895A - Pizza Separation
Заметим, что если один из секторов непрерывен, то все оставшиеся куски также образуют непрерывный сектор. Для каждого непрерывного сектора найдем его угол, то есть сумму углов кусков входящих в него. Если угол одного сектора равен x, то разница углов секторов равна |x - (360 - x)| = |2 * x - 360| = 2 * |x - 180|. Переберем сектор, зная его угол x обновим ответ.
Асимптотика O(n2) или O(n).
895B - XK Segments
Для начала узнаем, как посчитать количество чисел на отрезке делящихся на x. Пусть левая граница отрезка это l, а правая r. Тогда количество чисел делящихся нацело на x и принадлежащих [l, r] равно r/x – (l-1)/x. Отсортируем массив a по возрастанию. Переберем левую границу отрезка, пусть это a[i]. Тогда на роль правой границы подходят все числа a[j] такие, что a[j] / x–(a[i] - 1) / x = k. Значение (a[i] - 1) / x мы знаем, а a[j] / x монотонно возрастает при возрастающем a[j]. То есть можно сделать бинарный поиск по отсортированному массиву, который найдет индексы минимального и максимального подходящего a[j], а значит и их количество.
Асимптотика O(n * log(n)).
895C - Square Subsets
Заметим, что число x является квадратом некоторого натурального числа <=> в разложение x на простые множители каждое простое число входит четное количество раз. Простых чисел меньших 70 всего 19. Посчитаем битмаску для каждого из чисел от 1 до 70 по следующему принципу: В битовом представлении маски в разряде k стоит 1, если k-ое простое число входит в разложение этого числа нечетное количество раз. Иначе 0. Для каждого различного значения a[i] нас на самом деле интересует только войдет оно четное количество раз в произведение или нечетное. Пусть f1[i], f0[i] это количество способов взять из a нечетное и четное количество чисел i соответственно. Будем считать динамику по битмаскам. Обозначим за dp[i][j] количество способов выбрать некоторые элементы массива <= i таким образом, чтобы в их произведении в нечетных степенях содержались только те простые числа, на месте порядкового номера которых в битовом представлении j стоит 1. Изначально dp[0][0] = 1. Переходы следующие:
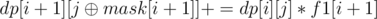
dp[i + 1][j] + = dp[i][j] * f0[i + 1]
Тогда ответ это dp[70][0].
Асимптотика O(max*2^cnt(max)), где max максимальное значение a[i], а cnt(max) количество простых чисел не больших max.
895D - String Mark
Пусть мы умеем вычислять функцию f(s) равную количеству перестановок строки a строго меньших s. Тогда ответ равен f(b) - f(a)–1. Теперь надо научиться находить значение f(s). Посчитаем количество вхождений каждой буквы в строку a – cnt[26]. Будем перебирать позицию первого различного символа в перестановке a и строке s и обновлять количество оставшихся символов cnt[26]. Для каждой такой позиции переберем символ в перестановке a который будет стоять на этой позиции. Он должен быть меньше символа на этой позиции в строке s. Для каждой такой ситуации надо вычислить и прибавить к ответу количество различных перестановок которые можно получить используя не задействованные на данный момент символы. Их количество хранится в cnt[26]. В простейшем виде это решение работает за O(n * k2), где k размер алфавита. Такое решение не проходит тесты, но его можно оптимизировать до O(n * k), что уже проходит по времени.
Асимптотика O(n * k), где k размер алфавита.
895E - Eyes Closed
Будем поддерживать для каждой позиции математическое ожидание значения на ней. Изначально для позиции i оно равно a[i]. Пусть надо обработать запрос первого типа. Каждое число из отрезка [l1, r1] останется на своем месте с вероятностью (r1–l1) / (r1–l1 + 1). Вероятность того, что оно будет заменено числом из [l2, r2] равна 1 / (r1 - l1 + 1). Математическое ожидание числа, на которое оно будет заменено есть среднее арифметическое математических ожидании чисел в [l2, r2], обозначим его за x. Тогда чтобы обновить матожидание числа из [l1, r1] надо умножить его на (r1–l1) / (r1–l1 + 1) и прибавить x / (r1–l1 + 1). То есть запрос первого типа сводится к запросу домножить все числа на отрезке и прибавить к ним число. Чтобы обработать второй запрос надо находить сумму чисел на отрезке. Все эти запросы можно обрабатывать деревом отрезков.
Асимптотика O(n + q * log(n)).










Nice :) It was good problems!
Что значит "Пусть f1[i], f0[i] это количество способов взять из a нечетное и четное количество чисел i соответственно"?
Hi! As a tester, I enjoyed solving the problems. Thanks to NBAH for problems.
Problem E was nice segment tree with advanced lazy propagation problem, the special lazy propagation in this problem was instructive.
Problem D was mixing of the known dp-on-digits idea and some combinatorics, it was a bit hard for this position.
Problem C could be solved by a straight-forward meet-in-the-middle solution that is really hard for this position. Also, it could be solved with dp-on-masks. I think that this idea is a bit hard for div.2 C problem, too.
To summarize, although the round was a bit hard, because of problems C and D, anyway, the problems were nice.
I don't think D was that hard for Div2 D. Neither the idea or the implementation of the procedure described in the editorial isn't very difficult, you don't have to do DP on digits. The required combinatorics knowledge wasn't unreasonable, too. D was arguably easier than C, I think.
Can you explain the meet in the middle soluton?
Show each number as a 19-digit mask. There is at most 44 different masks (you can test). Divide this masks into two groups. For each group find all of the different masks they can make by xor of some subset. The answer can be calculated easily using meet in the middle.
Could someone please explain in problem C what exactly
dp[i][j]is? I understood thatiis the upper limit of the number but what exactly isj? Also, ifiis the upper limit then shouldn't thedparray bell dp[71][1<<20], so why does the author's solution set it asll dp[2][1 << 20];. Please explain. Thanks.If you understand the definition of
dp[71][1<<20], then you're on the right track! For this case,dp[i][j]is only dependent ondp[i-1][j]— previous step, therefore, we don't need to store all steps untili-1(exclusively).Oh! Silly me. Thanks. :)
Would anyone mind explaining the solution to Problem C in more detail? I understand the bitmask, but I don't understand the definitions for f1[i], f0[i] and the dp[i][j] it uses.
Lol f1[i] is the number of ways to choose an odd number of numbers out of a set of a[i] numbers, and f0[i] is the number of ways to choose an even number of numbers out of a set of a[i] numbers.
It ends up being:
f1[i] = 0 if a[i] = 0 and f1[i] = 2a[i] - 1 otherwise.
f0[i] = 1 if a[i] = 0 and f0[i] = 2a[i] - 1 otherwise.
Basically know that for k ≥ 1, the number of ways to choose an odd number of elements out of a set of k elements is equal to the number of ways to choose an even number of elements out of a set of k elements, and they are both equal 2k - 1. Here is a proof.
OK, but what does this have to do with the rest of the problem? Why is this being computed in the first place?
Because the mask j becomes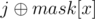 if you take an odd number of x but stays as j if you take an even number of x.
if you take an odd number of x but stays as j if you take an even number of x.
What do you mean by odd number of x ?
vb7401, did you get it? Because, I didn't.
Its like basic knapsack, if you include x or don't. If you include x, the mask becomes j ^ mask[x] whereas if you don't include x, the mask remains j only. The point is if you include x , you can include odd number of times x , the mask will still remain j ^ mask[x] ( xor properties) and if you take even number of times of x , the mask will still be j.
Here's another explanation.
Suppose you multiply,
2^3. 3^1. 5^2, with 2^5. 3^2. 5 ^3,
What do you get ?
2^8. 3^3. 5^5
The first number's mask = 110 Second number's mask = 101
Now, their product = 011
(it is like adding the bits, with no carry — this is another definition of the XOR operation).
So, if
f(i, mask) is the number of ways to use the first i numbers and get a product such that we get a prime with an odd power if the corresponding bit is set in mask, then.
f(i + 1, mask) = f(i, XOR(mask, MASK(i + 1)) )*f1(i + 1) + f(i, mask)*f0(i + 1)
This is because if we choose (i + 1) an even number of times, it doesn't affect the mask. But, if we choose it an odd number of times, we must perform bitwise addition of the mask and the MASK of (i + 1).
I tried to solve this problem inspired by these comments. I used top-down DP and my solution works for the first 12 test cases but fails with test case 13 and I don't get why. My code is very short. I would really appreciate if somebody could help me understand what I'm doing wrong :S. Here is the code: https://codeforces.net/contest/895/submission/45750333
a[i] in your explanation is not the same array that was given in the problem right? The way I understand it is that it is a new array that counts number of occurrences of a given number i, which can be in the range of [1,70] which in the problem was referred to as ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 70)
Yeah you are right, what a[i] means in my comment above is the number of times i appears in the input.
Although the answer is same, I reached at it in a different way.
If there was a lower constraint on n, what would have been the solution?
Note that, it does not matter in which order we process a[i] , the above dp holds.
Let's come back to the original problem. Let's sort all the numbers. We will take advantage of the fact that there are only 70 distinct numbers and try to simulate the dp correspondigly.
If the frequency of a number would have been 1,
If the frequency of a number would have been 2,
Extending,
Now you easily shrink the first dimension from 105 to 70.
Can anyone tell me why this submission 32697001 for problem C gets TLE? This 32697019 got ac, as you can see the only difference is the order i build dp states but the complexity remains the same
Hi, I think it has the same problem I had.
It is calling fast_pow(2, freq[num] — 1), that is log(n) in EVERY state of the recursion, when it could be calculated at most 70 times.
Hope this helps!
Hi,
Both submissions call fast pow(2, freq[num] — 1) in every state of the recursion, and one of them got accepted, so i don't think that should be a problem.
Thanks for the reply anyway
EDIT: Actually, precalculating powers of two up to n gives ac in first submission.
I find it a pretty nice coincidence that both today's C and the F from the last educational round required to calculate C(n, 0) + C(n, 2) + C(n, 4) + ... as a subproblem.
In the educational round, I spent some time thinking about the sum, eventually arriving to the conclusion that it's equal with 2^(n-1). Today's round, I simply brute forced the sum, without too much thought. When I looked at other submissions, I saw the 2^(n-1) term in them, and I was something like "hmmm... okay... I solved this just 3 days ago and I've already forgotten about it".
C can be solved in a more (maybe) straightforward way.
Let dp[i][mask] be the number of way to choose some subset of first i elements and their product has j-th prime with odd degree(if j-th bit of mask is 1). Directly implementing this solution results in a O(N × 219) solution which is too slow.
However, for each number x ≤ 70, only 2, 3, 5, 7 can have power more than 1. If we group up all the number whose prime divisor contains 11, we can have a smaller dp state as dp[mask][11?] denoting the parity of current product on 2, 3, 5, 7, 11. After going through all these numbers, we can get rid of everything about 11 and only store the information of dp[mask][0]. Then, considering all the number whose prime divisor contains 13, and so on.
The time complexity is O(N × 25). In this way, we can even solve the problem with different weight on each element(i.e. sum of total weight of choosing a subset whose product is a square number).
That idea make me remember this problem.
https://community.topcoder.com/stat?c=problem_statement&pm=12074
C can be solved by equation set module 2。 like a_11x_1+a_12x_2...+a_1nx_n=0 a_ij dones whether the jth number have the ith prime odd times or even times,x_i dones whether the ith number will be chosed. And the solution for these equations is the answer for the problem.It can be solved in O(n*19) using bitmask.
C can be solved by equation set module 2。 like a_11x_1+a_12x_2...+a_1nx_n=0 a_ij dones whether the jth number have the ith prime odd times or even times,x_i dones whether the ith number will be chosed. And the solution for these equations is the answer for the problem.It can be solved in O(n*19) using bitmask.
You mean the number of solutions of this system of equations gives the answer, right?! How do you find it?
If M is the matrix whose i-th column is xi, then (1+) the answer is the cardinal of the kernel of M, which is (rank-nullity theorem). The rank can be computed using Gaussian elimination in
(rank-nullity theorem). The rank can be computed using Gaussian elimination in 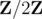 .
.
Can B be solved using two pointers. If so, then how?
I think yes. First you sort array a. Then for every a[i], you have pointer l which a[l] is the first element has (a[l] — 1) / x == a[i] / x — k, and a[l] <= a[i]; and pointer r which a[r] is the last element has (a[r] — 1) / x == a[i] / x — k and a[r] <= a[i]. You can find r by brute-force from the current l, and for next i, you can find l by brute-forces from the last l
32681970
I still don't get C. :-(
How to slove B?
Read this solution. Ask me, what you don't understand.
Div 2B Solution
Why order? this is a continuous interval and ((a[i] — 1) / x) what does it mean?
We have sorted the array, so we have an increasing function => the interval is continuous.
Assuming that a[i] is a left border we can calculate how many integers divisible by x there are in interval [0; a[i]]. It will be a[i] / x obviously. We can do the same operation with the right border. Okay, now we want to calculate amount of integers on a segment [l; r]. It seems like it will be a[right] / x — a[left] / x, but it's wrong. For example: x = 3, a[left] = 3, a[right] = 5. We can do the following operation and get 0, but we need 1. Therefore we need to use a[i] — 1 to prevent this situation when the a[left] divisible by x.
My solution with only binsearch http://codeforces.net/contest/895/submission/32701257
Could you further explain this answer to me? What's the reasoning behind:
Also, why do you use lower_bound? Why not upper_bound?
Just cos u need to find all numbers in [max((long long)a[i], (long long)x * (k + (a[i] — 1) / x)); max((long long)a[i], (long long)x * (k + 1 + (a[i] — 1) / x))), not in() (We include lower bound)
max()call in second search is redundant.a[j]in that equation is always greater than or equal toa[i]If k == 0 then x * (k + (a[i] — 1) / x) can < a[i].
I mean second search, first one is correct. Given that
x >= 1andk >= 0:You are right.
What do odd and even numbers have to do with the dp tranisition ?
If u use i even number of times, mask will not change because even number of x means that you will multiply with a square. If u use i odd number of times, you must change mask, because it wont stay same.
3 rounds in a row we have a task on bin_pow. Coincidence?:D
C can be solved much faster by considering prime factorisation exponents as vector space over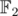 and then answer is just 2n - b - 1 where b is size of basis.
and then answer is just 2n - b - 1 where b is size of basis.
What is the principle?
Your idea is great. Could you give more details or code here? Thanks a lot!
I think D can be solved in O(n*logk) if we use Fenwick Tree to keep the number of each letters,where k is the size of the alphabet.It doesn't work better for this problem,but things will be different if k is up to 10^5 or more.
My submission
Can anyone please, tell me the technique to solve problem A in O(n)?
Use prefix sum and 2 pointers.
Thanks :) and Can you please explain, uses of those pointers?
Got that Idea. Thanks again :)
Could you tell me how to Use prefix sum and 2 pointers? Thanks a lot
You can google it "2 pointer algorithm codeforces" :)
Can anyone explain, why in Problem A on the test 8:
The answer is 40? We can take 90 40 50 and 110 70 — 180 and 180, so the answer is 0, isn't it? Or did I misunderstand it?
Because, in the question it is said that you have to take continuous sector
can anyone please tell me about the query which i will present you below.. read it carefully
""""
I solved problem A. by this way... let us consider an example where
now i arrange these pieces in a fashion like this: starting from the +x axis extreme right going anticlockwise through each sector angle and then making the 4 pieces in anticlockwise sense such that the order follows (0)->(1)->(2)->(3)->(0)
now the possible combinations for the 2 continuous sectors can be like this if starting from (0) (i.e first piece) By considering the clockwise format
Note that sector-1 will not contains the all 4 pieces then in that case min diff will be max.(which will not be the ans) similarly if starting pos is (1),(2)or (3) all possible combinations can be obtained But the point here is .. i am just considered the clockwise direction initially and wrote my code and it gets accepted verdict . here is link http://codeforces.net/contest/895/submission/32719630 But now just figure out this thing when i consider the anti-clockwise direction of these cutted pieces the possible permutations for the case when starting done at (0) (i.e 1 piece is) like this :
I am not checking for these cases it might be possible that i get more minimum value here than the previous cases Can plzz anyone tell me why my code gets accepted even though i not checked for anticlockwise direction ... plzz clear this doubt it just sucks me :/
""""
There is more combinations those your solution will check, when the while loop completes its iteration.
Such as,
For clockwise
It will continue till it reaches (1) and these cases are also included in anti-clockwise.
ya i just recognize this thing .. thnks for ur help bro can u otimize my solution or can u tell me the one given in editorial !
Check My Solution
Am I getting this logic right for Problem B?
Is this logic correct? I think I am still getting TLE because I am not using Binary Search. I got a bit lost in the editorial starting at step 3.
In The Problem A Test case no 50. input is: 7 41 38 41 31 22 41 146
There have minimal difference is 6. 41+41+41+38+22=183 146+31=177 So, 183-177=6. But How to ans is 14?
Anyone Explain please!!
Because the numbers you have chosen are not continuous.
THIS IS VERY IMPORTANT !!! I submitted my solution for problem A during the contest and it passed the pretests then I got RTE on test 49 during system test phase, after the contest I resubmitted the exact same code and I got ACCEPTED !!!! submission during contest : http://codeforces.net/contest/895/submission/32683171 submission after the contest : http://codeforces.net/contest/895/submission/32733925 PLEASE nbah CHECK THIS PROBLEM ! THANKS.
For primes greater than 35 the only number that can affect the mask that correspond to that primes is exactly that prime, and those nombers doesn't affect the other bits on the mask. So, the unic solution for each of those numbers is to select en even ammount of them, and for primes <= 35 you can solve using the Editorial approach in O(70* 2 ^ 11) which is the overall complexity 32702420
can you explain the sample test case 3 for problem E?
after 2 moves
[1 1 5 6 10]
[1 1 5 6 10]
the mathematical expectation should be
[2.6 3.6 4.6 5.6 6.6 4.4 5.4 6.4 7.4 8.4]
then [1 1 3 6 9]
the mathematical expectation of left should be 3.6 and the mathematical expectation of right should be 5.9
so the answer of query [2 1 3] should be 2.6+3.6+4.6+5.9-3.6=13.1 why it is 14?
I am afraid that this is incorrect.
E[6:10] after first move = (40-8+3)/5 = 7
E[1] after the first move = (1*0.8 + 8*0.2) = 2.4
E[1] after the second move = (2.4*0.8 + 7*0.2) = 3.32
How to solve A if the segments need not to be continuous ?
Use subset sum dp and check possible sum nearest to 180. If the sum is S, your answer will be 2|180 - S|.
r / x–(l - 1) / x what does this mean?
I am getting TLE in D, because my solution is running in O(n * k * k). I am not able to reduce it to O(n * k). The code given in the editorial is not clear to me. It doesn't look very intuitive. Can someone please help?
Check out my code, or someone else's.
When trying to count the permutations of A less than B, fix the prefix that will be the same for both strings (N ways). Then, the next character of A has to be less than the character of B at that place. So, if you have countA[26], telling you how many of which character you have in A after the prefix, you can in O(k) add, for each character c < B[i], if countA[c] > 0, the number of ways to finish the string, which is just the number of permutations of the letters you have in countA[] (without c).
You can make it so that you only call the fast_pow(x, y) function O(n) times, so the complexity is O(n(k + log mod)).
You can also precompute the required modular inverses in O(n) with some maths knowledge, which leads to a O(nk) solution.
Thanks a lot !! Beautifully explained :)
in problem D's solution,most people use two array fac and ifac,fac[i]=i! ifac[i]=fac[i]^1e9+5.can anyone tell me what's the usage of ifac and why is it right? thanks in advance...
See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fermat%27s_little_theorem
thank you, dalao
For people struggling to convert O(n * k * k) to O(n *k), this is a very good submission that I found. Hope it helps.
Submission
For people struggling to convert O(n * k * k) solution to O(n * k) , this is a very clear submission that I happened to find. Hope it helps.
Submission
Verdict: wrong answer in test case 13 problem: 895C - Square Subsets submission: 32803738
tried to solve it by recursive dp+bitmask. long long int produces MLE and int produces WA.
would you mind giving me suggestion how to get rid of this situation? manually tested all the small test cases and they are ok.
Your big_mod function and the following two lines can overflow.
long long int p1=((ncr[p]%mod)*(fun(p+1,m^mask[p])%mod))%mod;
long long int p2=((ncr[p]%mod)*(fun(p+1,m)%mod))%mod;
Add 1LL before the multiplication. fix: 32808994
thank u very much, but may i ask u, how did those function cause overfolw? i am not sure about that.
mod = 1000000007
x%mod can be 1000000006;
so x*x larger than 32 bit;
add 1LL in front of it to force it to become a 64 bit integer first.
hope it's clear.
Problem A failed Test 50 7 41 38 41 31 22 41 146 Output 6 Answer 14 Checker Log wrong answer 1st numbers differ — expected: '14', found: '6'
But the right output shouldn' be 6 as the minimum ? A takes 146 + 31 = 177 B takes 41 * 3 +38 + 22 = 183
The elements should be continuous, 146 and 31 are not. Also they can be continuous in circular fashion (i.e 146 is next to 7)
In problem C; I think we can only use the prime number in [1,35],because if the prime number is bigger than 35,it means the number is equal it;So we can ignore them,and the solution will get Accepted(Its time complexity is O(n*cnt(2^(max/2))). Time complexity O(max*cnt(2^(max/2))) It is very quick! Sorry about for my poor English.
Could you give me more details or code about your idea? Thanks a lot
Hi everyone! I ran into a weird bug in my code for problem D. This http://codeforces.net/contest/895/submission/32918069 solution gets accepted and this http://codeforces.net/contest/895/submission/32918020 does not. The only difference between the two is I REPLACED THE FORMAT OF STRING INPUT FROM SCANF TO CIN, not the other way around, and the corresponding data types from char array to string. Could anyone please help? Thanks in advance :)
For some weird reason, gcc decided not to hoist the
strlen(a)call out of the for loop. Sincestrlen()is linear-time, that particular for loop is quadratic in the length of a.string::size()is O(1) because strings store their length.This is a standard optimization (though, to be honest, you should never rely on it), so I am not sure why gcc failed to do it. Clang does well here.
Problem C. Square Subsets can be done in $$$O(N)$$$, with $$$N$$$ is the constraint in the problem ($$$N <= 1e5$$$) if combine eddy1021's solution above and the editorial solution. Here: 83570186
HELP, Can anyone point out the problem in the code 216499815, Why MOD operations are so costly? when I make some changes in the mod operation it passes 216501286