660A - Co-prime Array
The problem was suggested by Ali Ibrahim C137.
Note that we should insert some number between any adjacent not co-prime elements. On other hand we always can insert the number 1.
Complexity: O(nlogn).
660B - Seating On Bus
The problem was suggested by Srikanth Bhat bharsi.
In this problem you should simply do what was written in the problem statement. There are no tricks.
Complexity: O(n).
660C - Hard Process
The problem was suggested by Mohammad Amin Raeisi Smaug.
Let's call the segment [l, r] good if it contains no more than k zeroes. Note if segment [l, r] is good than the segment [l + 1, r] is also good. So we can use the method of two pointers: the first pointer is l and the second is r. Let's iterate over l from the left to the right and move r while we can (to do that we should simply maintain the number of zeroes in the current segment).
Complexity: O(n).
660D - Number of Parallelograms
The problem was suggested by Sadegh Mahdavi smahdavi4.
It's known that the diagonals of a parallelogram split each other in the middle. Let's iterate over the pairs of points a, b and consider the middle of the segment 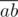 :
: 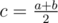 . Let's calculate the value cntc for each middle. cntc is the number of segments a, b with the middle c. Easy to see that the answer is
. Let's calculate the value cntc for each middle. cntc is the number of segments a, b with the middle c. Easy to see that the answer is 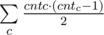 .
.
Complexity: O(n2logn).
660F - Bear and Bowling 4
The problem was prepared by Kamil Debowski Errichto. The problem analysis is also prepared by him.
The key is to use divide and conquer. We need a recursive function f(left, right) that runs f(left, mid) and f(mid+1, right) (where mid = (left + right) / 2) and also considers all intervals going through mid. We will eventually need a convex hull of lines (linear functions) and let's see how to achieve it.
For variables L, R (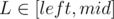 ,
, 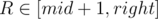 ) we will try to write the score of interval [L, R] as a linear function. It would be good to get something close to aL·xR + bL where aL and bL depend on L, and xR depends on R only.
) we will try to write the score of interval [L, R] as a linear function. It would be good to get something close to aL·xR + bL where aL and bL depend on L, and xR depends on R only.
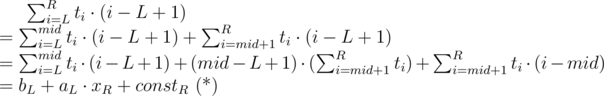
For each L we should find a linear function fL(x) = aL·x + bL where aL, bL should fit the equation ( * ):
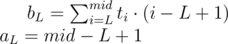
Now we have a set of linear functions representing all possible left endpoints L. For each right endpoint R we should find xR and constR to fit equation ( * ) again. With value of xR we can iterate over functions fL to find the one maximizing value of bL + aL·xR. And (still for fixed R) we should add constR to get the maximum possible score of interval ending in R.
Now let's make it faster. After finding a set of linear functions fL we should build a convex hull of them (note that they're already sorted by slope). To achieve it we need something to compare 3 functions and decide whether one of them is unnecessary because it's always below one of other two functions. Note that in standard convex hull of points you also need something similar (but for 3 points). Below you can find an almost-fast-enough solution with a useful function bool is_middle_needed(f1, f2, f3). You may check that numbers calculated there do fit in long long.
Finally, one last thing is needed to make it faster than O(n2). We should use the fact that we have built a convex hull of functions (lines). For each R you should binary search optimal function. Alternatively, you can sort pairs (xR, constR) and then use the two pointers method — check the implementation in my solution below. It gives complexity 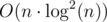 because we sort by xR inside of a recursive function. I think it's possible to get rid of this by sorting prefixes
because we sort by xR inside of a recursive function. I think it's possible to get rid of this by sorting prefixes 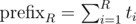 in advance because it's equivalent to sorting by xR. And we should use the already known order when we run a recursive function for smaller intervals. So, I think
in advance because it's equivalent to sorting by xR. And we should use the already known order when we run a recursive function for smaller intervals. So, I think 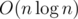 is possible this way — anybody implemented it?
is possible this way — anybody implemented it?
Complexity: O(nlog2n).







