Statement
If we resume, then it says: "We've got an array S of length N (with distinct values) and two arrays Jx , Jy of length M (all arrays filled with values from 0 to N-1). Then the game starts and it consist of M turns, each turn i goes this way:
- A: We swap S[Jx[i]] with S[Jy[i]] (Jx[i] can be equal to Jy[i])
- B: Then we're allowed to do any swap (we can swap a value with itself). I will call this custom moves
The objective of the game is to make the array S sorted with the lower amount of turns. We're guaranteed that there is a solution with an amount of turns lower or equal than M.
Limits:
- N ≤ 200000
- M ≤ 600000
- M = 3N, so M > N
First Procedure
We'll first to solve the problem without trying to get the lower amount of turns. This solution (that is pretty) hard, will then make us solve the harder sub-task with a simple binary search with no modifications of the algorithm.
This solution points to make the array to be sorted when M turns have passed. Not after, not before.
Note that the sorted array must be [0, 1, 2, ...N - 1], or, in other words 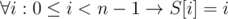 . We need all S[i] to be equal to its index.
. We need all S[i] to be equal to its index.
We know that we make the array sorted when M turns passed. This must happen. So, we can predict how items will move until the M turns have passed. We can answer for each item i, where its value will be when all M moves have passed. Also we can answer "where the item i in the final sequence is in the actual sequence" if we don't make more additional moves of course. We know that the item i in the final sequence must be equal to i! And we know where this item in the final sequence is in the current sequence. So we'll only need to swap (in the first turn), the sequence with value i to the place that will go to the index i in the final sequence.
We'll need to repeat this process in each of the M turns. And in each turn we'll update two arrays
- F = "where the item i in the final sequence is in the actual sequence
- E = "where is the item with value i in the actual sequence"
This way we will in each turn swap E[i] with F[i], this means, "the place where i value is" to "the place that will be in the final array in i". Of course in the case E[i]! = F[i], otherwise we increase i and try to swap the next one. The idea is that in each turn we'll have "up to i-1" values already in its right position, and in case all i values are in its right position, then we only need to wait until M moves happened (and until then we don't swap anything (swap 0,0))
The final approach: Binary Search
We will need to consider trying to solve the problem "If there only were W ≤ M turns". We the algorithm of above with can answer to solve the answer "Can we solve the problem on W turns?". So with a binary search we will test to get the lower W that makes it possible to solve the problem. That will be the answer with a total algorithm complexity of O(log(M) * (M + N)).
Conclusion
This is an extremely hard task, Although no special algorithm is needed, you need some observations and to not get lost while thinking things because there is a good amount of deep thinking needed. Good Luck.










Auto comment: topic has been updated by ariel.nowik (previous revision, new revision, compare).
Before reading this, I'll try on my own, but I think I'll end up reading here hahaha
Auto comment: topic has been updated by ariel.nowik (previous revision, new revision, compare).
Auto comment: topic has been updated by ariel.nowik (previous revision, new revision, compare).
Auto comment: topic has been updated by ariel.nowik (previous revision, new revision, compare).
I participated in the olympiad itself and this task wasn't in any way easy for me — but I wouldn't call it extremely hard, especially in IOI standards. It's not an easy problem, but in my opinion the same-day problem Towns was much more difficult. Nice explanation though :)
right, haha, comparatively with other IOI problems, this one is easy. However, for my level of programming is not so trivial. But yes, maybe I will edit the evaluative thoughts.
This problem couldn't be considered extremely hard because of its 59 solved contestants in comparison with other tasks: 9 in Scales, 14 in Teams and 7 in Towns. However, during the contest, I could only solve for 36 points and luckily earned 54 points 15 minutes before the end with an unproven greedy algorithm. Hence, the high number of accepted solutions really surprised me.