This article is an English translation of the NOIP Round 1 (the Qualification Round) problems. Here are some backgrounds about it.
- matthew99 has written an Introduction to Chinese OI contests, but he ignored this for some reason; maybe this exam is too easy for him in his province.
- It is literally a "preliminary contest".
- Basically, this is a qualification round for NOIP.
- This is a written examination.
- The exam lasts for 2 hours.
- The total score is 100. You may need to get ~80 scores (in provinces like Zhejiang) or ~20 scores (in provinces like Inner Mongolia) to pass.
- This translation may be not 100% exact, but you can feel the flavor of the NOIPR1.
In part IV and V, the translator modified and formatted the source codes with clang-format .
Part I: Single Choice Problems
2 score for each problem.
1.
In the following four numbers in different positional notation, which one is different from the other three?
- A. (269)16
- B. (617)10
- C. (1151)8
- D. (1001101011)2
2.
Which of the following programming language is run by a interpreter?
- A. C
- B. C++
- C. Pascal
- D. Python
3.
When did Chinese Computer Federation found the NOI competitions? (it was called "National High School Students' Computer Programming Contest")
- A. 1983
- B. 1984
- C. 1985
- D. 1986
4.
Define the depth of a single node to be 0. What is the number of nodes of a full k-ary tree of depth h?
- A. (kh + 1 - 1) / (k - 1)
- B. kh - 1
- C. kh
- D. (kh - 1) / (k - 1)
5.
There is an algorithm whose time-cost function is T(n) = T(n - 1) + n, T(0) = 1. What is its time complexity?
- A.
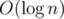
- B.
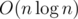
- C. O(n)
- D. O(n2)
6.
What is the prefix form (Polish notation) of the expression a*d-b*c?
- A.
a d * b c * - - B.
- * a d * b c - C.
a * d - b * c - D.
- * * a d b c
7.
Choose two points A and B randomly on a segment of length 1. What's the expected length of |AB| ?
- A. 1 / 2
- B. 1 / 3
- C. 2 / 3
- D. 3 / 5
8.
Catalan Numbers is Cn = (2n)! / (n + 1)! / n! . Which of the following is wrong?
- A. Cn = the number of different binary trees of n+1 nodes
- B. Cn = the number of legal bracket sequence of length 2n
- C. Cn = the number of possible "pop sequence" if we push 1,2,...,n into a stack
- D. Cn = the number of ways to triangulate a convex (n+2)-gon
9.
Assume there is a machine with a button. Whenever you push that button, it will randomly give you either a red ball or a blue ball with 1/2 probability each. Infinitively many people play with this machine. Each of them push that button until a blue ball is given. Then they will put all their balls into a big box. Let U be the number of blue balls in the box and R be the number of red balls. What is U:R?
- A. 1 : 2
- B. 2 : 1
- C. 1 : 3
- D. 1 : 1
10.
You need to write a code to compute the number of 1's in the binary form of a natural number n.
Here is the code:
int CountBit(int x)
{
int ret = 0;
while (x)
{
ret++;
________;
}
return ret;
}
What should you fill in the blank?
- A.
x >>= 1 - B.
x &= x - 1 - C.
x |= x >> 1 - D.
x <<= 1
Part II: Multiple Choice Problems
There are several choices in each problem. No less than one of them is correct. You must find them all to get 2 score for each problem in this part.
11.
What can you take into the exam room in NOIP Round 1?
- A. Pen or Pencil
- B. Eraser
- C. Mobile phone (turned off)
- D. Draft paper
12.
The 2-3 tree is a special kind of rooted trees. They satisfy:
- all non-leaf nodes have 2 or 3 children;
- all leaf has the same depth.
If a 2-3 tree have 10 leaves, how many non-leaf nodes may it have?
- A. 5
- B. 6
- C. 7
- D. 8
13.
Which of the following statements are true?
- A. if there is no negative cycle but negative edges in a graph, Dijkstra's algorithm may not calculate the single source shortest paths
- B. if there is no negative edge, calling Dijkstra's algorithm multiple times may calculate the shortest paths between any pair of nodes
- C. if there is negative cycles, you can call Dijkstra's algorithm one time to calculate single source shortest paths
- D. when there is no negative edge, calling Dijkstra's algorithm once cannot be used to calculate the shortest paths between any pair of nodes
14.
Which of the following properties do a tree have?
- A. there is no cycle
- B. there is only one simple path between any pair of nodes
- C. have and only have one simple cycle
- D. the number of edges equals to the number of nodes minus one
15.
Which of the following statements about the Turing Award are true?
- A. it is set up by Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
- B. the only Chinese who has got the Award is Yao Qizhi
- C. its name is from the pioneer of computer science, the British scientist Alan Mathison Turing
- D. it's the most famous and most honored award in computer field. It was honored as the "Nobel Prize in computer field".
Part III: Problem Solving
5 score for each task.
Task 1
There are four friends. let's call them Jia, Yi, Bing and Ding. They are deciding whether they will go out for a hike.
- if it rains and Yi doesn't go out, then Jia will not go out;
- if Yi goes out, then Ding will go out;
- if Bing goes out, Ding must not go out;
- if Ding doesn't go out and Jia doesn't go out, then Bing won't go out.
Now you can see Bing is going out. So:
- Does Jia go out?
- Does Yi go out?
- Does Ding go out?
- Is it raining? The last problem is 2 scores; the other 1 score.
Task 2
How many pairs of solution does the equation a*b = (a and b)*(a or b) have when a,b are integers in range [0,31]? (* means multiplication, and, or are bitwise operations)
Part IV: Read the Source Code and Write the Output
8 scores for each task.
Task 1
#include <cstdio>
int main() {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < x; ++i) {
if (i * i % x == 1) {
++res;
}
}
printf("%d", res);
return 0;
}
The input is: 15
What's the output?
Task 2
#include <cstdio>
int n, d[100];
bool v[100];
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", d + i);
v[i] = false;
}
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (!v[i]) {
for (int j = i; !v[j]; j = d[j]) {
v[j] = true;
}
++cnt;
}
}
printf("%d\n", cnt);
return 0;
}
The input is: 10 7 1 4 3 2 5 9 8 0 6
What's the output?
Task 3
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
string s;
long long magic(int l, int r) {
long long ans = 0;
for (int i = l; i <= r; ++i) {
ans = ans * 4 + s[i] - 'a' + 1;
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
cin >> s;
int len = s.length();
int ans = 0;
for (int l1 = 0; l1 < len; ++l1) {
for (int r1 = l1; r1 < len; ++r1) {
bool bo = true;
for (int l2 = 0; l2 < len; ++l2) {
for (int r2 = l2; r2 < len; ++r2) {
if (magic(l1, r1) == magic(l2, r2) && (l1 != l2 || r1 != r2)) {
bo = false;
}
}
}
if (bo) {
ans += 1;
}
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
The input is: abacaba
What's the output?
Task 4
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
bool isUse[N];
int n, t;
int a[N], b[N];
bool isSmall() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
if (a[i] != b[i])
return a[i] < b[i];
return false;
}
bool getPermutation(int pos) {
if (pos > n) {
return isSmall();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (!isUse[i]) {
b[pos] = i;
isUse[i] = true;
if (getPermutation(pos + 1)) {
return true;
}
isUse[i] = false;
}
}
return false;
}
void getNext() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
isUse[i] = false;
}
getPermutation(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
a[i] = b[i];
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &t);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= t; ++i) {
getNext();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
printf("%d", a[i]);
if (i == n)
putchar('\n');
else
putchar(' ');
}
return 0;
}
The first input is: 6 10 1 6 4 5 3 2
The second input is: 6 200 1 5 3 4 2 6
What are the outputs?
Part V: Program Blank Fill-in
In this part, you are given several programs with their descriptions, but some expressions in the programs are deleted. Fill in the blanks to make the programs work as described.
Task 1
You have a 1-indexed permutation P of length n. We define array Q as: Qi is the smallest j satisfying 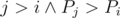 . If such j doesn't exist, Qi = n + 1 .
. If such j doesn't exist, Qi = n + 1 .
For example, if n = 5, P = {1, 5, 4, 2, 3}, then Q = {2, 6, 6, 5, 6}.
The following program reads P and calculates Q with double-linked list. It is guaranteed that n ≤ 105.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n;
int L[N], R[N], a[N];
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int x;
cin >> x;
/*fill in(1)*/;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
R[i] = /*fill in(2)*/;
L[i] = i - 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
L[/*fill in(3)*/] = L[a[i]];
R[L[a[i]]] = R[/*fill in(4)*/];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
cout << /*fill in(5)*/ << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Task 2
Piggy wants to buy n objects. n ≤ 1000. He can choose from two shops, A and B.
Each of these n objects are sold in both shops. If Piggy buy the i-th object at A shop, the cost is a[i]. If Piggy buy the i-th object at B shop, the cost is b[i]. All the prices are no less than 0 and no more than 10000. If the total price in shop A is no less than 50000, everything Piggy buy at A shop will have a 5% discount. That is, if total_a >= 50000, result = total_a * 0.95 + total_b.
Calculate the minimum amount of money does Piggy need to buy the n objects.
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int Inf = 1000000000;
const int threshold = 50000;
const int maxn = 1000;
int n, a[maxn], b[maxn];
bool put_a[maxn];
int total_a, total_b;
double ans;
int f[threshold];
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
total_a = total_b = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
scanf("%d%d", a + i, b + i);
if (a[i] <= b[i])
total_a += a[i];
else
total_b += b[i];
}
ans = total_a + total_b;
total_a = total_b = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (/*fill in(1)*/) {
put_a[i] = true;
total_a += a[i];
} else {
put_a[i] = false;
total_b += b[i];
}
}
if (/*fill in(2)*/) {
printf("%.2f", total_a * 0.95 + total_b);
return 0;
}
f[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < threshold; ++i)
f[i] = Inf;
int total_b_prefix = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (!put_a[i]) {
total_b_prefix += b[i];
for (int j = threshold - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
if (/*fill in(3)*/ >= threshold && f[j] != Inf)
ans = min(ans, (total_a + j + a[i]) * 0.95 + /*fill in(4)*/);
f[j] = min(f[j] + b[i], j >= a[i] ? /*fill in(5)*/ : Inf);
}
}
printf("%.2f", ans);
return 0;
}
The answer is here.





