity (may be O(1) but I can't prove it yet, I'm still working on it).
time complexity (may be O(1) but I can't prove it yet, I'm still working on it).
This problem is just a simplest application and segment tree can solve it in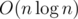 .
.
BTW, I prefer to call this trick "Segment Tree Beats". I like this name very much :)
Any news about the blog post? Thanks in advance :)
Any news about the blog post? Thanks in advance :)
My final exam is finally finished. I'm going to start to work now :)
Sorry for the long delay.
Yeah, great... And then we are wondering how people managed to squeeze naive bruteforces
Any special reason to subtract mod instead of just taking the modulus ?, does not seem to save any complexity of computation or coding.
(IN PROBLEM C)
Can someone give me a readable code for problem D, I find it hard to understand author's code.
When will you provide the editorial for the last problem? It's been two weeks.
Added now.
Thanks a lot.
Can Anyone please elaborate more on 855G solution , especially proof of 2nd statement and bit more explanation of 4th statement