Hello everyone,
finding the diameter is one of the most frequent ways to solve problems about trees. In this tutorial we will see how to find a diameter and some of its properties, and we will use them to solve some problems of increasing difficulty. I tried to put a lot of examples to make the understanding easier.
The first part of the tutorial is quite basic, so feel free to skip it and jump to the problems if you already know the concepts.
Target: rating $$$[1400, 2100]$$$ on CF
Prerequisites: basic graph theory, greedy
The diameter
Given an unweighted tree, let's define $$$\text{dist}(a, b) =$$$ the number of edges in the simple path $$$a \rightarrow b$$$.
A diameter of the tree is a simple path $$$a \rightarrow b$$$ that maximizes $$$\text{dist}(a, b)$$$ over all pairs of nodes. If there are multiple diameters, let's pick any of them.
The same definition is valid for a weighted tree with nonnegative weights (with $$$\text{dist}(a, b) =$$$ the sum of the weights of the edges in the simple path $$$a \rightarrow b$$$).
Finding a diameter
Given a tree with $$$n$$$ nodes are multiple ways to find a diameter. Here is one of the simplest ways:
Run a DFS from any node $$$p$$$. Let $$$a$$$ be a node whose distance from node $$$p$$$ is maximized. Run another DFS from node $$$a$$$. Let $$$b$$$ be a node whose distance from node $$$a$$$ is maximized. $$$a \rightarrow b$$$ is a diameter.
Tree = edges of a diameter + forest
Before proving the previous algorithm, let's analyze the structure of the tree (we will mention the diameter, but we will not use the fact that $$$a \rightarrow b$$$ is actually a diameter before proving it).
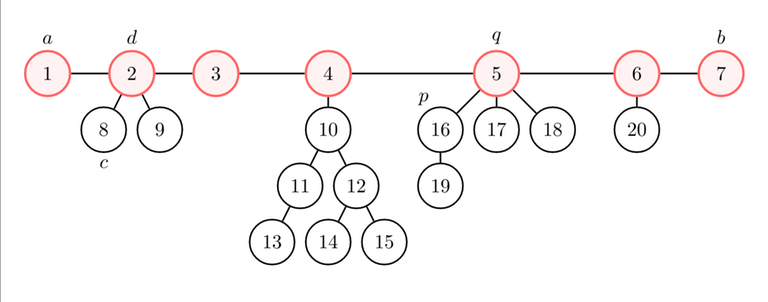
We started a DFS from node $$$p = 16$$$, and we got that node $$$a = 1$$$ is the farthest from $$$p$$$, and node $$$b = 7$$$ is the farthest from $$$a$$$.
Let's represent the diameter on a line. If you remove the edges of the diameter, you get a forest (i.e., several trees). Let's root each tree at the node in the diameter. What's the height (i.e., the maximum distance from the root to any node) of each component?
Let $$$q$$$ be the root of the component of $$$p$$$. Let's consider any component whose root $$$d$$$ is between $$$a$$$ (included) and $$$q$$$ (excluded), and one of its nodes $$$c$$$.
We get
$$$\text{dist}(p, a) \geq \text{dist}(p, c) \implies \text{dist}(p, a) - \text{dist}(p, d) \geq \text{dist}(p, c) - \text{dist}(p, d) \implies \text{dist}(a, d) \geq \text{dist}(c, d)$$$.
In other words, the height of each component with root in the left half of the diameter (i.e., $$$\text{dist}(a, d) < \text{dist}(d, b)$$$) is at most the distance of the root of the component from the left end of the diameter.
You can prove the same statement for the right half of the diameter (i.e., $$$\text{dist}(a, d) \geq \text{dist}(d, b)$$$), using that $$$b$$$ is the farthest node from $$$a$$$.
Farthest node for each node
For each node $$$i$$$, let's find a node $$$j$$$ such that $$$\text{dist}(i, j)$$$ is maximum.
Claim: $$$j = a$$$ or $$$j = b$$$ always works.
Proof:
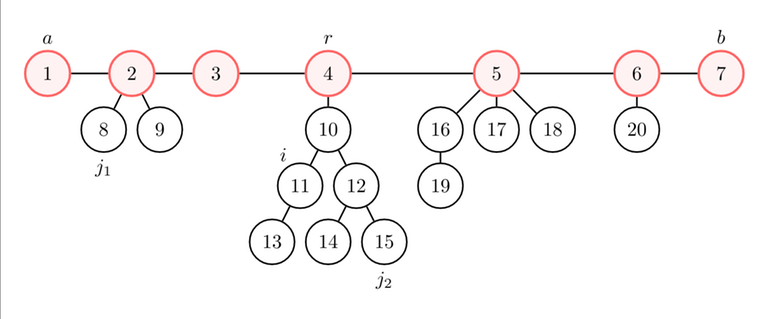
- If $$$j = j_1$$$ works ($$$j_1$$$ is not in the same component of $$$i$$$; let's assume without loss of generality that $$$j_1$$$ is closer to $$$a$$$ than to $$$b$$$), $$$\text{dist}(i, j_1) = \text{dist}(i, r) + \text{dist}(r, j_1) \leq \text{dist}(i, r) + \text{dist}(r, a) = \text{dist}(i, a)$$$. Then, $$$j = a$$$ also works.
- If $$$j = j_2$$$ works ($$$j_2$$$ is in the same component of $$$i$$$), $$$\text{dist}(i, j_1) \leq \text{dist}(i, r) + \text{dist}(r, j_1) \leq \text{dist}(i, r) + \text{dist}(r, a) = \text{dist}(i, a)$$$. Then, $$$j = a$$$ also works.
Proof that $$$a \rightarrow b$$$ is a diameter
Now we can finish the proof.
Suppose that $$$u \rightarrow v$$$ is a diameter. We have either $$$\text{dist}(u, a) \geq \text{dist}(u, v)$$$ or $$$\text{dist}(u, b) \geq \text{dist}(u, v)$$$ (see "Farthest node for each node").
Let's suppose without loss of generality that $$$\text{dist}(u, b) \geq \text{dist}(u, v)$$$. We get $$$\text{dist}(a, b) \geq \text{dist}(u, b) \geq \text{dist}(u, v)$$$, so $$$a \rightarrow b$$$ is a diameter.
Counting inversions in $$$O(n \log n)$$$
You can use a Fenwick tree (or a segment tree). There are other solutions (for example, using divide & conquer + merge sort), but they are usually harder to generalize.
For each $$$j$$$, calculate the number of $$$i < j$$$ such that $$$a_i > a_j$$$.
The Fenwick tree should contain the frequency of each value in $$$[1, n]$$$ in the prefix $$$[1, j - 1]$$$ of the array.
So, for each $$$j$$$, the queries look like
- $$$res := res + \text{range_sum}(a_j + 1, n)$$$
- add $$$1$$$ in the position $$$a_j$$$ of the Fenwick tree
Observations / slight variations of the problem
By using a Fenwick tree, you are actually calculating the number of inversions for each prefix of the array.
You can calculate the number of swaps required to sort an array (not necessarily a permutation, but for now let's assume that its elements are distinct) by compressing the values of the array. For example, the array $$$[13, 18, 34, 38, 28, 41, 5, 29, 30]$$$ becomes $$$[2, 3, 7, 8, 6, 9, 1, 4, 5]$$$.
You can also calculate the number of swaps required to get an array $$$b$$$ (for now let's assume that its elements are distinct) starting from $$$a$$$, by renaming the values. For example,
$$$a = [2, 3, 7, 8, 6, 9, 1, 4, 5], b = [9, 8, 5, 2, 1, 4, 7, 3, 6]$$$
is equivalent to
$$$a = [4, 8, 7, 2, 9, 1, 5, 6, 3], b = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]$$$
$$$a^{-1}$$$ (a permutation such that $$$(a^{-1})_{a_x} = x$$$, i.e. $$$(a^{-1})_x$$$ is equal to the position of $$$x$$$ in $$$a$$$) has the same number of inversions as $$$a$$$. For example, $$$[2, 3, 7, 8, 6, 9, 1, 4, 5]$$$ and $$$[7, 1, 2, 8, 9, 5, 3, 4, 6]$$$ have both $$$16$$$ inversions. Sketch of a proof: note that, when you swap two elements in adjacent positions in $$$a$$$, you are swapping two adjacent values in $$$a^{-1}$$$, and the number of inversions in $$$a^{-1}$$$ also increases by $$$1$$$ or decreases by $$$1$$$ (like in Proof 1).
1430E - Переворот строки (rating: 1900)
103148B - Luna Likes Love (EGOI 2021/2)
arc088_e (rating: 2231)
arc097_e (rating: 2247)
Other problems
IOI 2019/1
arc120_c (suggested by Ghassane)
Hackerearth — Swapping numbers (Inferno03)
Hackerearth — Make the strings equal (Inferno03)
1526D - Убить Антона (somil_jain_120)
JOI 2021/3 (Final Round) (you can submit here)
Conclusions
We've seen that a lot of problems where you have to swap adjacent elements can be tackled with greedy observations, such as looking at the optimal relative positions of the values in the final array; then, a lot of these problems can be reduced to "find the number of inversions" or similar.
Of course, suggestions/corrections are welcome. In particular, please share in the comments other problems where you have to swap adjacent elements.
I hope you enjoyed the blog!






