Problem A Elephant
It's optimal to do the biggest possible step everytime. So elephant should do several steps on distance 5 and one or zero step on smaller distance. Answer equals to
Unable to parse markup [type=CF_TEX]
Problem B
We are given array which contains only ones and zeroes. We must divide it on parts with only one 1.
Tricky case: when array contains only zeroes answer equals to 0.
In general. Between two adjacent ones we must have only one separation. So, answer equals to product of posi - posi - 1 where posi~--- position of i-th one.
Bonus: what's the maximal answer for n ≤ 100?
Problem C
First radius equals to zero or distance from first fountain to some flower. Let's iterate over this numbers. Second radius equals to maximal distance from second fountain to flower which doesn't belong to circle with first radius. Now we should choose variant with minimal r12 + r22.
Bonus: It's O(n2) solution. Can you solve problem in O(nlogn)?
Problem D.
Answer equals to one if all coordinates x or y of points are same.
When answer equals to two? Let's iterate over all pairs of points. Let first point in pair is beginning of chain, second point is end. Only one or two such chains exist. If third point is on the chain it belongs to rectangle with corners in first two points. We can just check it.
Else answer equals to three. We can build vertical lines which contains the most left and the most right point and horizontal line through third point. If we erase some excess rays we will get chain.
Problem E.
We have array a.
Let's calculate array pref (pref[0] = 0, 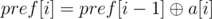 ). Xor of subarray a[l...r] equals to
). Xor of subarray a[l...r] equals to 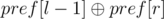 .
.
So query (l, r)~--- count number of pairs i, j (l - 1 ≤ i < j ≤ r) 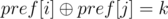 .
.
Let we know answer for query (l, r) and know for all v cnt[v]~--- count of v in a[l - 1...r]. We can update in O(1) answer and cnt if we move left or right border of query on 1. So we can solve problem offline in 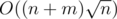 with sqrt-decomposion (Mo's algorithm).
with sqrt-decomposion (Mo's algorithm).






