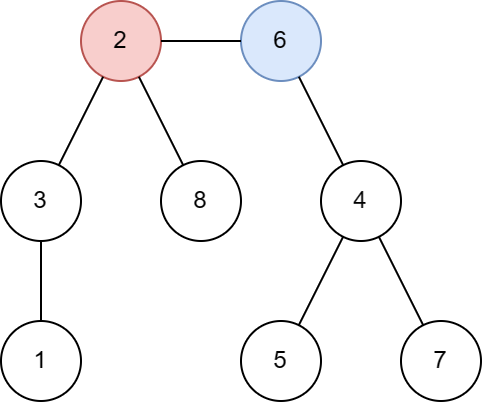
I've found that I can't talk at all. I record myself to track down any inefficiencies and I decided to talk during some sessions.
I miss words, I use wrong words. Sometimes I completely go silent when working out a tricky part.
My hypothesis is that the implementation part should be 2nd nature and I should be able to talk through it. So I'm probably switching from notepad to editor too quickly.