1043A — Elections
We can observe that result cannot exceed 201 — Awruk gets at least 101 votes from one person and Elodreip cannot get more than 100 votes from one person. So we can iterate over every possible integer from 1 to 201 and check if Awruk wins with k set to this integer. We have to remember that k — ai is always at least 0, so we have to check this condition too. Complexity O(n * M), where M denotes maximum possible value of ai. Try to solve it in O(n).
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
int mx = 0, sum = 0;
int main(){
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
int a; scanf("%d", &a);
mx = max(mx, a);
sum += a;
}
sum *= 2;
sum += n;
sum /= n;
printf("%d", max(sum, mx));
return 0;
}
Author: Anadi
1043B — Lost Array
First, let's observe that we can replace array ai with array bi = ai - ai - 1, because all we care about are differences between neighboring elements. Now, we can see that our lost array can have length d if and only if for every j such that j + d ≤ n, bj = bj + d. So we can iterate over every possible d from 1 to n and check if it is correct in O(n). Complexity of whole algorithm is O(n2).
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1007;
int n;
int in[N];
bool ok(int d){
for(int i = 0; i + d < n; ++i)
if(in[i + 1] - in[i] != in[i + d + 1] - in[i + d])
return false;
return true;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
scanf("%d", &in[i]);
vector <int> res;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
if(ok(i))
res.push_back(i);
printf("%d\n", res.size());
for(int v: res)
printf("%d ", v);
return 0;
}
Author: Anadi
1043C — Smallest Word
Basically in problem we are given a word in which for every i we can reverse prefix of first i elements and we want to get the smallest lexicographically word. We will show that we can always achieve word in form ajbn - j.
Let's say that we solved our problem for prefix of length i and for this prefix we have word ajbi - j (at the beginning it's just empty word). If our next letter is b then we do nothing, because we will get word ajbi - j + 1 which is still the smallest lexicographically word. Otherwise we want to reverse prefix of length i, add letter a and reverse prefix of length i + 1, so we get a word aj + 1bi - j, which is still fine for us.
There is still a problem — what if we have already reversed prefix i and we just said that we will reverse it second time. But instead of reversing it second time, we can deny it's first reverse.
Final complexity is O(n).
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1007;
string s;
bool write[N];
int main(){
cin >> s;
for(int i = 1; i < s.size(); ++i)
if(s[i] == 'a'){
write[i - 1] ^= 1;
write[i] = 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i)
printf("%d%c", write[i], i + 1 == (int)s.size() ? '\n' : ' ');
return 0;
}
Author: Anadi
1043D — Mysterious Crime
Deleting prefix and suffix is nothing more than taking a subarray. If subarray is common for all permutations then it has to appear in first permutation. We renumber all permutations such that first permutation is 1, 2, ..., n - 1, n.
Now for every i in every permutation we count how long is subarray starting at i which looks like i, i + 1, ..., i + k. It can be easily done in O(n) for one permutation with two pointers technique.
Now for every element i we compute reach[i] equal the longest subarray starting in i which looks like i, i + 1, ..., i + k and it apears in all subarrays. It is just minimum over previously calculated values for all permutations.
Now we can see that our result is 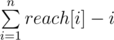 . Final complexity O(nm).
. Final complexity O(nm).
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 7;
int n, m;
int mn[N];
int ren[N];
int perm[15][N];
int main(){
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
scanf("%d", &perm[i][j]);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
ren[perm[1][i]] = i;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
perm[i][j] = ren[perm[i][j]];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
mn[i] = n;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
int cur = 1;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j){
if(cur < j)
++cur;
while(cur < n && perm[i][cur + 1] == perm[i][cur] + 1)
++cur;
mn[perm[i][j]] = min(mn[perm[i][j]], perm[i][cur]);
}
}
LL res = 0;
int now = 1;
while(now <= n){
int cur = mn[now] - now + 1;
res += 1LL * (cur + 1) * cur / 2LL;
now = mn[now] + 1;
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
return 0;
}
Author: Anadi
1043E — Train Hard, Win Easy
Let's compute result if there are no edges, we can add them later. If there are no edges then result for pair (i, j) is min(xi + yj, xj + yi). First let's fix i for which we want to compute result. Then calculate result with all pairs j such that xi + yj ≤ xj + yi. After some transformations we get that xi - yi ≤ xj - yj. Similarly we have that yi + xj < xi + yj if xi - yi > yj - xj.
So let's sort over differences of xi - yi and compute prefix sums of xi and suffix sums of yi. Now we can compute for every i result in O(1). Then we can iterate over every edge (u, v) and subtract min(xu + yv, xv + yu) from result of u and v.
Complexity O(nlogn).
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int LL;
#define st first
#define nd second
#define PII pair <int, int>
const int N = 3e5 + 7;
int n, m;
PII diff[N];
int place[N];
vector <int> G[N];
LL ans[N];
int x[N], y[N];
LL pref[N], suf[N];
int main(){
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
scanf("%d %d", &x[i], &y[i]);
diff[i] = {y[i] - x[i], i};
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
int u, v;
scanf("%d %d", &u, &v);
G[u].push_back(v);
G[v].push_back(u);
}
sort(diff + 1, diff + n + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
place[diff[i].nd] = i;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
pref[i] = pref[i - 1] + y[diff[i].nd];
for(int i = n; i >= 1; --i)
suf[i] = suf[i + 1] + x[diff[i].nd];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
int u = diff[i].nd;
LL res = pref[i - 1] + suf[i + 1] + 1LL * (i - 1) * x[u] + 1LL * (n - i) * y[u];
for(int v: G[u])
res -= min(x[u] + y[v], x[v] + y[u]);
ans[u] = res;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
printf("%lld ", ans[i]);
return 0;
}
Author: Rzepa
1043F — Make It One
First let's observe that if there exists valid subset then it's size is at most 7 (because product of 7 smallest primes is bigger then 3 * 105). Let's define dp[i][j] — number of ways to pick i different elements such that their gcd is equal to j. We can use inclusion--exclusion principle to calculate it. Then dp[i][j] = 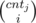 —
— 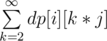 , where cntj denotes number of ai such that j | ai. Because for k * j > 3 * 105, dp[i][k * j] = 0 we have to check only k * j ≤ 3 * 105.
, where cntj denotes number of ai such that j | ai. Because for k * j > 3 * 105, dp[i][k * j] = 0 we have to check only k * j ≤ 3 * 105.
Our answer is the smallest i such that dp[i][1] is non-zero. Since dp[i][j] can be quite big we should compute it modulo some big prime.
Final complexity is O(logM * (n + M)), where M is equal to maximum of ai.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 3e5 + 7;
const int MX = 1e9 + 7;
int n;
int cnt[N];
int sil[N];
int odw[N];
int dp[20][N];
int fast(int a, int b){
int ret = 1;
while(b){
if(b & 1)
ret = (1LL * ret * a)%MX;
b >>= 1;
a = (1LL * a * a)%MX;
}
return ret;
}
int newton(int a, int b){
if(b < 0 || a < b) return 0;
return (((1LL * sil[a] * odw[b])%MX) * odw[a - b])%MX;
}
void sub(int &a, int b){
a -= b;
if(a < 0)
a += MX;
}
int main(){
sil[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < N; ++i)
sil[i] = (1LL * sil[i - 1] * i)%MX;
odw[N - 1] = fast(sil[N - 1], MX - 2);
for(int i = N - 1; i >= 1; --i)
odw[i - 1] = (1LL * odw[i] * i)%MX;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
cnt[a]++;
}
for(int i = 1; i < N; ++i)
for(int j = i + i; j < N; j += i)
cnt[i] += cnt[j];
for(int i = 1; i < 20; ++i){
for(int j = N - 1; j >= 1; --j){
dp[i][j] = newton(cnt[j], i);
for(int k = j + j; k < N; k += j)
sub(dp[i][j], dp[i][k]);
}
if(dp[i][1] > 0){
printf("%d\n", i);
return 0;
}
}
puts("-1");
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 3e5 + 7;
int n;
int cnt[N];
int roz[N];
int dist[N];
queue <int> Q;
vector <int> dv[N];
int base(int a){
int ret = 1;
while(a > 1){
if(ret%roz[a] != 0)
ret *= roz[a];
a /= roz[a];
}
return ret;
}
void getEdges(int u, int d){
vector <int> cur;
vector <int> val;
while(u > 1){
cur.push_back(roz[u]);
u /= roz[u];
}
for(int v: cur)
u *= v;
int T = 1 << (int)cur.size();
val.resize(T);
for(int i = 0; i < T; ++i){
val[i] = u;
for(int j = 0; j < (int)cur.size(); ++j)
if(i & (1 << j))
val[i] /= cur[j];
}
for(int i = 0; i < T; ++i){
int s = 0;
for(int j = i; true; j = (j - 1) & i){
if(__builtin_popcount(i ^ j) & 1)
s -= cnt[val[j]];
else
s += cnt[val[j]];
if(j == 0)
break;
}
assert(s >= 0);
if(s && dist[val[i]] == -1){
dist[val[i]] = d;
Q.push(val[i]);
}
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 2; i < N; ++i){
if(roz[i] != 0)
continue;
for(int j = i; j < N; j += i)
roz[j] = i;
}
for(int i = 1; i < N; ++i)
for(int j = i; j < N; j += i)
dv[j].push_back(i);
for(int i = 1; i < N; ++i)
dist[i] = -1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
a = base(a);
if(dist[a] != -1)
continue;
dist[a] = 1;
Q.push(a);
for(int v: dv[a])
cnt[v]++;
}
while(!Q.empty()){
int u = Q.front();
Q.pop();
getEdges(u, dist[u] + 1);
}
printf("%d\n", dist[1]);
return 0;
}
Author: Anadi
1043G — Speckled Band
Let's solve the problem for some string s for any time.
Let's say, that partition of string s into k strings s1s2... si1, si1 + 1... si2, ..., {sik - 1 + 1}... sik is good if at least one pair of this strings are equal. We want to find a minimal possible number of different strings in all good partitions.
It's easy to see, that the answer is - 1 if and only if all symbols in s are different. And if we have two equal symbols si = sj (i < j) we can cut a string into strings s1... si - 1, si, si + 1... sj - 1, sj, sj + 1... sn and it is a good partition. In this partition there is at most 4 different strings.
So the answer can be - 1, 1, 2, 3, 4.
The answer is - 1 if all symbols in s are different (case 0).
The answer is 1 if the string s = aaa... a, for some string a (case 1).
The answer is 2 if the string s is aab, aba or baa for some strings a and b (case 2).
The answer is 3 if the string s is baac, bcaa or aabc for some strings a, b, c. In two last cases it's easy to see, that |a| = 1 (case 3).
To solve our problem let's build suffix array with lcp for string s. And let's find lti~--- minimal possible number r, such that sisi + 1... sr is a tandem (the string, that can be presented as aa for some string a) and rti~--- maximal possible number l such that slsl + 1... si is a tandem. This numbers can be found using Main and Lorentz algorithm for finding tandem repetitions in the string.
Now we can solve query for segment [l, r]: \begin{itemize} \item Case 0: if r - l ≥ 26, there exists equal symbols, otherwise we can check it by O(r - l); \item Case 1: to check that s[l... r] = aa... a we can see that |a| is a divisor of (r - l + 1) and (r - l + 1) / |a| is a prime number (if we take a longest possible string a). So we should check only O(log(n)) lenghts of string a; \item Case 2: s = aab  ltl ≤ r, s = baa
ltl ≤ r, s = baa  rtr ≥ l. In the last case we should check, that s[l... r] has a border. It's the most interesting part of the problem, let's solve it in the end; \item Case 3: s = abac
rtr ≥ l. In the last case we should check, that s[l... r] has a border. It's the most interesting part of the problem, let's solve it in the end; \item Case 3: s = abac  sl exists on sl + 1... sr (can be done using prefix sums), s = baca
sl exists on sl + 1... sr (can be done using prefix sums), s = baca  sr exists on sl... sr - 1 (can be done using prefix sums). To check s = baac we can check, that lti ≤ r for some l ≤ i ≤ r, that can be done using minimum on segment in the array lt. \end{itemize}
sr exists on sl... sr - 1 (can be done using prefix sums). To check s = baac we can check, that lti ≤ r for some l ≤ i ≤ r, that can be done using minimum on segment in the array lt. \end{itemize}
Now we should the hardest part of this problem~--- we have some segments [l, r]. For all of them, we should check that the border of s[l... r] exists. Here I know two methods, that uses only suffix array. Easiest of them:
We have segment [l, r]. Let's check for all lengths 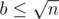 , that s[l... (l + b - 1)] = s[(r - b + 1)... r]. If we don't find border, if it exists, it's length
, that s[l... (l + b - 1)] = s[(r - b + 1)... r]. If we don't find border, if it exists, it's length 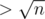 . Let's define i~--- maximal index i such that lcp(l, i) ≥ r - i + 1, and string s[i... r] is a border of s[l... r]. So
. Let's define i~--- maximal index i such that lcp(l, i) ≥ r - i + 1, and string s[i... r] is a border of s[l... r]. So 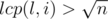 . But it's easy to see, that the distance between l and i in suffix array
. But it's easy to see, that the distance between l and i in suffix array 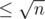 , so we need to check only
, so we need to check only 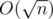 variants of i.
variants of i.
Another method can check that border exists for all segments [l, r] using offline algorithm by O(q·log(n)2) time.
So the total complexity will be 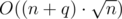 or O((n + q)·log(n)2).
or O((n + q)·log(n)2).
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int BIG = 1e9 + 239;
const int M = 2 * 1e5 + 239;
const int L = 19;
const int A = 30;
const int T = (1 << 19);
const int two = 2;
int flm[two][M];
inline void z_function(string &s, int c)
{
int n = s.length();
flm[c][0] = 0;
int l = 0;
int r = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
flm[c][i] = min(flm[c][i - l], r - i);
if (flm[c][i] < 0) flm[c][i] = 0;
while (i + flm[c][i] < n && s[flm[c][i]] == s[i + flm[c][i]]) flm[c][i]++;
if (i + flm[c][i] > r)
{
l = i;
r = i + flm[c][i];
}
}
}
int a[M], lcp[M], pos[M];
inline void suffix_array(string s)
{
s += (char)(31);
int n = s.length();
vector<pair<char, int> > v;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
v.push_back(make_pair(s[i], i));
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
vector<pair<int, int> > num;
int last = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
num.push_back(make_pair(last, v[i].second));
if (v[i].first != v[i + 1].first) last++;
}
num.push_back(make_pair(last, v.back().second));
vector<int> u(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) u[num[i].second] = num[i].first;
int d = 1;
vector<pair<pair<int, int>, int> > t;
vector<vector<pair<int, int> > > h;
while (d < n)
{
t.clear();
h.clear();
h.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int l = num[i].second - d;
if (l < 0) l += n;
h[u[l]].push_back(make_pair(num[i].first, l));
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (pair<int, int> r : h[i])
t.push_back(make_pair(make_pair(i, r.first), r.second));
last = 0;
num.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
num.push_back(make_pair(last, t[i].second));
if (t[i].first != t[i + 1].first) last++;
}
num.push_back(make_pair(last, t.back().second));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) u[num[i].second] = num[i].first;
d <<= 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) a[i - 1] = num[i].second;
}
string s;
inline void kasai()
{
int n = s.size();
suffix_array(s);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
pos[a[i]] = i;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (pos[i] == n - 1) continue;
while (s[i + k] == s[a[pos[i] + 1] + k] && a[pos[i] + 1] + k < n && i + k < n) k++;
lcp[pos[i]] = k;
k = max(0, k - 1);
}
}
int n, lw[M], rw[M];
string prr, rvl;
vector<int> open_l[M], close_l[M];
vector<int> open_r[M], close_r[M];
multiset<int> nw;
inline void func(int l, int r)
{
if (r - l == 1) return;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
func(l, mid);
func(mid, r);
rvl = "";
for (int i = mid - 1; i >= l; i--) rvl += s[i];
z_function(rvl, 0);
prr = "";
for (int i = mid; i < r; i++) prr += s[i];
prr += '#';
for (int i = l; i < mid; i++) prr += s[i];
z_function(prr, 1);
for (int c = l; c < mid; c++)
{
int k1 = 0;
if (c > l) k1 = flm[0][mid - c];
int k2 = flm[1][r - mid + 1 + c - l];
int len = mid - c;
int lg = max(len - k2, 0);
int rg = min(len - 1, k1);
if (rg >= lg)
{
open_l[c - rg].push_back((2 * len));
close_l[c - lg].push_back((2 * len));
open_r[c - rg + 2 * len - 1].push_back((2 * len));
close_r[c - lg + 2 * len - 1].push_back((2 * len));
}
}
rvl = "";
for (int i = mid; i < r; i++) rvl += s[i];
z_function(rvl, 0);
prr = "";
for (int i = mid - 1; i >= l; i--) prr += s[i];
prr += '#';
for (int i = r - 1; i >= mid; i--) prr += s[i];
z_function(prr, 1);
for (int c = mid; c < r; c++)
{
int k1 = 0;
if (c != r - 1) k1 = flm[0][c + 1 - mid];
int k2 = flm[1][r - c + mid - l];
int len = c - mid + 1;
int lg = max(len - k2, 0);
int rg = min(len - 1, k1);
if (rg >= lg)
{
open_l[c + lg - 2 * len + 1].push_back((2 * len));
close_l[c + rg - 2 * len + 1].push_back((2 * len));
open_r[c + lg].push_back((2 * len));
close_r[c + rg].push_back((2 * len));
}
}
for (int i = l; i < r; i++)
{
for (int len : open_l[i]) nw.insert(len);
if (!nw.empty()) lw[i] = min(lw[i], *nw.begin());
for (int len : close_l[i]) nw.erase(nw.lower_bound(len));
open_l[i].clear();
close_l[i].clear();
}
for (int i = l; i < r; i++)
{
for (int len : open_r[i]) nw.insert(len);
if (!nw.empty()) rw[i] = min(rw[i], *nw.begin());
for (int len : close_r[i]) nw.erase(nw.lower_bound(len));
open_r[i].clear();
close_r[i].clear();
}
}
int mn[L][M], st2[M], lc[L][M], kol[A][M];
inline int getmin(int l, int r)
{
int u = st2[r - l + 1];
return min(mn[u][l], mn[u][r - (1 << u) + 1]);
}
inline int gett(int l, int r)
{
if (l == r) return (n - l);
l = pos[l];
r = pos[r];
if (l > r) swap(l, r);
r--;
int u = st2[r - l + 1];
return min(lc[u][l], lc[u][r - (1 << u) + 1]);
}
int q, la[M], ra[M], has[M], mnp[M];
inline void init()
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) mn[0][i] = lw[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) lc[0][i] = lcp[i];
for (int i = 1; i < L; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
int r = (j + (1 << (i - 1)));
if (r >= n)
{
mn[i][j] = mn[i - 1][j];
continue;
}
mn[i][j] = min(mn[i - 1][j], mn[i - 1][r]);
}
for (int i = 1; i < L; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n - 1; j++)
{
int r = (j + (1 << (i - 1)));
if (r >= n - 1)
{
lc[i][j] = lc[i - 1][j];
continue;
}
lc[i][j] = min(lc[i - 1][j], lc[i - 1][r]);
}
st2[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
st2[i] = st2[i - 1];
if ((1 << (st2[i] + 1)) <= i) st2[i]++;
}
}
int in[L][M], gl[T];
inline void build(int i, int l, int r)
{
if (i == 0) gl[i] = 0;
else gl[i] = gl[(i - 1) / 2] + 1;
if (r - l == 1)
{
in[gl[i]][l] = a[l];
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(2 * i + 1, l, mid);
build(2 * i + 2, mid, r);
merge(in[gl[i] + 1] + l, in[gl[i] + 1] + mid, in[gl[i] + 1] + mid, in[gl[i] + 1] + r, in[gl[i]] + l);
}
inline bool is_on(int i, int l, int r, int ql, int qr, int xl, int xr)
{
if (r <= ql || qr <= l) return false;
if (ql <= l && r <= qr)
{
int it = upper_bound(in[gl[i]] + l, in[gl[i]] + r, xl) - in[gl[i]] - l;
if (it == r - l) return false;
return (in[gl[i]][it + l] <= xr);
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (is_on(2 * i + 1, l, mid, ql, qr, xl, xr)) return true;
return is_on(2 * i + 2, mid, r, ql, qr, xl, xr);
}
inline bool check_all(int l, int r)
{
int len = (r - l + 1);
int pl = pos[l];
int lf = pl;
int rf = n;
while (rf - lf > 1)
{
int h = (lf + rf) / 2;
if (gett(a[h], l) >= len) lf = h;
else rf = h;
}
int rg = lf + 1;
lf = -1;
rf = pl;
while (rf - lf > 1)
{
int h = (lf + rf) / 2;
if (gett(a[h], l) >= len) rf = h;
else lf = h;
}
int lg = rf;
return is_on(0, 0, n, lg, rg, l, r);
}
int par[M];
set<int> cmp[M];
set<pair<int, int> > sc[M];
vector<int> ok[M];
vector<pair<int, int> > mg[M];
inline void border_check()
{
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) has[i] = false;
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) ok[ra[i] - la[i]].push_back(i);
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) mg[lcp[i]].push_back(make_pair(a[i], a[i + 1]));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
par[i] = i;
cmp[i].insert(i);
}
for (int c = n; c >= 1; c--)
{
for (int i : ok[c - 1])
sc[par[la[i]]].insert(make_pair(ra[i], i));
for (pair<int, int> t : mg[c])
{
int l = par[t.first];
int r = par[t.second];
if (cmp[l].size() > cmp[r].size()) swap(l, r);
for (int x : cmp[l])
while (true)
{
auto it = sc[r].lower_bound(make_pair(x, 0));
if (it == sc[r].end() || it->first > x + c - 1) break;
has[it->second] = true;
sc[r].erase(it);
}
for (pair<int, int> u : sc[l])
{
int id = u.second;
auto uk = cmp[r].lower_bound(ra[id] - c + 1);
if (uk != cmp[r].end() && (*uk) <= ra[id])
has[id] = true;
else
sc[r].insert(u);
}
for (int x : cmp[l])
{
par[x] = r;
cmp[r].insert(x);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++)
if (!has[i] && check_all(la[i], ra[i]))
{
has[i] = true;
continue;
}
}
inline bool checkno(int l, int r)
{
if (r - l + 1 > 26) return false;
vector<int> kol(26, 0);
for (int x = l; x <= r; x++)
{
if (kol[s[x] - 'a'] > 0) return false;
kol[s[x] - 'a']++;
}
return true;
}
inline bool try_kol(int l, int r, int p)
{
int len = (r - l + 1) / p;
return (gett(l, l + len) >= (r - l + 1 - len));
}
inline bool ison(int l, int r, char x)
{
return (kol[x - 'a'][r + 1] > kol[x - 'a'][l]);
}
inline int query(int l, int r, int id)
{
if (checkno(l, r)) return -1;
int len = (r - l + 1);
while (len > 1)
{
int p = mnp[len];
if (try_kol(l, r, p)) return 1;
while ((len % p) == 0) len /= p;
}
if (lw[l] <= r) return 2;
if (rw[r] >= l) return 2;
if (has[id]) return 2;
if (ison(l + 1, r, s[l])) return 3;
if (ison(l, r - 1, s[r])) return 3;
if (getmin(l, r) <= r) return 3;
return 4;
}
int main()
{
cin.sync_with_stdio(0);
cin >> n >> s;
memset(mnp, -1, sizeof(mnp));
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
if (mnp[i] == -1)
for (int j = i; j <= n; j += i)
if (mnp[j] == -1)
mnp[j] = i;
memset(kol[0], 0, sizeof(kol[0]));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < 26; x++) kol[x][i + 1] = kol[x][i];
kol[s[i] - 'a'][i + 1]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
lw[i] = n + 1;
rw[i] = n + 1;
}
func(0, n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (lw[i] == n + 1) lw[i] = n;
else lw[i] += (i - 1);
if (rw[i] == n + 1) rw[i] = -1;
else rw[i] = (i - rw[i] + 1);
}
kasai();
init();
build(0, 0, n);
cin >> q;
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++)
{
cin >> la[i] >> ra[i];
la[i]--, ra[i]--;
}
border_check();
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) cout << query(la[i], ra[i], i) << "\n";
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define TIME (clock() * 1.0 / CLOCKS_PER_SEC)
const int BIG = 1e9 + 239;
const int M = 2 * 1e5 + 239;
const int L = 19;
const int A = 30;
const int T = (1 << 19);
const int two = 2;
int flm[two][M];
inline void z_function(string &s, int c)
{
int n = s.length();
flm[c][0] = 0;
int l = 0;
int r = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
flm[c][i] = min(flm[c][i - l], r - i);
if (flm[c][i] < 0) flm[c][i] = 0;
while (i + flm[c][i] < n && s[flm[c][i]] == s[i + flm[c][i]]) flm[c][i]++;
if (i + flm[c][i] > r)
{
l = i;
r = i + flm[c][i];
}
}
}
int a[M], lcp[M], pos[M];
inline void suffix_array(string s)
{
s += (char)(31);
int n = s.length();
vector<pair<char, int> > v;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
v.push_back(make_pair(s[i], i));
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
vector<pair<int, int> > num;
int last = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
num.push_back(make_pair(last, v[i].second));
if (v[i].first != v[i + 1].first) last++;
}
num.push_back(make_pair(last, v.back().second));
vector<int> u(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) u[num[i].second] = num[i].first;
int d = 1;
vector<pair<pair<int, int>, int> > t;
vector<vector<pair<int, int> > > h;
while (d < n)
{
t.clear();
h.clear();
h.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int l = num[i].second - d;
if (l < 0) l += n;
h[u[l]].push_back(make_pair(num[i].first, l));
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (pair<int, int> r : h[i])
t.push_back(make_pair(make_pair(i, r.first), r.second));
last = 0;
num.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
num.push_back(make_pair(last, t[i].second));
if (t[i].first != t[i + 1].first) last++;
}
num.push_back(make_pair(last, t.back().second));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) u[num[i].second] = num[i].first;
d <<= 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) a[i - 1] = num[i].second;
}
string s;
inline void kasai()
{
int n = s.size();
suffix_array(s);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
pos[a[i]] = i;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (pos[i] == n - 1) continue;
while (s[i + k] == s[a[pos[i] + 1] + k] && a[pos[i] + 1] + k < n && i + k < n) k++;
lcp[pos[i]] = k;
k = max(0, k - 1);
}
}
int n, lw[M], rw[M];
string prr, rvl;
vector<int> open_l[M], close_l[M];
vector<int> open_r[M], close_r[M];
multiset<int> nw;
inline void func(int l, int r)
{
if (r - l == 1) return;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
func(l, mid);
func(mid, r);
rvl = "";
for (int i = mid - 1; i >= l; i--) rvl += s[i];
z_function(rvl, 0);
prr = "";
for (int i = mid; i < r; i++) prr += s[i];
prr += '#';
for (int i = l; i < mid; i++) prr += s[i];
z_function(prr, 1);
for (int c = l; c < mid; c++)
{
int k1 = 0;
if (c > l) k1 = flm[0][mid - c];
int k2 = flm[1][r - mid + 1 + c - l];
int len = mid - c;
int lg = max(len - k2, 0);
int rg = min(len - 1, k1);
if (rg >= lg)
{
open_l[c - rg].push_back((2 * len));
close_l[c - lg].push_back((2 * len));
open_r[c - rg + 2 * len - 1].push_back((2 * len));
close_r[c - lg + 2 * len - 1].push_back((2 * len));
}
}
rvl = "";
for (int i = mid; i < r; i++) rvl += s[i];
z_function(rvl, 0);
prr = "";
for (int i = mid - 1; i >= l; i--) prr += s[i];
prr += '#';
for (int i = r - 1; i >= mid; i--) prr += s[i];
z_function(prr, 1);
for (int c = mid; c < r; c++)
{
int k1 = 0;
if (c != r - 1) k1 = flm[0][c + 1 - mid];
int k2 = flm[1][r - c + mid - l];
int len = c - mid + 1;
int lg = max(len - k2, 0);
int rg = min(len - 1, k1);
if (rg >= lg)
{
open_l[c + lg - 2 * len + 1].push_back((2 * len));
close_l[c + rg - 2 * len + 1].push_back((2 * len));
open_r[c + lg].push_back((2 * len));
close_r[c + rg].push_back((2 * len));
}
}
for (int i = l; i < r; i++)
{
for (int len : open_l[i]) nw.insert(len);
if (!nw.empty()) lw[i] = min(lw[i], *nw.begin());
for (int len : close_l[i]) nw.erase(nw.lower_bound(len));
open_l[i].clear();
close_l[i].clear();
}
for (int i = l; i < r; i++)
{
for (int len : open_r[i]) nw.insert(len);
if (!nw.empty()) rw[i] = min(rw[i], *nw.begin());
for (int len : close_r[i]) nw.erase(nw.lower_bound(len));
open_r[i].clear();
close_r[i].clear();
}
}
int mn[L][M], st2[M], lc[L][M], kol[A][M];
inline int getmin(int l, int r)
{
int u = st2[r - l + 1];
return min(mn[u][l], mn[u][r - (1 << u) + 1]);
}
inline int gett(int l, int r)
{
if (l == r) return (n - l);
l = pos[l];
r = pos[r];
if (l > r) swap(l, r);
r--;
int u = st2[r - l + 1];
return min(lc[u][l], lc[u][r - (1 << u) + 1]);
}
int q, mnp[M];
inline void init()
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) mn[0][i] = lw[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) lc[0][i] = lcp[i];
for (int i = 1; i < L; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
int r = (j + (1 << (i - 1)));
if (r >= n)
{
mn[i][j] = mn[i - 1][j];
continue;
}
mn[i][j] = min(mn[i - 1][j], mn[i - 1][r]);
}
for (int i = 1; i < L; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n - 1; j++)
{
int r = (j + (1 << (i - 1)));
if (r >= n - 1)
{
lc[i][j] = lc[i - 1][j];
continue;
}
lc[i][j] = min(lc[i - 1][j], lc[i - 1][r]);
}
st2[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
st2[i] = st2[i - 1];
if ((1 << (st2[i] + 1)) <= i) st2[i]++;
}
}
int u, len;
inline bool check(int l, int r)
{
for (int t = 1; t <= min(len, ((r - l + 1) / 2)); t++)
if (gett(l, r - t + 1) >= t)
return true;
for (int i = max(0, pos[l] - len); i <= min(n - 1, pos[l] + len); i++)
if (l < a[i] && a[i] <= r && gett(l, a[i]) >= r - a[i] + 1)
return true;
return false;
}
inline bool checkno(int l, int r)
{
if (r - l + 1 > 26) return false;
vector<int> kol(26, 0);
for (int x = l; x <= r; x++)
{
if (kol[s[x] - 'a'] > 0) return false;
kol[s[x] - 'a']++;
}
return true;
}
inline bool try_kol(int l, int r, int p)
{
int len = (r - l + 1) / p;
return (gett(l, l + len) >= (r - l + 1 - len));
}
inline bool ison(int l, int r, char x)
{
return (kol[x - 'a'][r + 1] > kol[x - 'a'][l]);
}
inline int query(int l, int r)
{
if (checkno(l, r)) return -1;
int len = (r - l + 1);
while (len > 1)
{
int p = mnp[len];
if (try_kol(l, r, p)) return 1;
while ((len % p) == 0) len /= p;
}
if (lw[l] <= r) return 2;
if (rw[r] >= l) return 2;
if (check(l, r)) return 2;
if (ison(l + 1, r, s[l])) return 3;
if (ison(l, r - 1, s[r])) return 3;
if (getmin(l, r) <= r) return 3;
return 4;
}
int main()
{
cin.sync_with_stdio(0);
cin >> n >> s;
memset(mnp, -1, sizeof(mnp));
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
if (mnp[i] == -1)
for (int j = i; j <= n; j += i)
if (mnp[j] == -1)
mnp[j] = i;
memset(kol[0], 0, sizeof(kol[0]));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < 26; x++) kol[x][i + 1] = kol[x][i];
kol[s[i] - 'a'][i + 1]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
lw[i] = n + 1;
rw[i] = n + 1;
}
func(0, n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (lw[i] == n + 1) lw[i] = n;
else lw[i] += (i - 1);
if (rw[i] == n + 1) rw[i] = -1;
else rw[i] = (i - rw[i] + 1);
}
kasai();
init();
cin >> q;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (i * i >= n)
{
len = i + 3;
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++)
{
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
l--, r--;
cout << query(l, r) << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
Author: isaf27










Auto comment: topic has been updated by Anadi (previous revision, new revision, compare).
Superfast editorials!!!
Auto comment: topic has been updated by Anadi (previous revision, new revision, compare).
There's an appearance issue in C tutorial
Wow this G solution...
This solution of Problem G is saying, "You need an editorial for me? Meh, just take a look at me, I don't need one."
Author had solution for G, but this tutorial is too small to contain it.
Auto comment: topic has been updated by Anadi (previous revision, new revision, compare).
For F, you may have considered this right end part of formula: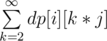 , right now it's confusing.
, right now it's confusing.
Thank you. Fixed.
Auto comment: topic has been updated by Anadi (previous revision, new revision, compare).
There is one correct solution for G as scoreboard showes. Who is this one? Or it is error?
I think LHiC solved it after contest.
Thx. I think it is wrong behavior to show count of solutions that are not showing at table.
Auto comment: topic has been updated by Anadi (previous revision, new revision, compare).
What am I missing for problem D, 31th test case : 10 3
7 4 10 8 3 6 2 9 5 1
7 4 10 8 3 6 2 9 5 1
2 9 5 1 7 4 10 8 3 6
We have subarrays {2,9,5,1} and {4,10,8,3,6}, so I'm calculating number 26. (4*3/2+5*4/2)+length_of_array(when subbaray is one number)
Well, if you observe more closely, you'll see that the second group contains the 7, too (it appears on all of the 3 permutations!), so you get 6 elements for the second group! Answer: 4 * 5 / 2 + 6 * 7 / 2 = 10 + 21 = 31 elements.
(note that we can include the single elements when we are calculating the answer for each group, by adding one more number. Please note that if a group is single (only 1 element), the answer is 1, because we include only that element and note that 1 * 2 / 2 = 1. This makes the calculations easier! :) )
In problem F:
"Our answer is the smallest i such that dp[i][1] is non-zero. Since dp[i][j] can be quite big we should compute it modulo some big prime."
Can we be sure that if dp[i][j] % p is 0 then dp[i][j] must be 0 as well?
As you only need to check seven numbers probability of collision is extremely low.
You can take 2 DP arrays with different big primes, to reduce the chances of collision.
Why is the distance in a suffix array not greater than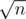 ?
?
As i is defined as the maximum index, it means that s[i..r] has no suffix that is also a prefix. Thus the suffixes between l and i in the suffix array (they share at least the same prefix as l and i) must have indexes such that the distance between them is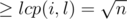 . An thus there are at most
. An thus there are at most 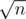 such indexes.
such indexes.
In G's solution, isn't aabc == aab and bcaa == baa or did I misunderstand something?
it should probably be abac & baca
tex formatting is broken in G
what is a border?
Equal prefix and suffix of the string
I am interested in how everybody solved D.
Personally, I did some prefix hashing and then binary search on maximum length substring starting at value k for a mnlogn solution.
Some ones I've heard:
1) Some type of Map solution (a lot of people did this)
2) O(nm) DSU solution (rotavirus mentioned)
3) Rolling hash (anyone else did prefix hash... ?)
I'm especially interested in DSU explanation, but also I've seen some variation in how people have used map, and want to hear how you guys approached that. For example, I saw radoslav11 make some suffix automaton, which unfortunately got TLE on 36, but with some constant optimization it could work.
Please tell me about your solutions for this problem!
i made a dsu of size n, then for each pair of adjacent elements in the first permutation, i checked whether these elements are adjacent in all other permutations, if yes, i united them. So, if two numbers are in the same disjoint set, then they form a valid subarray, so i counted the number of pairs in each disjoint set and printed the sum of them.
I had a vector consisting of all pairs of adjacent numbers in the permutation and used binary search to find the count of occurance of a pair instead of using a map for keeping track of the count. I prefer doing this instead of using a map generally when the time limits are strict. My Submission
I used a revolutionary new data structure. For some people it can take years to master, but once you figure out how to use "array", you are set for life.
I just keep track of the position of each element in each permutation for a linear-time solution. See the code.
The only observation needed is that if the first permutation's substring starting at index i is valid until index j, then the substring starting at i + 1 is valid until at least j as well.
what is difference between rolling hashing and prefix hashing? what's prefix hashing btw?
Basically you store the prefix sum of a[i]*BASE^i so that: h[i] = h[i-1] + a[i]*BASE^i
So when you want to get hash code for substring (L, R) in O(1) you can do it like this
(h[R]-h[L-1]) * invPow[L]
invPow[i] represents BASE^(-i)
For rolling hash you just keep a window (actually a number to represent the window) of size k and you "pop" and "push" to slide the window.
For example, you maintain k = 3 at i: a[i]*BASE^2, a[i+1]*BASE^1, a[i+2]*BASE^0
You would subtract a[i]*BASE^(k-1), multiply everything by BASE, then add a[i+k] (BASE^0 is just 1)
You could also maintain it in reverse and "divide" with modular inverses, but that's just more work.
For F, I got accepted by a randomized algorithm with some greedy at the beginning (45016248).
What is the expected runtime?
The expected runtime is just a big constant for the randomization part, around O(1, 000, 000 × 50) but can change 50 to 7 or 8 as it is the maximum possible answer.
Actually, neal showed below that the expected runtime of one iteration is not 7.
We cap the 7, if after picking 7 numbers doesn't give a GCD of 1 then skip and restart the iteration.
This number btw can be lower, as we keep track the progress of iterations.
Thanks, then it is deterministic runtime :)
Here's a test case that your algorithm will have trouble on:
[10, 21, 6 * p for all primes p that fit]
The answer is 2 because you can pick 10 and 21. However every other pair of numbers in this array will have a GCD greater than 1. So you only have a roughly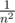 chance of picking the right pair on every attempt you make, and n can get fairly large, over 5,000.
chance of picking the right pair on every attempt you make, and n can get fairly large, over 5,000.
Ah, that's correct; I only did calculation for case of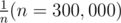 instead and found out
instead and found out 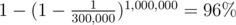 of success. The success percentage of your case is just 4% for my program. I guess I got lucky then, ><
of success. The success percentage of your case is just 4% for my program. I guess I got lucky then, ><
I think that in the last paragraph of tutorial of problem E it should be
Similarly we have that yi + xj < xi + yj if xi - yi > xj - yj.
can some admin link this to the problems, right now only the announcement is linked, thanks
It looks like instead of linking the tutorial, the announcement was unlinked!
Please fix, thanks.
There are no contests this week.
:(
How to Solve C ?
I add 'b' to input string at last. Then if i see 'ba' or 'ab' in string then revers at that point. You can try some examples to better understanding of this approach.
my code
The answer is 3 if the string s is baac, bcaa or aabcCases bcaa and aabc don't make sense. It probably should be baca and abac.
I solved Problem C during contest. But I wanted to know DP approach for solving it. Can anyone share DP approach to solve Problem C ?
Pure stl challenge for problem A :)
I solved C with another interesting approach.
Let's have a recursive function
sol(int pos, bool asc).posis the position (or prefix) till which we need the answer, andasctells us whether to make this prefix ascending or descending.The final answer is
sol(n, true).Let's call the position with the rightmost 'a' (or the minimum character in the prefix) inside the current prefix as
idx. (rightmost max character in case of asc == false)Now, to get the optimal answer, we need to flip at position
idx.But, to make sure that this flip will be optimal, we have to make the prefix before
idxin descending order, so we callsol(idx - 1, !asc)which will make the prefix in the optimal descending order, and then let recursion do its job.Base case would be when we reach the prefix of size 1, where it doesn't matter whether to flip or not.
My submission — 45069274.
UPD: It seems I have solved this problem for a regular string (without the restriction of containing only as and bs) :D
I need to read problems more carefully!
I know i am late, but if you are still reading this.. i don't understand this part "But, to make sure that this flip will be optimal, we have to make the prefix before idx in descending order"
Can you elaborate? thanks.
UPD: i got it, when we flip the prefix 0..idx, we want the 0..idx-1 to be in biggest to smallest order so that when we split upto idx...it is the smallest possible order.
First compute for each i from 1 to MAX how many multiples of i are there. Then iterate over all input numbers, find it prime factors, iterate over all subsets of its prime divisors, get number of numbers divisible by all those prime numbers from precomputed table. Use it to calculate for each subset how many numbers divisible by exactly those prime factors are there. Now use basic dp to find out what is minimal number of numbers in set, whose elements gcd is divisible by particular subset of those primes. Start with dp[product of all] = 1, then iterate over smaller and smaller subsets and for each subset m such, that there is at least one number divisible by exactly those set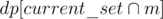 to dp[current_set] + 1
to dp[current_set] + 1
To optimize it a bit we can first replace each number by product of it's distinct prime factors and then remove duplicates and numbers divisible by some smaller number from input.
Solution complexity is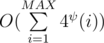 , where ψ(x) is number of distinct prime divisors.
, where ψ(x) is number of distinct prime divisors.
Implementation: 45104292
Very cool and fast editoral, thank you!
my solution for D looks asymptotically correct but it gives TLE at testcase 36 can someone help 45130338
In problem D :-> my solution is giving tle in O(M*n), i tried to take input in one go through string which makes it fast but giving wrong answer can anybody tell me where i am wrong?
Here is my submission by simply taking the input one by one: First Submission
By taking string as input: Second submmission
UPDATE: I GOT MY FLAW!! thanx if anyone GETTING TLE USING O(M*N) TRY TO TAKE INPUT USING GETLINE IN ONE GO,IT WILL REMOVE THE TLE PROBLEM!!
Will someone please explain problem F a bit more clearly..
You can remove the duplicates in the array and get the same result. Why? Because gcd(a,a) = a. So now let us force every element to be unique. If we greedily maximize how many element we can have it is 1, 2, 2*3, 2*3*5, ...2*3* 5*7*11*13 = 7 elements
This means we only care about making gcd(arr) = 1 with 7 elements at max.
So we can reduce O(n*maxA) DP to O(7 * maxA) states
We we want to know for a number j, how many ways can we use i elements to make gcd(the i elements) = kj. This is can be calculate with combination modulo some number. We can precalculate some value mult[j] which says "how many values are multiple of j" to achieve this.
But we want to exclude answers where k > 1, so we subtract those. This loop is actually (AlogA) because O(n + n/2 + n/3 ... 1) = O(nlogn)
So we get O(7 * maxA * logA) complexity
Another approach for problem F: Do a binary search first. Notice that: It's hard to determine whether a subset of size k and with its gcd equals to 1 exists directly, but calculating the number of such subsets modulo a big prime is easy: simply use the inclusion-exclusion principle(with the mobius function). Use a good prime and you'll get accepted. :P
Your approach sounds interesting. Can you explain a little more how you use inclusion-exclusion? And mobius function?
The number of ways to select k coprime elements from a multiset is sigma(mu(x) * comb(number_of_elements_that_is_a_multiple_of_x, k) for 1 <= x <= MAXA).
You can precalculate the factorials and the inverses of the factorials of each positive integer <= n to compute binomial coefficients and a sieve to compute mu(x) and number_of_elements_that_is_a_multiple_of_x for each x.
Time complexity: O(n + MAXA log MAXA)
45341495
my solution for D is WA on #7, can someone tell me what i'm doing wrong?
i'm counting for every 'i' the size of the largest array [i, i+1, ...] that is present on every array, then i sum all these values. my code returns correct results for all other testcases with small size
isaf27 About problem G , why the distance between l and i in suffix array <= sqrt(n)?
and what is the second solution to check if there exists a border for [l,r]
i have read some other solution for G and it's look like they don't find any tandem repetitions. Is there a easier solution for G? I think this solution is too hard to implement in contest. Tks you
I don't know if this is my first time to solve D by my own.
Well my approach is a little different from others. I stored first array as it is. While for other arrays I stored the position of each element (eg. [1, 4, 2, 3] will be stored as [1, 3, 4, 2]). We will also maintain an array p of m size for storing current positions of m arrays.
Now we traverse the elements of first array. If for all remaining arrays, the position in the array for current element in first array is 1 greater than the current array position i.e. if p[i] + 1 = array[i][array[1][p[1]]] then subarray size will be incremented. In case the condition is not true and if size of common subarray is k till now then ans will be incremented to k × (k + 1) / 2 and k will 1.
Complexity is O(mn).
Link to code
Could someone explain the alternative solution of Problem F(Solution 2) to me?
I confuse at bitmask-part in get_edge function.
in there anybody who can explain bit-mask solution for problem F ?
In G, the "finding a border" part can be done "easily" without a suffix array. The observation is that if a substring with length $$$L$$$ doesn't start with a tandem, then for any $$$K$$$, it contains at most $$$2L/K$$$ occurrences of its prefix with length $$$K$$$ -- otherwise, two of them are sufficiently close to create a tandem. I fix $$$K \approx \sqrt{N}$$$, precompute hashes of all $$$O(N)$$$ substrings with length exactly $$$K$$$, and for each query substring, check for all borders with length $$$\le K$$$, look at occurrences of its prefix with length $$$K$$$ inside it and check for each of these occurrences if the border's end half starts there. With $$$O(1)$$$ substring comparison using hashes, this is $$$O(\sqrt{N})$$$ as well.
On the other hand, I used a suffix array approach instead of Main-Lorentz, since I didn't know it.
For F, can someone please give me some intuition(or proof) behind the first line, that it not contain more than 7 elements...
any number up to 3e5, which is the constraint, doesn't have more than 7 distinct prime divisors, and thus the prime factorization would be at most of size 7 without the exponents kind of just think about intersection of pf's, if there aren't any then we could just take a non intersecting pair , there can't be more than 7 intersecting pf's since the size is at most 7, etc.
Please give me some hints for an F-like problem: Given an array with 2e5 number a[1], a[2], ..., a[n](a[i] <= 1e9). We have to find the subsequence of A such that their pairwise indices' gcd is equal to 1 and their sum of a[i] is as maximum as possible. For example, we have an array A = {1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 6}, so the answer is 8 because if we choose a[1], a[5], and a[6] because gcd(1, 5) = gcd(1, 6) = gcd(5, 6) = 1 and a[1] + a[5] + a[6] = 8 is the largest answer